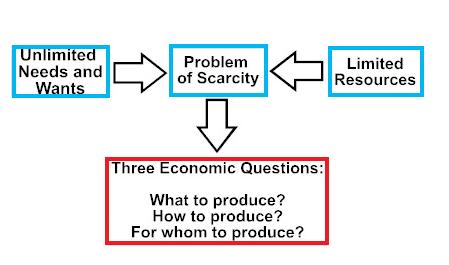
Economic system refers to the organizations and institutions created for the purpose of satisfying the wants of human beings. In a country, available resources have to be utilized to manufacture and distribute goods and services, which would meet the needs of the people so that they are satisfied. These institutions and organizations function with their own rules and regulations. The economic system has certain broad characteristics. The economic system always functions with scarcity of resources. How the system effectively and efficiently uses the resources will determine the extent to which the needs of the people are met. An economic system comprises people. That is, a society of human beings alone can constitute economic system. A set of institutions are created and used for the purpose of smooth functioning of an economic system. For example, banks, money, technology, government, price mechanism, planning etc., are all institutions through which the systems Continue reading
Global Business Environment
Unemployment – Meaning, Causes and Effects
The economists describe unemployment as a condition of jobless within an economy. Unemployment is lack of utilization of resources and it eats up the production of the economy. It can be concluded that unemployment is inversely related to productivity of the economy. Unemployment generally defined as the number of persons (It is the percentage of labor force depends on the population of the country) who are willing to work for the current wage rates in society but not employed currently. Unemployment reduces the long run growth potential of the economy. When the situation arises where there are more other resources for the production and no man power leads to wastage of economic resources and lost output of goods and services and this has a great impact on government expenditure directly. High unemployment causes less consumption of goods and services and less tax payments results in higher government borrowing requirements. The Continue reading
Economic Policies Affecting Business Environment
The economic environment of business is composed of various set of economic policies, economic system, strategy of economic growth and development, resource endowment, size of market and status of infrastructural facilities in a country. All these economic policies affecting business environment one way or the other. Economic policies include fiscal policy, monetary policy, foreign trade policy, price policy, etc. These policies lay the framework within which every organization has to function. To understand the impact of these policies on business environment, let us discuss each one of these components in detail. 1. Fiscal Policy By fiscal policy we mean, the government’s tax efforts, public expenditure and public borrowing. Through these the government can effectively encourage consumption, investment and savings habits and also restrict them. For example, suppose there is inflation in a country. Inflation implies that the people have high purchasing power and so they demand goods. To curb this, Continue reading
External Environment Factors of Business
Business involves activities, which links an organization with outside world. Within an organization, a business is governed by the behavior of its employees, management or decision makers. But externally a business is influenced by a score of factors, which range from customers to competitors and government. Therefore, a business cannot be independent of the influence of these external factors. It should also be noted that a business has absolute control over all the internal factors, it has no control over the external factors. So often it becomes necessary for business houses to modify their internal decisions and policies, on the basis of the pressure from external factors. This highlights the need to be ever- cognizant of changes and influences of external factors so as to conduct business on healthy lines. It is in this context that business environment assumes all significance. Business environment therefore refers to the influences and pressures Continue reading
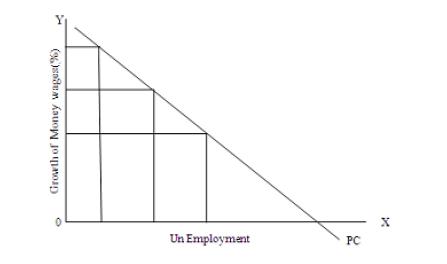
Stagflation and Phillips Curve
Meaning of Stagflation The present day inflation is the best explanation for stagflation in the whole world. It is inflation accompanied by stagnation on the development front in an economy. Instead of leading to full employment, inflation has resulted in un-employment in most of the countries of the world. It is a global phenomenon today. Both developed and developing countries are not free from its clutches. Stagflation is a portmanteau term in macro economics used to describe a period with a high rate of inflation combined with unemployment and economic recession. Inflationary gap occurs when aggregate demand exceeds the available supply and deflationary gap occurs when aggregate demand is less than the aggregate supply. These are two opposite situations. For instance, when inflation goes unchecked for some time, and prices reach very high level, aggregate demand contracts and a slump follows. Private investment is discouraged. Inflationary and deflationary pressures exist Continue reading
Business Competition
Meaning of Competition To a particular business, competition usually refers to firms that market similar or substitutable products in the same geographic area. In general, the term business competition refers to the rivalry among businesses for consumer dollars. For example, the manager of a fast food outlet in an airport views all other fast food outlets near the airport as competition but probably does not think fast food outlets in other geographic areas as competition. In general, all the fast food outlets near the airport compete for passengers’ dollars. In developing and implementing a marketing program, an organization must consider the types of business competition in its markets and assess the actions of its competition. Types of Business Competition The number of organizations that sell a product may affect the strength of competition. When there are many business selling a particular product, for example, price considerations and product differences are Continue reading