Globalization can be characterized by four factors; the growing worldwide interconnections, rapid, discontinuous change, increased number and diversity of participants, as well as growing complexity. According to the Dictionary of Economics the term; globalization, is defined as the geographical shifts in domestic activity around the world and away from the nation states. It can also be referred to the interdependence of economies, through the increase in cross-border movement of goods, service, technology and capital. Examples of such integrations can be seen in the growing presence of many multinational companies as they expand into new regions (i.e. McDonalds) and the outsourcing of manufacturing and services. Drivers of Globalization The four main areas of drivers for globalization are market, government; cost and competition. These external drivers affect the main conditions for the potential of globalization across industries, which are mainly uncontrollable by individual firms. Market drivers include areas such as common customer needs Continue reading
International Business Basics
Evaluation of Subsidiary Performance in Multinational Operations
A parent company may employ several criteria to evaluate the performance of its foreign subsidiaries. Sales growth, market share, stability in output, asset growth and returns on investment are some of these criteria. Out of these, Return On Investment (ROI) is the most widely-used criteria-because the interest of the parent company ultimately lies in the Return On its Investment. The ROI as calculated on the basis of reported profit repatriation may however not show the true return from the subsidiary. This is because it may be grossly-distorted, due to the following reasons. (i) The subsidiary’s profits are taxed in the host country and repatriation of profit may be subject to further tax. Therefore, the parent company tries to transfer the money from the subsidiary in various other ways such as high royalty, high interest on loan, high expert fees, etc. As a result the, profit repatriation becomes a grossly understated Continue reading
What is a Multinational Corporation (MNC)?
A multinational corporation may be defined company that operates in more than one country. According to the United Commission, Multinational Corporations or Global Corporation is a corporation, which operates in addition to the addition in which; it is incorporated, in one or more other, countries. Such a corporation owns and controls, business in two or more countries. In the words of W H Moreland, “Multinational Corporations or Companies are those enterprises whose management, ownership and controls are spread in more than one foreign country”. In common usage, multinational corporations are also called global corporations and international corporations. While in general these terms may be used interchangeably, there are actually subtle differences between them. Global corporation and multinational corporation represent two extremes whereas International corporation falls somewhere between these two. In a global corporation production facilities are generally centralized. These are located in oneor two countries to get the advantage of Continue reading
Import Process
Importing refers to the purchase of foreign products for use or sale in the home market. Importing involves searching foreign markets for acceptable products and sources of supply, providing for transfer of the product to the home market, arranging financing, negotiating the import documentation and customers procedure, and developing plans for use or for resale of the item of service. Thus, successful importing depends on more than good buying; it requires planning for acceptance of the product and delivery of the promised benefits. The importing firm has the responsibility to determine whether the foreign product or service will meet the needs to the home market. Essentially the import process comprise the following five stages: Determining market demand and purchases motivation. Locating and negotiating with sources of supply. Securing physical distribution. Preparing documentation and customs processing to facilitate movement among countries and organizations. Development a plan for resale or use. 1. Continue reading
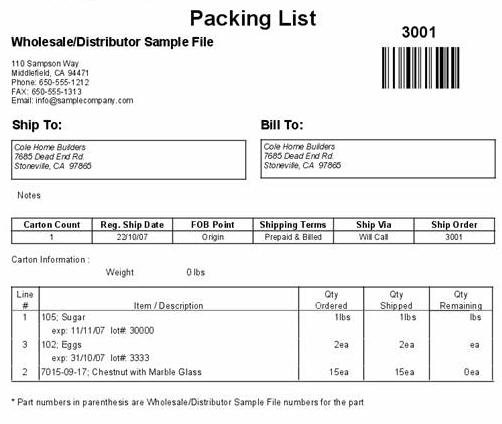
Export Packing List
The export packing list, which may be shown on the commercial invoice or separately, should contain item by item, the contents of cases or containers or of a shipment’s cases, with each item listed separately and with its weight and description set forth in such a manner as to permit a check of the contents by the customs on arrival at the port of destination as well as by the importer. The export packing list must be made in accordance with the instructions of the customer. Great care should be exercised to make certain that the contents of the packages are exactly as indicated in the export packing list. Any variation from what is shown in the export packing list, commercial invoice, or consular invoice may, and usually does, render the consignee liable to heavy fines. In short, in the matter of packing for overseas markets, the exporter should take Continue reading
Concept of Export Packing
The aim of every exporter must be to ensure that the goods arrive safely in the hands of the consumer. The fact that the goods are fully insured is in excuse for not bothering to check whether damage or pilferage occurs during the transit. Whilst the payment of the insurance claim may satisfy the buyer financially, it will not satisfy him mentally. The buyer orders the goods because he can sell them, before the vessel arrives. If he receives only a part of what he has handed in a salable condition, he will probably lose the goodwill of his customers and, in consequences, will blame the exporter. Distinction Between Packing and Packaging There is distinction between the terms export packing and packaging. Packaging refers to the job of providing specialized containers for the packing of goods. Packing is used for the general operation of putting goods into containers for shipment Continue reading