Total Quality Management (TQM) is a method by which management and employees can become involved in the continuous improvement of the production of goods and services. It is a combination of quality and management tools aimed at increasing business and reducing losses due to wasteful practices. Total Quality Management (TQM) views an organization as a collection of processes. It maintains that organizations must strive to continuously improve these processes by incorporating the knowledge and experiences of workers. The simple objective of TQM is “Do the right things, right the first time, every time.” TQM is infinitely variable and adaptable. Although originally applied to manufacturing operations, and for a number of years only used in that area, TQM is now becoming recognized as a generic management tool, just as applicable in service and public sector organizations. A preliminary step in Total Quality Management (TQM) implementation is to assess the organization’s Continue reading
Modern Management Approaches
Business Strategy Games
The Business Strategy Game is a hands on learning exercise that will give managers valuable decision-making practice and develop powers of business judgment. Business strategy games involving management process before confirming the decision to be made. Lesson learned taken from the business game, from the process and the content from the case (industry and situation & condition of the business) is used for decision making. Various processes involved in business strategy games are; Management Process Planning was the first process taken. Reading and understanding the relevant information was necessary and plays a significant role in planning process. Expectation was established in the planning, and followed stepping process until all aspects have been determined, including all distinctiveness in production (capacity, model, etc.), transportation (shipping), labor, etc. Planning is critical, and it was indicated in the business strategy games, in which it required quite some time to achieve an agreement. Time Continue reading
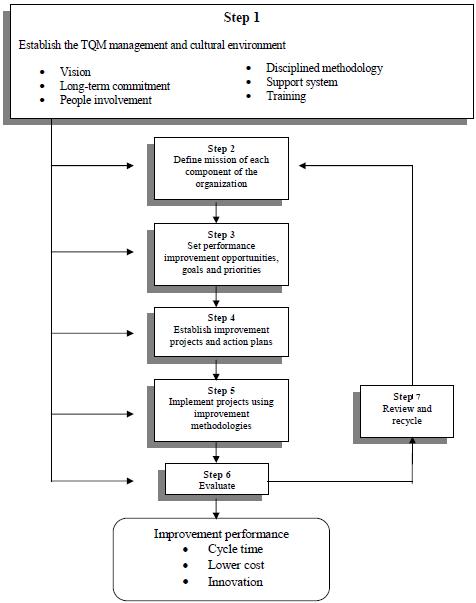
DSMC/ATI Organizational Performance Improvement Model
Out of the organizational performance improvement planning process come specific performance improvement interventions, tactics and techniques. Note that these interventions happen at five checkpoints. Upstream systems, inputs, process, outputs and downstream systems. Quality management efforts must be defined relative to these five checkpoints. In effect, transformation and continuous improvement efforts are commitments to a practice of managing all five-quality checkpoints. The management team then develops, through the performance improvement planning process, a balanced attack to improve total system performance, not just system sub-components. After interventions are made to the system, measure, assess and analyze organizational performance at the five checkpoints to determine whether the expected impact actually occurred. Based on these data, make an evaluation relative to the business strategy, the environment (both internal and external), the vision, the plan and the improvement actions themselves. Note that the process of evaluation is separate from the process of measurement. In addition, Continue reading
Concept of Organizational Climate
Organizations are social systems. Organizations combine science and people, technology and humanity. It is not possible for every organization to have the same type of technology and people and so the organizations differ in their characteristics and internal environment. The internal environment of an organization may be called the organizational climate. Organizational climate, a guide for dealing with people serves as a major influence on motivation and productivity of individuals and total work force. Organizational climate may be noted as the ‘personality’ of an organization as conceived by its employees. The organizational climate usually has a major influence on motivation, productivity and job satisfaction. The organizational climate is the major motivating factor responsible for satisfaction and dissatisfaction of employees in an organization and affects the quantum of employees’ turnover and satisfaction. It refers to the entire social system of a working group. Campbell defines organizational climate as a “set of Continue reading
Improving Quality of Work Life
Quality of work life improvement refers to any activity for greater organizational effectiveness through the enhancement of human dignity and growth process through which the work force of the organization learn how to work together for betterment to determine for themselves what actions, changes and improvements are desirable and workable. What work force feels about the work place? The ‘Economic Times’ in December 1999 collected the views from top level HR executives from Indian companies on the emerging workplace. The views expressed were as follows: There would be more celebrations. Music, poetry, and art at work to provide creative moments in between the lightening speed of work. People with high EQ levels would be valued far more than yesterday as coaches and facilitators orchestrate the output of knowledge workers. People tomorrow would want and deserve a workplace free from anxiety and stress, where each can contribute fully from their jobs Continue reading
Organizational Innovation
Organizational Innovation is a process of receiving and using new ideas to satisfy the stakeholders of an organization. It is the conversion of new knowledge into new products and services. Organizational Innovation is about creating value and increasing efficiency, and therefore growing business. It is a spark that keeps organizations and people moving ever onward and upward. “Without innovation, new products, new services, and new ways of doing business would never emerge, and most organizations would be forever stuck doing the same old things the same old way. “Innovation here is defined broadly, to include both improvements in technology and better methods or ways of doing things. It can be manifested in product changes, process changes, new approaches to marketing, new forms of distribution, and new conceptions of scope.” (Porter, 1990, p. 45) The term organizational innovations covers a wide spectrum of innovations; for example, it can mean innovations in Continue reading