Software Trends Several major software trends. First, there has been a major trend away from custom-designed programs developed by the professional programmers of an organization. Instead, the trends is toward the use of off-the-shelf software packages acquired by end users from software vendors. This trend dramatically in creased with the development of relatively inexpensive and easy-to-use application software packages and multipurpose software suites for microcomputers. The trend has accelerated recently, as software packages are designed with networking capabilities and collaboration features that optimize their usefulness for end users and work grounds on the Internet and corporate intranets and extranets. Second, there has been a steady trend away from (1) technical, machine-specific programming language using binary-based or symbolic codes, or (2) procedural languages, which use brief statements and mathematical expressions to specify the sequence of instructions a computer must perform. Instead, the trend is toward the use of a Continue reading
Information Systems Basics
Computer Storage Fundementals and Devices
Data and information must be stored until needed using a variety of storage methods. There are many types of storage media and devices. Computer Storage Fundamentals Data are processed and stored in a computer system through the presence or absence of electronic or magnetic signals in the computer’s circuitry or in the media it uses. This is called a “two-state” or binary representation of data, since the computer and the media can exhibit only two possible states or conditions. For example, transistors other semiconductor circuits are either in a conducting or nonconducting state. Media such as magnetic disks and tapes indicate these two states by having magnetized spots whose magnetic fields have one of two different directions, or polarities. This binary characteristic of computer circuitry and media is what makes the binary number system the basis for representing data in computers. Thus, for electronic circuits, the conducting (ON) state represents Continue reading
Commonly used Computer Input Devices
You can now enter data and commands directly and easily into a computer system through pointing devices like electronic mice and touch pads, and technologies like political scanning, handwriting conviction, and voice recognition. These developments have made it unnecessary to always record data on paper source documents (such as sales order forms, for example) and then keyboard the data into a computer in an additional data entry step. Further improvements in voice recognition and other technologies should enable an even more natural user interface in the future. Pointing Devices: Keyboards are still the most widely used devices for entering data and text into computer systems. However, pointing devices are a better alternative for issuing commands, making choices, and responding to prompts displays on your video screen. They work with you operating systems graphical user interface (GUI), which presents you with icons, menus, windows, buttons, bars, and so on, for your Continue reading
Computer System Concepts and Components
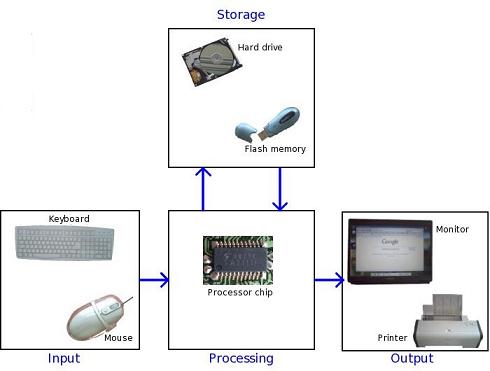
The Computer System Concept. A computer is more than a high-powered collection of electronic devices performing a variety of information processing chores. A computer is a system, an interrelated combination of components that performs the basic system functions of input, processing, output, storage, and control, thus providing end users with a powerful information processing tool. Understanding the computer as a computer system is vital to the effective use and management of computers. A computer is system of hardware devices organized according to the following system functions. Input. The input devices of a computer system include keyboards, touch screens, pens, electronic mice, optical scanners, and so on. Processing. The central processing unit( CPU) is the main processing component of a computer system. (In microcomputers, it is the main microprocessor.) In particular, the electronic circuits of the arithmetic-logic unit one of the CPU’s major components, perform the arithmetic and logic functions required Continue reading
Major Types of Computer Systems
A computer is a programmable machine. It accepts information in the form of digitized data and manipulates it for some result based on a program or sequence of instructions on how the data is to be processed. It consists of at least one processing element, typically a central processing unit (CPU) and some form of memory. The processing element carries out arithmetic and logic operations, and a sequencing and control unit that can change the order of operations based on stored information. Computers are also categorized on the basis of physical structures and the purpose of their use. Based on Capacity, speed and reliability they can be divided following categories of computers: 1. Microcomputer Systems Microcomputers are the most important category of computer systems for end users. Though usually called a personal computer, or PC, a microcomputer is much more than a small computer for use by an individual. The Continue reading
Generation of Computers
It is important to realize that major changes and trends in computer systems have occurred during the major stages-or generations-of computing, and will continue into the future. The first generation of computers developed in the early 1950s, the second generation blossomed during the late 1960s, the third generation took computing into the 1970s, and the fourth generation has been the computer technology of the 1980s and 1990s. A fifth generation of computers that accelerates the trends of the previous generations is expected to evolve as we enter the 21st century. Notice that computers continue to become smaller, faster, more reliable, less costly to purchase and maintain, and more interconnected within computer networks. First-generation computing involved massive computers using hundreds or thousands of vacuum tubes for their processing and memory circuitry. These large computers generated enormous amounts of heat; their vacuum tubes had to be replaced frequently. Thus, they had Continue reading