Conceptually, information systems in the real world can be classified in several different ways. For example, several types of information systems can be classified conceptually as either operations or management information systems. 1. Operations Support Systems Information systems have always been needed to process data generated by, and used in, business operations. Such operations support systems produce a variety of information products for internal and external use. However, they do not emphasize producing the specific information products that can best be sued by managers. Further processing by management information systems is usually required. The role of a business firm’s operations support systems is to efficiently process business transactions, control industrial processes, support enterprise communications and collaboration, and update corporate databases. 2. Transaction Processing Systems Operations support systems include the major category of transaction processing systems (TPS). Transaction processing systems record and process data resulting fro business transactions. Typically examples are Continue reading
Information Systems Basics
Information System Activities
The major activities of an information system are; 1. Input of Data Resource Data about business transactions and other events must be captured and prepared for processing by the input activity. Input typically takes the form of data entry activities such as recording and editing. End uses typically record data about transactions on some type of physical medium such as paper form, or enter it directly into a computer system. This usually includes a variety of editing activities to ensure that they have recorded data correctly. Once entered, data may be transferred onto a machine-readable medium such as a magnetic disk until needed for processing. For example, data about sales transactions can be recorded on source documents such as paper sales order forms. (A source document is the original formal record of a transaction). Alternately, salespersons can capture sales data using computer keyboards or optical scanning devices; they are visually Continue reading
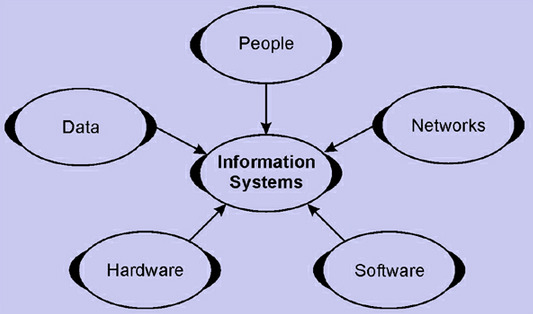
Components of an Information System
A system is a set of components (subsystems) that operate together to achieve certain objectives. The objectives of a system are realized in its outputs. An information system is a system that accepts data resources as input and processes them into information products as output. An information system depends on the resources of people (end users and IS specialists), hardware (machines and media), software (programs and procedures), data (data and knowledge basis), and networks (communications media and network support) to perform input, processing, output, storage, and control activities that convert data resources into information products. This information system model highlights the relationships among the components and activities of information systems. It provides a framework that emphasizes four major concepts that can be applied to all types of information systems: People, hardware, software, data, and networks are the five basic resources of information systems. People resources include end users and IS Continue reading
The Focus of Business Process Reengineering (BPR) on the Current Issues in Business
The existing system in the organization is totally reexamined and radically modified for incorporating the latest technology. This process of change for the betterment of the organization is called as Business process reengineering. With Business process being reengineered, the organizations have to change the workflow and business procedures for efficiency in the organization. Latest software are used and accordingly the business procedures are modified, so that documents are worked upon more easily and efficiently. This is called as workflow management. Business process reengineering is a major innovation changing the way organizations conduct their business. Such changes are often necessary for profitability or even survival. BPR is employed when major IT projects such as ERP are undertaken. Reengineering involves changes in structure, organizational culture and processes. Many concepts of BPR changes organizational structure. Team based organization, mass customization, empowerment and telecommuting are some of the examples. The support system in any Continue reading
E-Commerce and Factors Influencing the Evolution of Electronic Commerce
Electronic commerce has revolutionized the traditional business process of buying and selling on the high street shops by deploying the Internet and technology to reach a vast customer base. The increased use of Internet by the general public and the growth of information technology products to support effective and service transaction over the Internet have apparently fueled the growth of electronic commerce. This statement makes it clear that the electronic commerce has achieved a key position in the business process of an organization. The critical factors that contribute the growth of electronic commerce are: Growth of Internet: The Internet has seen a tremendous growth in the past five years making it a potential place for communicating to many customers both efficiently as well as cost effectively. The process of e marketing by which a customer over the Internet is reached through electronic mails or other form of adverts in the Continue reading
Introduction to Management Information Systems (MIS)
A management information system (MIS) can be defined as a system that: Provides information to support managerial functions like planning, organizing, directing, controlling. Collects information in a systematic and a routine manner which is in accordance with a well defined set of rules. Includes files, hardware, software and operations research models of processing, storing, retrieving and transmitting information to the users. A management information system (MIS) is a subset of the overall internal controls of a business covering the application of people, documents, technologies, and procedures by management accountants to solving business problems such as costing a product, service or a business-wide strategy. Management information systems are distinct from regular information systems in that they are used to analyze other information systems applied in operational activities in the organization. Academically, the term is commonly used to refer to the group of information management methods tied to the automation or support Continue reading