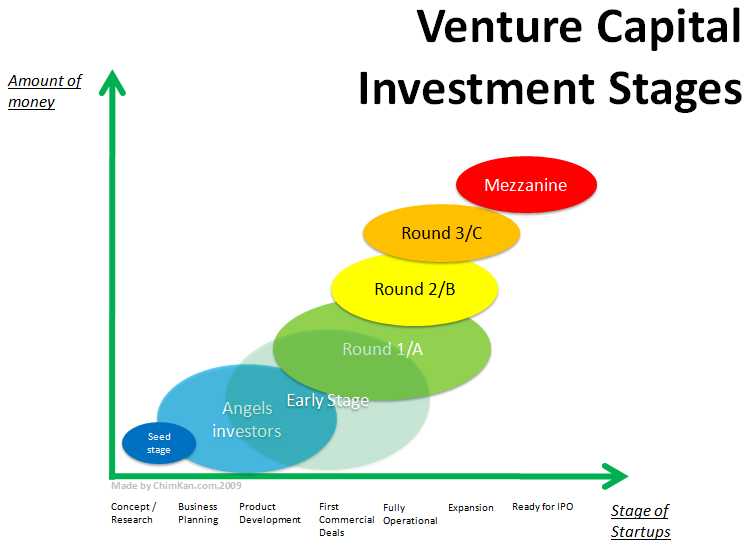
The Venture Capital Financing Spectrum
The requirements of funds vary with the life cycle stage of the enterprise. Even before a business plan is prepared the entrepreneur invests his time and resources in surveying the market, finding and understanding the target customers and their needs. At the seed stage the entrepreneur continue to fund the venture with his own or family funds. At this stage the funds are needed to solicit the consultant’s services in formulation of business plans, meeting potential customers and technology partners. Next the funds would be required for development of the product/process and producing prototypes, hiring key people and building up the managerial team. This is followed by funds for assembling the manufacturing and marketing facilities in that order. Finally the funds are needed to expand the business and attain the critical mass for profit generation. Venture capitalists cater to the needs of the entrepreneurs at different stages of their enterprises. Depending upon the stage they finance, venture capitalists are called angel investors or private equity supplier/investor.
Venture capital was started as early stage financing of relatively small but rapidly growing companies. However various reasons forced venture capitalists to be more and more involved in expansion financing to support the development of existing portfolio companies. With increasing demand of capital from newer business, Venture capitalists began to operate across a broader spectrum of investment interest. This diversity of opportunities enabled Venture capitalists to balance their activities in term of time involvement, risk acceptance and reward potential, while providing on going assistance to developing business.
Different venture capital firms have different attributes and aptitudes for different types of Venture capital investments. Hence there are different stages of entry for different Venture capitalists and they can identify and differentiate between types of Venture capital investments, each appropriate for the given stage of the investee company, These are:-
1. Early Stage Finance
- Seed Capital
- Start up Capital
- Early/First Stage Capital
- Later/Third Stage Capital
2. Later Stage Finance
- Expansion/Development Stage Capital
- Replacement Finance
- Management Buy Out and Buy ins
- Turnarounds
- Mezzanine/Bridge Finance
Not all business firms pass through each of these stages in a sequential manner. For instance seed capital is normally not required by service based ventures. It applies largely to manufacturing or research based activities. Similarly second round finance does not always follow early stage finance. If the business grows successfully it is likely to develop sufficient cash to fund its own growth, so does not require venture capital for growth.
The table below shows risk perception and time orientation for different stages of venture capital financing.
| Financing Stage | Period (funds locked in years) | Risk perception | Activity to be financed |
| Early stage finance Seed | 7-10 | Extreme | For supporting a concept or idea or R & D for product development |
| Start up | 5-9 | Very high | Initializing operations or developing prototypes |
| First stage | 3-7 | High | Start commercial production and marketing |
| Second stage | 3-5 | Sufficiently high | Expand market & growing working capital need |
| Later stage finance | 1-3 | Medium | Market expansion, acquisition & product development for profit making company |
| Buy out-in | 1-3 | Medium | Acquisition financing |
| Turnaround | 3-5 | Medium to high | Turning around a sick company |
| Mezzanine | 1-3 | Low | Facilitating public issue |
1. Seed Capital
It is an idea or concept as opposed to a business. European Venture capital association defines seed capital as “The financing of the initial product development or capital provided to an entrepreneur to prove the feasibility of a project and to qualify for start up capital”.
The characteristics of the seed capital may be enumerated as follows:
- Absence of ready product market
- Absence of complete management team
- Product/ process still in R & D stage
- Initial period / licensing stage of technology transfer
Broadly speaking seed capital investment may take 7 to 10 years to achieve realization. It is the earliest and therefore riskiest stage of Venture capital investment. The new technology and innovations being attempted have equal chance of success and failure. Such projects, particularly hi-tech, projects sink a lot of cash and need a strong financial support for their adaptation, commencement and eventual success. However, while the earliest stage of financing is fraught with risk, it also provides greater potential for realizing significant gains in long term. Typically seed enterprises lack asset base or track record to obtain finance from conventional sources and are largely dependent upon entrepreneur’s personal resources. Seed capital is provided after being satisfied that the entrepreneur has used up his own resources and carried out his idea to a stage of acceptance and has initiated research. The asset underlying the seed capital is often technology or an idea as opposed to human assets (a good management team) so often sought by venture capitalists.
Volume of Investment Activity
It has been observed that Venture capitalist seldom make seed capital investment and these are relatively small by comparison to other forms of venture finance. The absence of interest in providing a significant amount of seed capital can be attributed to the following three factors:
- Seed capital projects by their very nature require a relatively small amount of capital. The success or failure of an individual seed capital investment will have little impact on the performance of all but the smallest venture capitalist’s portfolio. Larger venture capitalists avoid seed capital investments. This is because the small investments are seen to be cost inefficient in terms of time required to analyze, structure and manage them.
- The time horizon to realization for most seed capital investments is typically 7-10 years which is longer than all but most long-term oriented investors will desire.
- The risk of product and technology obsolescence increases as the time to realization is extended. These types of obsolescence are particularly likely to occur with high technology investments particularly in the fields related to Information Technology.
2. Start up Capital
It is the second stage in the venture capital cycle and is distinguishable from seed capital investments. An entrepreneur often needs finance when the business is just starting. The start up stage involves starting a new business. Here in the entrepreneur has moved closer towards establishment of a going concern. Here in the business concept has been fully investigated and the business risk now becomes that of turning the concept into product.
Start up capital is defined as: “Capital needed to finance the product development, initial marketing and establishment of product facility. “
The characteristics of start-up capital are:
- Establishment of company or business. The company is either being organized or is established recently. New business activity could be based on experts, experience or a spin-off from R & D.
- Establishment of most but not all the members of the team. The skills and fitness to the job and situation of the entrepreneur’s team is an important factor for start up finance.
- Development of business plan or idea. The business plan should be fully developed yet the acceptability of the product by the market is uncertain. The company has not yet started trading.
In the start up preposition venture capitalists investment criteria shifts from idea to people involved in the venture and the market opportunity. Before committing any finance at this stage, Venture capitalist however, assesses the managerial ability and the capacity of the entrepreneur, besides the skills, suitability and competence of the managerial team are also evaluated. If required they supply managerial skills and supervision for implementation. The time horizon for start up capital will be typically 6 or 8 years. Failure rate for start up is 2 out of 3. Start up needs funds by way of both first round investment and subsequent follow-up investments. The risk tends t be lower relative to seed capital situation. The risk is controlled by initially investing a smaller amount of capital in start-ups. The decision on additional financing is based upon the successful performance of the company. However, the term to realization of a start up investment remains longer than the term of finance normally provided by the majority of financial institutions. Longer time scale for using exit route demands continued watch on start up projects.
Volume of Investment Activity
Despite potential for specular returns most venture firms avoid investing in start-ups. One reason for the paucity of start up financing may be high discount rate that venture capitalist applies to venture proposals at this level of risk and maturity. They often prefer to spread their risk by sharing the financing. Thus syndicates of investor’s often participate in start up finance.
3. Early Stage Finance
It is also called first stage capital is provided to entrepreneur who has a proven product, to start commercial production and marketing, not covering market expansion, de-risking and acquisition costs. At this stage the company passed into early success stage of its life cycle. A proven management team is put into this stage, a product is established and an identifiable market is being targeted.
British Venture Capital Association has vividly defined early stage finance as: “Finance provided to companies that have completed the product development stage and require further funds to initiate commercial manufacturing and sales but may not be generating profits.”
The characteristics of early stage finance may be:
- Little or no sales revenue.
- Cash flow and profit still negative.
- A small but enthusiastic management team which consists of people with technical and specialist background and with little experience in the management of growing business.
- Short term prospective for dramatic growth in revenue and profits.
The early stage finance usually takes 4 to 6 years time horizon to realization. Early stage finance is the earliest in which two of the fundamentals of business are in place i.e. fully assembled management team and a marketable product. A company needs this round of finance because of any of the following reasons:
- Project overruns on product development.
- Initial loss after start up phase.
The firm needs additional equity funds, which are not available from other sources thus prompting venture capitalist that, have financed the start up stage to provide further financing. The management risk is shifted from factors internal to the firm (lack of management, lack of product etc.) to factors external to the firm (competitive pressures, in sufficient will of financial institutions to provide adequate capital, risk of product obsolescence etc.)
At this stage, capital needs, both fixed and working capital needs are greatest. Further, since firms do not have foundation of a trading record, finance will be difficult to obtain and so Venture capital particularly equity investment without associated debt burden is key to survival of the business.
The following risks are normally associated to firms at this stage:
- The early stage firms may have drawn the attention of and incurred the challenge of a larger competition.
- There is a risk of product obsolescence. This is more so when the firm is involved in high-tech business like computer, information technology etc.
4. Second Stage Finance
It is the capital provided for marketing and meeting the growing working capital needs of an enterprise that has commenced the production but does not have positive cash flows sufficient to take care of its growing needs. Second stage finance, the second trench of Early State Finance is also referred to as follow on finance and can be defined as the provision of capital to the firm which has previously been in receipt of external capital but whose financial needs have subsequently exploded. This may be second or even third injection of capital.
The characteristics of a second stage finance are:
- A developed product on the market
- A full management team in place
- Sales revenue being generated from one or more products
- There are losses in the firm or at best there may be a break even but the surplus generated is insufficient to meet the firm’s needs.
Second round financing typically comes in after start up and early stage funding and so have shorter time to maturity, generally ranging from 3 to 7 years. This stage of financing has both positive and negative reasons.
Negative reasons include:
- Cost overruns in market development.
- Failure of new product to live up to sales forecast.
- Need to re-position products through a new marketing campaign.
- Need to re-define the product in the market place once the product deficiency is revealed.
Positive reasons include:
- Sales appear to be exceeding forecasts and the enterprise needs to acquire assets to gear up for production volumes greater than forecasts.
- High growth enterprises expand faster than their working capital permit, thus needing additional finance. Aim is to provide working capital for initial expansion of an enterprise to meet needs of increasing stocks and receivables.
It is additional injection of funds and is an acceptable part of venture capital. Often provision for such additional finance can be included in the original financing package as an option, subject to certain management performance targets.
5. Later Stage Finance
It is called third stage capital is provided to an enterprise that has established commercial production and basic marketing set-up, typically for market expansion, acquisition, product development etc. It is provided for market expansion of the enterprise. The enterprises eligible for this round of finance have following characteristics.
- Established business, having already passed the risky early stage.
- Expanding high yield, capital growth and good profitability.
- Reputed market position and an established formal organization structure.
“Funds are utilized for further plant expansion, marketing, working capital or development of improved products.” Third stage financing is a mix of equity with debt or subordinate debt. As it is half way between equity and debt in US it is called “mezzanine” finance. It is also called last round of finance in run up to the trade sale or public offer.
Venture capitalists prefer later stage investment vis a vis early stage investments, as the rate of failure in later stage financing is low. It is because firms at this stage have a past performance data, track record of management, established procedures of financial control. The time horizon for realization is shorter, ranging from 3 to 5 years. This helps the venture capitalists to balance their own portfolio of investment as it provides a running yield to venture capitalists. Further the loan component in third stage finance provides tax advantage and superior return to the investors.
There are four sub divisions of later stage finance.
- Expansion / Development Finance
- Replacement Finance
- Buyout Financing
- Turnaround Finance
Expansion / Development Finance
An enterprise established in a given market increases its profits exponentially by achieving the economies of scale. This expansion can be achieved either through an organic growth, that is by expanding production capacity and setting up proper distribution system or by way of acquisitions. Anyhow, expansion needs finance and venture capitalists support both organic growth as well as acquisitions for expansion.
At this stage the real market feedback is used to analyze competition. It may be found that the entrepreneur needs to develop his managerial team for handling growth and managing a larger business.
Realization horizon for expansion / development investment is one to three years. It is favored by venture capitalist as it offers higher rewards in shorter period with lower risk. Funds are needed for new or larger factories and warehouses, production capacities, developing improved or new products, developing new markets or entering exports by enterprise with established business that has already achieved break even and has started making profits.
Replacement Finance
It means substituting one shareholder for another, rather than raising new capital resulting in the change of ownership pattern. Venture capitalist purchase shares from the entrepreneurs and their associates enabling them to reduce their shareholding in unlisted companies. They also buy ordinary shares from non-promoters and convert them to preference shares with fixed dividend coupon. Later, on sale of the company or its listing on stock exchange, these are re-converted to ordinary shares. Thus Venture capitalist makes a capital gain in a period of 1 to 5 years.
Buy-out/Buy-in Financing
It is a recent development and a new form of investment by venture capitalist. The funds provided to the current operating management to acquire or purchase a significant share holding in the business they manage are called management buyout. Management Buy-in refers to the funds provided to enable a manager or a group of managers from outside the company to buy into it. It is the most popular form of venture capital amongst later stage financing. It is less risky as venture capitalist in invests in solid, ongoing and more mature business. The funds are provided for acquiring and revitalizing an existing product line or division of a major business. MBO (Management buyout) has low risk as enterprise to be bought have existed for some time besides having positive cash flow to provide regular returns to the venture capitalist, who structure their investment by judicious combination of debt and equity. Of late there has been a gradual shift away from start up and early finance to wards MBO opportunities. This shift is because of lower risk than start up investments.
Turnaround Finance
It is rare form later stage finance which most of the venture capitalist avoid because of higher degree of risk. When an established enterprise becomes sick, it needs finance as well as management assistance foe a major restructuring to revitalize growth of profits. Unquoted company at an early stage of development often has higher debt than equity; its cash flows are slowing down due to lack of managerial skill and inability to exploit the market potential. The sick companies at the later stages of development do not normally have high debt burden but lack competent staff at various levels. Such enterprises are compelled to relinquish control to new management. The venture capitalist has to carry out the recovery process using hands on management in 2 to 5 years. The risk profile and anticipated rewards are akin to early stage investment.
Bridge Finance
It is the pre-public offering or pre-merger/acquisition finance to a company. It is the last round of financing before the planned exit. Venture capitalist help in building a stable and experienced management team that will help the company in its initial public offer. Most of the time bridge finance helps improves the valuation of the company. Bridge finance often has a realization period of 6 months to one year and hence the risk involved is low. The bridge finance is paid back from the proceeds of the public issue.