The Shell Directional Policy Matrix (DPM) is another refinement upon the Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrix. Along the horizontal axis are prospects for business sector profitability, and along the vertical axis is a company’s competitive capability. Business sector profitability includes the size of the market, expected growth, lack of competition, profit margins within the market and other favorable political and socio-economic conditions. On the other hand company’s competitive capability is determined by the sales volume, the products reputation, reliability of service and competitive pricing. As with the GE Business Screen the location of a Strategic Business Unit (SBU) in any cell of the matrix implies different strategic decisions. However decisions often span options and in practice the zones are an Continue reading
Strategic Management
Strategic management is the art and science of formulating, implementing and evaluating cross-functional decisions that will enable an organization to achieve its objectives. It involves the systematic identification of specifying the firm’s objectives, nurturing policies and strategies to achieve these objectives, and acquiring and making available these resources to implement the policies and strategies to achieve the firm’s objectives. Strategic management, therefore, integrates the activities of the various functional sectors of a business, such as marketing, sales, production etc. , to achieve organizational goals. It is generally the highest level of managerial activity, usually initiate by the board of directors and executed by the firm’s Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and executive team.
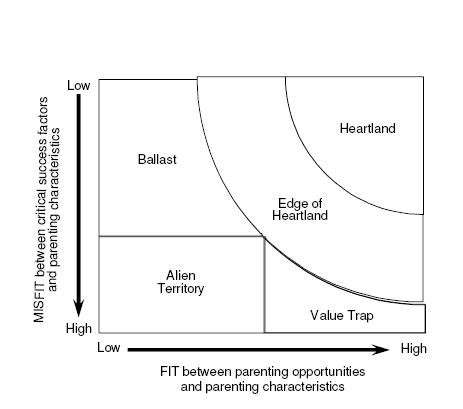
Parenting Fit Matrix
Normally multibusiness companies comprise two elements: business units, which could theoretically be independent companies, relating directly to the capital markets; and one or more layers of other line and staff managers above or outside the businesses, which we refer to collectively as “the parent”. The businesses are directly involved in value creation: they produce goods and services and attempt to sell them for more than their cost. But the parent is involved much less directly. Its ability to create value depends largely on its influence on the businesses and the way it supports them. The parent acts as an intermediary between the businesses and outside investors. It clearly incurs costs, both direct and indirect. It is therefore justified only if, Continue reading
Behavioural Issues in Strategy Implementation
It is vital to bear in mind that organizational change is not an intellectual process concerned with the design of ever-more-complex and elegant organization structures. It is to do with the human side of enterprise and is essentially about changing people’s attitudes, feelings and – above all else – their behavior. The behavioral of the employees affect the success of the organization. Strategic implementation requires support, discipline, motivation and hard work from all manager and employees. Influence Tactics: The organizational leaders have to successfully implement the strategies and achieve the objectives. Therefore the leader has to change the behavior of superiors, peers or subordinates. For this they must develop and communicate the vision of the future and motivate organizational members Continue reading
Strategic Leadership – What Does Strategic Leaders Do?
Concept of Strategic Leadership Strategic Leadership provides the vision and direction for the growth and success of an organization. To successfully deal with change, all executives need the skills and tools for both strategy formulation and implementation. Managing change and ambiguity requires strategic leaders who not only provide a sense of direction, but who can also build ownership and alignment within their workgroups to implement change. Leaders face the continuing challenge of how they can meet the expectations of those who placed them there. Addressing these expectations usually takes the form of strategic decisions and actions. For a strategy to succeed, the leader must be able to adjust it, as conditions require. But leaders cannot learn enough, fast enough, and Continue reading
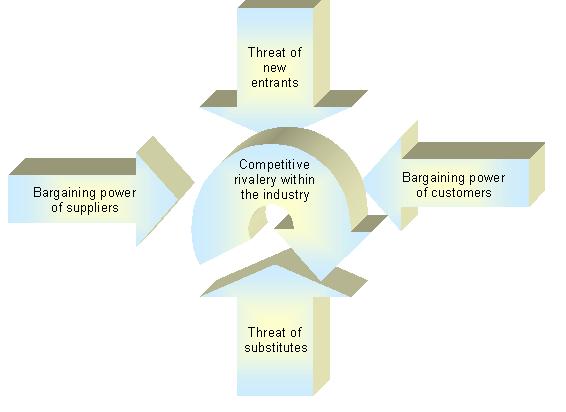
Porter’s Model of the Five Competitive Forces
The nature of competition in an industry in large part determines the content of strategy, especially business-level strategy. Based as it is on the fundamental economics of the industry, the very profit potential of an industry is determined by competitive interactions. Where these interactions are intense, profits tend to be whittled away by the activities of competing. Where they are mild and competitors appear docile, profit potential tends to be high. Yet a full understanding of the elements of competition within an industry is easy to overlook and often difficult to comprehend. Porter’s Competitive Forces Model is one of the most recognized framework for the analysis of business strategy. It is based on the insight that a corporate strategy should Continue reading
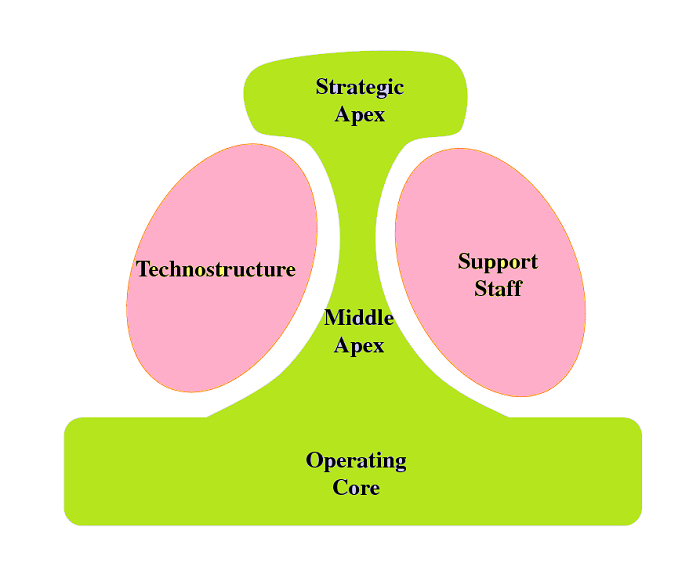
Mintzberg’s Model of Organizational Structure
Management expert Henry Mintzberg proposed that traditionally organizations (profit making or not for profit) can be divided into five components. In practice organizational structure may differ from proposed model. Factors influencing organizational structure are industry norms, size, experience, culture, external forces (competition, inflation, minimum wage legislation etc). Components identified by Mintzberg is useful for understanding the workflow of organizations. The structure of an organization can be defined simply as the sum total of the ways in which it divides its labor into distinct tasks and then achieves coordination among them” – The Structuring of Organizations, Henry Mintzberg. 1. Strategic Apex Strategic apex is the most senior level in the organization. Management working at this level is referred as Continue reading