The key difference between Japanese and Western management style is not one of method but of attitude and philosophy. The Japanese have studied the Western style of management, concentrating mainly on American management styles for the past 30 years and have adapted what they believed to be useful methods to their own work environment. It now appears that Western companies are studying some of the Japanese management styles, attitudes, and philosophy and have adopted areas of work ethic, which they believe to be valuable to their companies. It is necessary that Western companies study and deploy various Japanese management styles because the most important reason behind successful Japanese outcome in productivity and quality is the quality of their work force. Western companies aren’t often able to compete with Japanese companies. They must simply adjust their human relations and ways of management in order to become more competitive with not only Continue reading
Management Concepts
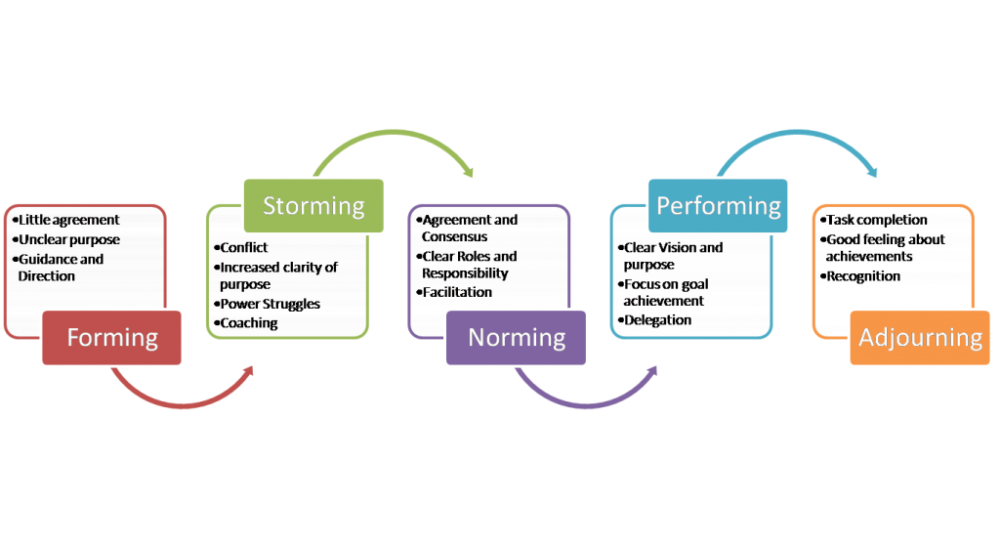
Tuckman’s Team-Building Model
Forming – Storming – Norming – Performing is a model of team development, first proposed by Bruce Tuckman in 1965, who maintained that these phases are all necessary and inevitable in order for the team to grow, to face up to challenges, to tackle problems, to find solutions, to plan work, and to deliver results. He added a fifth stage, Adjourning, in the 1970s. The Forming Storming Norming Performing theory is an elegant and helpful explanation of team development and behavior. Tuckman’s team-building model explains that as the team develops maturity and ability, relationships establish, and the leader changes leadership style. Beginning with a directing style, moving through coaching, then participating, finishing delegating and almost detached. According to Tuckman, all of the phases are necessary and inevitable. In order for the team to grow they most face up to challenges, problems, find solutions to problems, planning as a team, and Continue reading
Stages of Group Development
A group can be defined as two or more interacting and interdependent individuals who come together to achieve specific goals. Although a groups often have goals, but there’s not state that group members must share a goal or motivation. Many people used the word team and group interchangeably, but there are actually many differences between the word team and group. It is much easier to form a group than a team. In group, they could be grouped according to gender, experience, age or other common factors. Although the effectiveness of the group may be variable, but forming a group just based on a certain commonality is not particularly difficult. A group’s strength may come from sheer volume or willingness to carry out a single leader’s commands. On the other hand, a team can be more difficult to form. The members will selected for their complementary skills, not a single commonality. Continue reading
Six Elements of Organizational Design
Organizational design is a process of developing and changing the organization’s structure by its managers. It is a chart containing the reporting structure i.e. who reports to whom. Organizational structure is thus a framework on which an organization is patterned for coordinating and carrying out organizational tasks. Organizational design involves decisions about the following six elements: 1. Work Specialization: Work specialization describes to which the overall task of the organization is broken down and divided into smaller component parts. For example, one person would paint a wall and another person fixes a door. So by breaking jobs up into small tasks, it could be performed over and over every 10 seconds while using employees who had relatively limited skills. The main thought of this process is that the entire job is not done by an individual and it is broken down into steps, and a different person completes each step. Continue reading
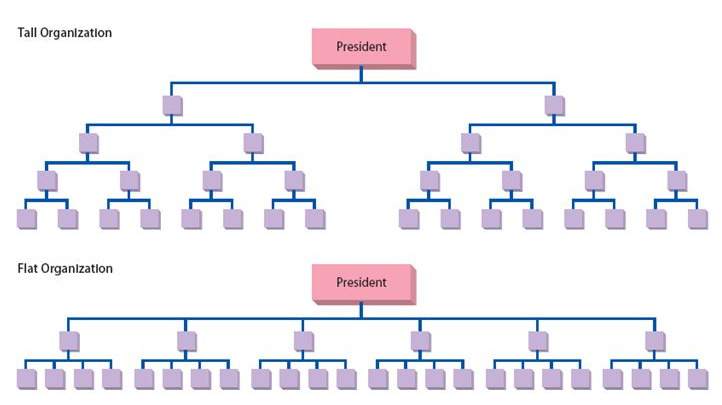
Difference Between Tall and Flat Organizational Structure
The concept of organization is born when two or more people work together in order to achieve a common goal. Purpose of an organisation is to create responsibilities and positions by which an organisation can carry out the work. Organisation may be formed in different sizes. All people working in the same organisation have their own functions, attitudes and techniques to apply for achieving their common goal. In order to manage and control the resources, an organisation needs to be structured. Organization structure is formal system that makes the organisation to run smoothly and helps to focus the common goals and objectives. It gives a clear idea about the chain of command that need to be prioritized when a problem arise. It also defines what people are responsible in the organisation for different reasons. A solid structure provides the framework to deliver on business strategy. The structure of an organisation Continue reading
Unemployment – Meaning, Causes and Effects
The economists describe unemployment as a condition of jobless within an economy. Unemployment is lack of utilization of resources and it eats up the production of the economy. It can be concluded that unemployment is inversely related to productivity of the economy. Unemployment generally defined as the number of persons (It is the percentage of labor force depends on the population of the country) who are willing to work for the current wage rates in society but not employed currently. Unemployment reduces the long run growth potential of the economy. When the situation arises where there are more other resources for the production and no man power leads to wastage of economic resources and lost output of goods and services and this has a great impact on government expenditure directly. High unemployment causes less consumption of goods and services and less tax payments results in higher government borrowing requirements. The Continue reading