A Comparison Between Future and Forward Markets As a common trend and general preference, it is most unlikely that the investors would ever involve in the forward market, it is important to understand some of the attitudes, particularly as a good deal of the literature on pricing futures contracts typically refers to those contracts interchangeably. Specially differences resulting from liquidity, credit risk, margin, taxes and commissions could cause futures and forward contracts not to be priced identically. For example, in dealing with price risk, futures contracts have several advantages of transaction in comparison to forward contracts. Sequential spot contracts, which is also known as spot contracts where the terms of the contract are re negotiated as events unfold, do not inject any certainty into the transaction. Such a method of contracting is particularly liable to the hazards of opportunism and may deter investment because of the relatively high probability that Continue reading
Forex Trading
Spot and Forward Foreign Exchange Rates
There are two types of foreign exchange rates, namely the spot rate and forward rates ruling in the foreign exchange market. The spot rate of exchange refers to the rate or price in terms of home currency payable for spot delivery of a specified type of foreign exchange. The forward rate of exchange refers to the price at which a transaction will be consummated at some specified time in future. In modern times the system of forward rate of foreign exchange has assumed great importance in affecting the international capital movements and foreign exchange banks play an important role in this respect by matching the purchases and sales of forward exchange on the part of would be importers and would be exporters respectively. The system of forward foreign exchange rate has actually been developed to minimize risks resulting from the possibility of fluctuations over time in the spot exchange rate Continue reading
Swaps Risk and Exposure
The great bulk of swap activity of date has concentrated on currencies and interest rates, yet these do not exhaust the swap concept’s applicability. As one moves out the yield curve, the primary interest rate swap market becomes dominated by securities transactions and in particular the Eurodollar bond market. The advent of the swap market has meant that the Eurodollar bond market now never closes due to interest rate levels: issuers who would not come to market because of high interest rates now do so to the extent that a swap is available. Indeed, the Eurodollar bond market owes much of its spectacular growth to the parallel growth of its swap market. The firms that now dominate lead management roles in the Eurodollar bond market all have substantial swap capabilities and this trend will continue. One extension is seen in the beginning of the market for equity swaps- an exchange Continue reading
Fixed-Rate Currency Swaps and Currency Coupon Swaps
Fixed-Rate Currency Swaps A fixed rate currency swap consists of the exchange between two counter-parties of fixed rate interest in one currency in return for fixed rate interest in another currency. Following are the main steps to all currency swaps: Initial Exchange for the Principal: The counter-parties exchange the principal amounts on the commencement of the swap at an agreed rate of exchange. Although this rate is usually based on the spot exchange rate, a forward rate set in advance of the swap commencement date can also be used. This initial exchange may be on a notional basis of alternatively a physical exchange. The sole importance of the initial exchange on being either on physical or notional basis, is to establish the quantum of the respective principal amounts for the purpose of (i) calculating he ongoing payments of interest and (ii) the re-exchange of principal amounts under the swap. Ongoing Continue reading
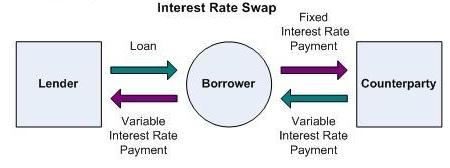
Interest Rate Swaps
The basic structure of an interest rate swap consists of the exchange between two counter-parties of fixed rate interest or floating rate interest in the same currency calculated by reference to a mutually agreed notional principal amount. This principal amount, which would normally equate to the underlying assets or liabilities being “swapped” by the counter-parties, is applicable solely for the calculation of the interest to be exchanged under the swap. At no time it is physically passed between the counter-parties. The counter-parties are able to convert an underlying fixed rate asset/ liability and vice-versa, through this straight forward swap structure. The majority of the interest rate swap transactions are driven by the cost savings to be obtained by each of the counter-parties. These cost savings are substantial and result from differentials in the credit standing of the counter-parties and other structural considerations. Generally investors in fixed rate instruments are more Continue reading
Interest Rate Parity (IRP) Theory of Exchange Rate
When Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) Theory applies to product markets, Interest Rate Parity (IRP) condition applies to financial markets. Interest Rate Parity (IRP) theory postulates that the forward rate differential in the exchange rate of two currencies would equal the interest rate differential between the two countries. Thus it holds that the forward premium or discount for one currency relative to another should be equal to the ratio of nominal interest rate on securities of equal risk (and duration) denominated in two currencies. For example, where the interest rate in India and US are respectively 10% and 6% and the dollar-rupees spot exchange rate is Rs.42.50/US $. The 90 day forward exchange rate would be calculated as per IRP as follows: = 42.50 (1+0.10/4)/(1+0.06/4) = Rs.42.9250 And hence, the forward rate differential [forward premium (p)] will be; (42.9250 — 42.50)/42.50 = 1% And the interest rate differential will be; Continue reading