Banking environment has become highly competitive today. To be able to survive and grow in the changing market environment banks are going for the latest technologies, which is being perceived as an ‘enabling resource’ that can help in developing learner and more flexible structure that can respond quickly to the dynamics of a fast changing market scenario. It is also viewed as an instrument of cost reduction and effective communication with people and institutions associated with the banking business.
The Software Packages for Banking Applications in India had their beginnings in the middle of 80s, when the Banks started computerising the branches in a limited manner. The early 90s saw the plummeting hardware prices and advent of cheap and inexpensive but high powered PC’s and Services and banks went in for what was called Total Branch Automation (TBA) packages. The middle and late 90s witnessed the tornado of financial reforms, deregulation globalisation etc. coupled with rapid revolution in communication technologies and evolution of novel concept of convergence of communication technologies, like internet, mobile/cell phones etc. Technology has continuously played on important role in the working of banking institutions and the services provided by them. Safekeeping of public money, transfer of money, issuing drafts, exploring investment opportunities and lending drafts, exploring investment being provided.
Information Technology enables sophisticated product development, better market infrastructure, implementation of reliable techniques for control of risks and helps the financial intermediaries to reach geographically distant and diversified markets. Internet has significantly influenced delivery channels of the banks. Internet has emerged as an important medium for delivery of banking products and services.
The customers can view the accounts; get account statements, transfer funds and purchase drafts by just punching on few keys. The smart card’s i.e., cards with micro processor chip have added new dimension to the scenario. An introduction of ‘Cyber Cash’ the exchange of cash takes place entirely through ‘Cyber-books’. Collection of Electricity bills and telephone bills has become easy. The upgradeability and flexibility of internet technology after unprecedented opportunities for the banks to reach out to its customers. No doubt banking services have undergone drastic changes and so also the expectation of customers from the banks has increased greater.
IT is increasingly moving from a back office function to a prime assistant in increasing the value of a bank over time. IT does so by maximizing banks of pro-active measures such as strengthening and standardising banks infrastructure in respect of security, communication and networking, achieving inter branch connectivity, moving towards Real Time gross settlement (RTGS) environment the forecasting of liquidity by building real time databases, use of Magnetic Ink Character Recognition and Imaging technology for cheque clearing to name a few. Indian banks are going for the retail banking in a big way
The key driver to charge has largely been the increasing sophistication in technology and the growing popularity of the Internet. The shift from traditional banking to e-banking is changing customer’s expectations.
E-Banking:
E-banking made its debut in UK and USA 1920s. It becomes prominently popular during 1960, through electronic funds transfer and credit cards. The concept of web-based baking came into existence in Eutope and USA in the beginning of 1980.
In India e-banking is of recent origin. The traditional model for growth has been through branch banking. Only in the early 1990s has there been a start in the non-branch banking services. The new pribate sector banks and the foreign banks are handicapped by the lack of a strong branch network in comparison with the public sector banks. In the absence of such networks, the market place has been the emergence of a lot of innovative services by these players through direct distribution strategies of non-branch delivery. All these banks are using home banking as a key “pull’ factor to remove customers away from the well entered public sector banks.
Many banks have modernized their services with the facilities of computer and electronic equipments. The electronics revolution has made it possible to provide ease and flexibility in banking operations to the benefit of the customer. The e-banking has made the customer say good-bye to huge account registers and large paper bank accounts. The e-banks, which may call as easy bank offers the following services to its customers:
- Credit Cards/Debit Cards
- ATM
- E-Cheques
- EFT (Electronic Funds Transfer)
- DeMAT Accounts
- Mobile Banking
- Telephone Banking
- Internet Banking
- EDI (Electronic Data Interchange)
Benefits of E-banking:
To the Customer:
- Anywhere Banking no matter wherever the customer is in the world. Balance enquiry, request for services, issuing instructions etc., from anywhere in the world is possible.
- Anytime Banking — Managing funds in real time and most importantly, 24 hours a day, 7days a week.
- Convenience acts as a tremendous psychological benefit all the time.
- Brings down “Cost of Banking” to the customer over a period a period of time.
- Cash withdrawal from any branch / ATM
- On-line purchase of goods and services including online payment for the same.
To the Bank:
- Innovative, scheme, addresses competition and present the bank as technology driven in the banking sector market
- Reduces customer visits to the branch and thereby human intervention
- Inter-branch reconciliation is immediate thereby reducing chances of fraud and misappropriation
- On-line banking is an effective medium of promotion of various schemes of the bank, a marketing tool indeed.
- Integrated customer data paves way for individualised and customised services.
Impact of IT on the Service Quality:
The most visible impact of technology is reflected in the way the banks respond strategically for making its effective use for efficient service delivery. This impact on service quality can be summed up as below:
- With automation, service no longer remains a marketing edge with the large banks only. Small and relatively new banks with limited network of branches become better placed to compete with the established banks, by integrating IT in their operations.
- The technology has commoditising some of the financial services. Therefore the banks cannot take a lifetime relationship with the customers as granted and they have to work continuously to foster this relationship and retain customer loyalty.
- The technology on one hand serves as a powerful tool for customer servicing, on the other hand, it itself results in depersonalising of the banking services. This has an adverse effect on relationship banking. A decade of computerization can probably never substitute a simple or a warm handshake.
- In order to reduce service delivery cost, banks need to automate routine customer inquiries through self-service channels. To do this they need to invest in call centers, kiosks, ATM’s and Internet Banking today require IT infrastructure integrated with their business strategy to be customer centric.
Impact of IT on Banking System:
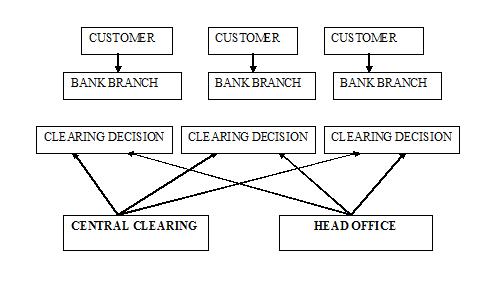
The banking system is slowly shifting from the Traditional Banking towards relationship banking. Traditionally the relationship between the bank and its customers has been on a one-to-one level via the branch network. This was put into operation with clearing and decision making responsibilities concentrated at the individual branch level. The head office had responsibility for the overall clearing network, the size of the branch network and the training of staff in the branch network. The bank monitored the organisation’s performance and set the decision making parameters, but the information available to both branch staff and their customers was limited to one geographical location.
Traditional Banking Sector
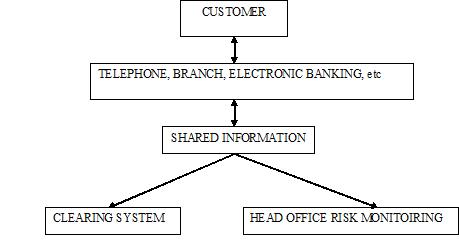
The modern bank cannot rely on its branch network alone. Customers are now demanding new, more convenient, delivery systems, and services such as Internet banking have a dual role to the customer. They provide traditional banking services, but additionally offer much greater access to information on their account status and on the bank’s many other services. To do this banks have to create account information layers, which can be accessed both by the bank staff as well as by th customers themselves.
The use of interactive electronic links via the Internet could go a ling way in providing the customers with greater level of information about both their own financial situation and about the services offered by the bank.
The New Relationship Oriented Bank
Impact of IT on Privacy and Confidentiality of Data:
Data being stored in the computers, is now being displayed when required on through internet banking mobile banking, ATM’s etc. all this has given rise to the issues of privacy and confidentially of data are:
- The data processing capabilities of the computer, particularly the rapid throughput, integration, and retrieval capabilities, give rise to doubts in the minds of individuals as to whether the privacy of the individuals is being eroded.
- So long as the individual data items are available only to those directly concerned, everything seems to be in proper place, but the incidence of data being cross referenced to create detailed individual dossiers gives rise to privacy problems.
- Customers feel threatened about the inadequacy of privacy being maintained by the banks with regard to their transactions and link at computerised systems with suspicion.
Aside from any constitutional aspect, many nations deem privacy to be a subject of human right and consider it to be the responsibility of those who concerned with computer data processing for ensuring that the computer use does not revolve to the stage where different data about people can be collected, integrated and retrieved quickly. Another important responsibility is to ensure the data is used only for the purpose intended.
Good post, thanks for sharing. Any more information on DMA best practices?
Thanks.
Antonio
Wonderful, this is a great site that provides very great academic knowledge. Thanks for your existence.
just superb
tell me the role of IT act in Banking sector
Nice article..