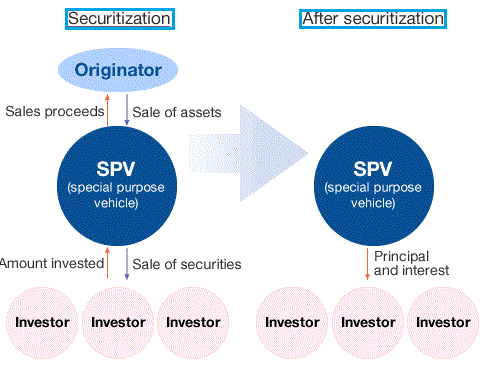
Securitization, also known as asset-backed securitization or structured financing, has been defined as a financing instrument whereby a company transfers rights in current or future receivables or other financial assets to an entity that serves as a “special purpose vehicle” (SPV), which in turn issues securities to capital market investors and uses the proceeds from the issue to pay for the financial assets. The source of the receivables could be any right of payment or asset that generates an income with a stable cash flow. The existing or future receivables could be the income generated, among others things by residential or commercial loans, credit card receivables, automobile loans, student loans, royalties on intellectual property, tax receivables or any other income source that is regular and predictable. Read More: The Concept of Securitization Securitization can also be considered a form of arbitrage between a less-efficient traditional debt market and a more-efficient Continue reading
Financial Management Tools
Steps Involved in the Process of Securitization
Securitization, a process by which illiquid financial assets are transformed into tradable commodities, is one of the most significant innovations of the financial world. Having originated in 1970 in mortgage markets in the USA, securitization has already converted over $90 trillion worth of non-tradable assets into marketable securities. As a powerful tool of liquidity and risk management, securitization has had a tremendous impact on the welfare of the world economy. In mortgage markets in many countries it provides a cheaper source of financing, and thus promotes the demand for housing. In the banking sector, securitization is widely used for allocating capital more efficiently, transforming risk into a tradable security, and reducing the overall cost of capital. It has enabled developing countries to emerging market institutions to raise their sovereign ratings ceilings and thereby tap international capital markets for lower-rate financing. Read More: The Concept of Securitization The process of securitization Continue reading
Most Important Types of Budgets in Managerial Accounting
Definitively, a budget refers to forecast of company’s incomes and expenses anticipated for a given period of time. With a budget, an organization is able to analyze how much money they are making and spending, and they are able to figure the best way to channel it among various categories and departments. Budgeting depicts the entire process of analyzing and planning using a budget. Since budgets are vital tools for management and planning, the process of budgeting generally affects all types of organizations regardless of their size and composition. Many organizations participate in budgeting process with the view of determining the most cost effective and efficient strategies of making profits and intensifying its capital and asset base. In management, budgeting guides an organization to use its scarce resources in a way that exploits the existing business opportunities well. Good budgeting concepts integrate efficient business judgment and help the management to Continue reading
Objectives and Scope of Internal Audit
Internal audit is and self-governing assessment function established by the management of an organisation for the review of the internal control system as a service to the organisation. It separately examines, evaluates and reports on the sufficiency of internal control as a involvement to the correct, economic and successful use of resources Scope of Internal Auditing The possibility of internal auditing currently embraces wider concepts of community governance: risk and power – recognizing that organize exists within an organization basically to manage risk and advance valuable governance . The most significant vary is that the internal auditors are estimated to modify their mindset: from faultfinders to advisers. Internal auditors should take care of the auditee as their consumer. As with a client, the internal auditor should obviously communicate with the auditee, engage management in the audit development process, consider organizational risks that are prospective areas of audit anxiety, work with Continue reading
Approaches to Accounting Theories
Accounting theory is a set of basic assumptions, definitions, principles, and concepts surrounding the accounting rule. It includes the reporting of accounting and financial information to relevant or interested parties. There are several approaches that are used in the development of accounting theory. The two main ones are normative theory approach and the positive theory approach. Normative theory approach is a theory that is not based on observation. It is based on how things in the accounting process should be done. This approach comprises of different approaches to have a single but effective accounting approach. This kind of approach uses a formula to come up with an income based on value, not costs. On the other hand, positive or descriptive theoretical approach to accounting theory is a set of theories that is concerned with what accountants actually do. These theories rely on a process of inductive thinking, which involves making Continue reading
Use of Return on Investment (ROI) to Assess the Performance of Organizations
Analysis of financial statements has being part of the bed rock of finance itself. For publicly traded companies, the greater level of participation by the general publics and sometimes global stakeholders has meant comprehensive assessments are done on their financial statements. Some of the basic reasons for the assessment of the financial statement of companies include the evaluation of current operations, compare the current performance with past performance, make comparison against other firms and industry standards, study the effectiveness and efficiency of operations and the level of efficiency in the utilization of resources. The rationale behind the assessment of a firm’s financial statement is such that a firm has being given resources; it is supposed to convert those resources into profit through the production of goods and the provision of services. Accounting ratios are meant to measure the relationships between resources and financial flows to show ways in which the Continue reading