In the presence of globalization, financial statements have become the standard measurement in judging a company’s performance. Financial statements are an overall impression of the company which shows profitability, efficient utilization of assets, settlement of outstanding debts, management of equity, and liquidity position to make economic and business decisions by both internal and external users. The analysis of financial statements is the application of financial activities and additional facts of the business, the examination of historical, present, and possible results and monetary situation to make investing, financing, and commercial decisions. External decision makers of an organization are defined as potential shareholders, clients, creditors (banks), and tax authorities who need a financial record to give decisions about investment, approval of loan application, acquisition of products, and compliance with applicable tax laws and regulations. This article will assess the importance of financial statements to external users in addition to a qualitative factor. Continue reading
Financial Concepts
The Importance of the Conceptual Framework for Accounting
An accounting framework is a coherent system of inter-related objectives and fundamentals that should lead to consistent standards that prescribe the nature, function and limits of financial accounting and financial statements. The main reason for developing a conceptual framework are that gives a framework for setting accounting standards, a basis for resolving accounting disputes and fundamental principles which then do not have to be repeated in accounting standards. Furthermore, Conceptual Framework can be categorized in terms of the distinctive function of management accounting within the management process in organizations. Moreover, the way in which the utility of the outcomes of the management accounting process can be tested. Conceptual Framework is a criteria which can be used to assess the value of the processes and work technologies used in management accounting and capabilities necessarily associated with the effectiveness of the management accounting function overall. Conceptual Framework plays an important role in Continue reading
Assessment of Agency Theory
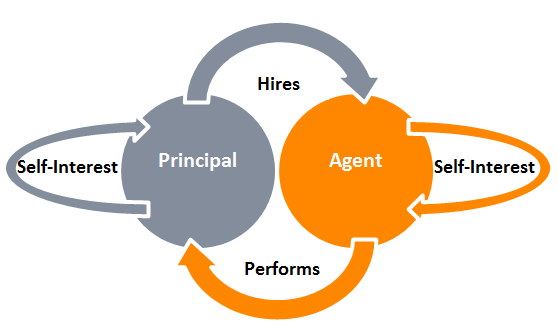
Agency theory refers to a contract whereby principals engage with agents to perform some act on their behalf. The act involved giving power to an agent for some decision-making. Everyone work on the feet of benefit that can be gained for oneself. That’s why it is strongly agreed that the agent, as a utility maximizer will not act in the best interest of the principal. Therefore, agents may cheat if they were not monitored by the principal, and the principal, on the other hand, must bear agency costs to avoid suffering loss. These agency costs include monitoring costs of an agent, bonding costs whereby the agent will try to show that they are not self-serving, and residual losses that are too costly to monitor. In general, agency cost is one of a type of internal cost incurred from or must be paid to, an agent acting on behalf of a Continue reading
Why Shareholder Wealth Maximization is Important in Business?
In modern finance, it is proven that shareholder wealth maximization is the superior goal of a firm and shareholders are the residual claimants; therefore maximizing shareholder returns usually implies that firms must also satisfy stakeholders such as customers, employees, suppliers, local communities, and the environment first. Also, a firm’s value can not be maximized if the management board or shareholders ignores the interest of its stakeholders. Thus, the main goal of a firm is to maximize shareholder wealth but it does not mean that management should disregard stakeholders. To begin with, it is necessary to understand what is shareholder wealth and why maximizing shareholder wealth is a superior objective? Maximizing shareholder wealth is defined as maximizing purchasing power as well as the flow of dividends to shareholders through time and it is a long-term perspective. In addition, a very important point to explain why shareholder wealth maximization is superior objective Continue reading
Predicting Financial Distress and Corporate Failure
The financial failure of a company can have a devastating effect on all seven users of financial statements e.g. present and potential investors, customers, creditors, employees, lenders, the general public, etc. As a result, users of financial statements as indicated previously are interested in predicting not only whether a company will fail, but also when it will fail e.g. to avoid high profile corporate failures at Enron, Arthur Anderson, and WorldCom, etc. Users of financial statements can predict the financial position of an organization using the Altman Z score model, Argenti A score model, and by looking at the financial statements i.e. balance sheet, income statements, and cash flow statements. Business failure is defined as the unfortunate circumstance of a firm’s inability to stay in the business. Business failure occurs when the total liabilities exceed the total assets of a company, as total assets are considered a measure of the Continue reading
Relationship Between Agency Theory and the Existing Accountancy Practices
The agency theory is a mixture of the relationships between principals and agents, it occurs when the principal and the agents create a delegation. The agency theory argues that in modern corporations, where share ownership is widely held, managerial actions depart from those required to maximize the shareholder’s return. In Agency theory terms, the owners are principals and the managers are agents and there is an Agency loss which is the extent to which returns to the residual claimants, the owners, fall below what they would be if the principals, and the owners, exercised direct control of the corporation. The long-term strategies for agency theory include the principle of the company, business, franchise, etc. providing incentives such as increasing commission, continuing to provide advertising, training, and motivation to increase outlet operations. Regarding the exogenous factor, outlet managers have an incentive to shirk and misrepresent their abilities because the firm is Continue reading