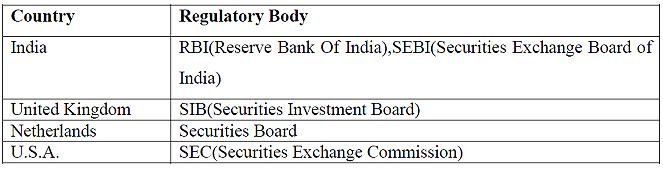
Guidelines Issued by Reserve Bank of India for the Regulation of Financial Markets
1) Management oversight, policy/operational guidelines – The management of a Primary Dealer should bear primary responsibility for ensuring maintenance of appropriate standards of conduct and adherence to proper procedures by the entity. Primary Dealers (PD) should frame and implement suitable policy guidelines on securities transactions. Operational procedures and controls in relation to the day-to-day business operations should also be worked out and put in place to ensure that operations in securities are conducted in accordance with sound and acceptable business practices. With the approval of respective Boards, the PDs should clearly lay down the broad objectives to be followed while undertaking transactions in securities on their own account and on behalf of clients, clearly define the authority to put through deals, procedure to be followed while putting through deals, and adhere to prudential exposure limits, policy regarding dealings with brokers, systems for management of various risks, guidelines for valuation of the portfolio and the reporting systems etc.… Read the rest