For more than three decades, the investment banking activity was mainly confined to merchant banking services. The foreign banks were the forerunners of merchant banking in India. The erstwhile Grindlays Bank began its merchant banking operations in 1967 after obtaining the required license from RBI. Soon after Citibank followed through. Both the banks focused on syndication of loans and raising of equity apart from other advisory services. In 1972, the Banking Commission report asserted the need for merchant banking activities in India and recommended a separate structure for merchant banks totally different from commercial banks structure. The merchant banks were meant to manage investments and provide advisory services.… Read the rest
Indian Banking System
Customer Service Strategies in Banking Sector
Today, banking sector is seen as a catalyst in economic growth of a country and, lot is expected from the banking fraternity. The recognition of banking, as a tool for all inclusive growth by economists, financial planners, reformist etc has made it an important sector in the Government’s planning of economic growth. The banking sector in India is there fore witnessing tremendous changes because of political, social and economic changes that are taking place domestically and internationally.
The concept of banking, which was earlier restricted to accepting of deposits from public for the purpose of, has also undergone sea change. Today the banking sector is seen as a vehicle for all inclusive economic growth, social responsibility and equiv-distribution of national resources.… Read the rest
Role of RBI (Reserve Bank of India) in Payment Systems
The Reserve Bank of India participates in the payment systems as a user of the system, as the service provider for various components of the systems and is also the regulator of the systems in many instances.
As a user, the RBI submits instruments for clearing in the cheque-based clearing operations. RBI also participates as a user in the Electronic Clearing Service (ECS)and EFT systems for making its own internal payments to its employees, vendor payments etc. Similarly, RBI transactions in Repo / Reverse Repo under LAF, Open Market Operations etc., would also be settled through the respective components of payment systems.… Read the rest
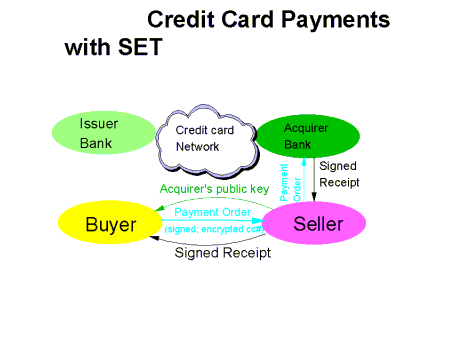
Secure Electronic Transaction (SET)
Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) is a standard protocol for securing credit card transactions over insecure networks, specifically, the Internet. SET is not itself a payment system, but rather a set of security protocols and formats that enables users to employ the existing credit card payment infrastructure on an open network in a secure fashion.
Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) was developed by VISA and MasterCard (involving other companies such as GTE, IBM, Microsoft, Netscape, RSA and VeriSign) starting in 1996. SET is based on X.509 certificates with several extensions. SET uses a blinding algorithm that, in effect, lets merchants substitute a certificate for a user’s credit-card number.… Read the rest
Interest Rate Administration by Reserve Bank of India (RBI) during Global Recession/Subprime Crisis
The subprime crises triggered by a dramatic rise in mortgage delinquencies and foreclosures in the United States, lead to major adverse consequences for banks and financial markets around the globe. Administered interest rates are one of the major measures for controlling the money supply in an economy. Bank rate, repo rate and reverse repo rate are administered by the Reserve Bank of India. The records show high fluctuation in the interest rates in the past in India. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) made drastic cuts in interest rates during the recession period to make sure that the banks and individuals get the benefit of higher credit availability.… Read the rest
Risk Management in Banks: Regulatory Issues and Capital Adequacy
Individual banks risks create Systematic risk, i.e., the risk that the whole banking system fails. Systematic risk results from the high interrelations between banks through mutual lending and borrowing commitments. The failure of single institution generates a risk of failure for all banks that have ongoing commitments with the defaulting bank. Systematic Risk is a major challenge for the regulator.
A number of rules, aimed at limiting risks in a simple manner, have been in force for a long time. For instance, certain ratios are subject to minimum values, say Capital Adequacy Ratio, certain caps are placed viz., Single Borrowers etc.,… Read the rest