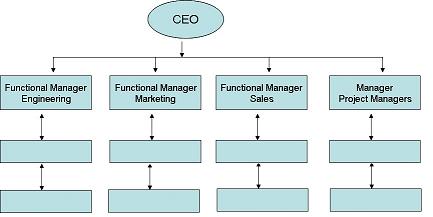
Functional organization is technically called functional foreman-ship because the function itself becomes a supervisor and the employees automatically perform their respective duties. The emphasis of functional organization structure is on operations rather than on management. Functional organization is commonly used in business organizations. The spirit of organization, which involves grouping tasks together and allocating them to genuine employees is observed in functional organization.
Functional sets like marketing, finance, production and personal are grouped systematically. Departments and sub departments are developed according to the requirements of the business. Functional organization is the basic building block or module from which other forms of organization are built. Functional organization is characterized by function, sub-goal emphasis, division of work, functional relationship, centralization and decentralization, span of control, divisionalization of product and regionalization. All employees are not equal; they have distinctive and special interests in different activities, while some of them having similar interests and qualities are grouped together to form a set of similar activities. Their performance and control becomes easy. Effectiveness of the organization is increased with the development of functional organization which may be horizontal or vertical. Horizontal functions include those activities which are performed with the same amount of authority and responsibilities at the same level.
In functional organization structure, the finance, marketing, human resources, production and other activities are at the same level in the hierarchy of an organization, whereas the relationship between the general manager and other functional managers is vertical. The higher level has influence over lower-level individuals. People who are connected with the formulation of policies, having a high degree of authority and responsibility are termed as General Manager, top manager or top executives. The persons at the lower levels are responsible for carrying out functions to achieve the goals set by the top executives. Other persons having skills of performance, supervision, grouping and driving spirit are put at the lower level of management. Similarly, work can be subdivided according to each level of the total activity, and suitable people are entrusted the jobs of performance.
Functional organization is developed for exploiting the specialties of people who concentrate on their specialization and preference. Sub-unit goals are achieved effectively with specialized functioning. Growth is possible with the use of horizontal and vertical organization. The advantages of line and staff organization can be fully achieved only with the development of functional organization within them. Performance and achievements are operating goals of organization, which can be attained if the functions, sub-functions and other lower functions are diversified and well-defined, and suitable persons are entrusted with these diversified functions, being held personally responsible for operations and achievements.
Although multiple supervisors come into operation, the main functions of organization are not diluted, as functional authority is next to line authority which exists in every type of organization. Functional specialists are endowed with command of functions and their effective performance. The coordination of different functions id done by the line organization. Centralized authority and decentralized functioning are visible in such cases. With a suitable span of management, control of different functions becomes easy under functional organization. The advantages of functional organization are available in the form of specialization, coordination, suitability, skill development, economics of scale and flexibilities. When some similar activities are grouped together and developed for meeting the challenges of organization, specialization comes into the picture. Each manager is concerned with only one kind of job. It develops the hierarchy of skills and retention of functional organization. The specialization helps in economic use of physical and human resources, increase in quantity and quality and diversification of product functions.
Innovation and modernization will be feasible when some specialized persons are performing selected jobs, and coordination of all functions becomes essential. Individual functions are linked and brought under the umbrella of the corporate objective. If the segregated functions are not properly aggregated, and advantages of specialization will not be achieved by the company. The top executives control the activities of all the departments, which are allowed to function on specialization. The coordination helps maintain uniformity, unity of command and standardized functioning. Functional organization is suitable for all sizes of business and production units, as it facilitates their efficiency, product quality and automatic operations. Standardization has become an essential function of management. It helps in the skill development of employees who are exposed to a range of functional activities in their respective departments. Discipline is maintained by the experts not on an abstract basis, but at an operational level. A functional structure is economical as only one function is given to an employee who performs the job quickly and qualitatively. All the factory plants, machinery, raw materials and money are utilized effectively and efficiently. The cost of production and distribution per unit is minimized as more production is possible with the existing resources.
Functional organization is not rigid; it can increase or decrease along with the line of business operation. Divisionalization may cover total expansion while the closure of one division will result in the shrinking of business activities. Lower level staff may be promoted to a higher level in case of expansion and the higher level staff may be given lower level jobs in case of contraction of business functions. Centralized leadership is made flexible in order to incorporate any sort of expansion and contraction in functional organization.