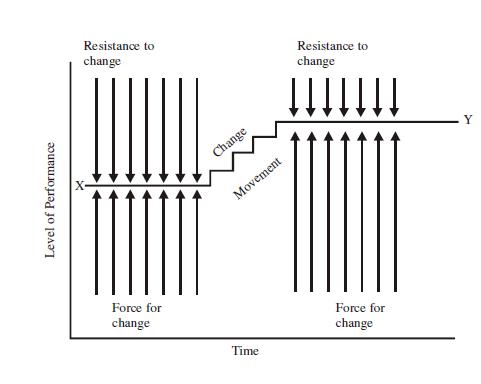
Change management is a methodical approach to handling with change, not only from the angle of an organization but on the individual level. A rather vague term, change management has more than three different dimensions, adapting to change, controlling change, and effecting change included. A proactive approach to handling with change is at the central part of all three aspects. For an organization, change management means making the definition and implementation of procedures and/or technologies to handle with changes in the business environment and to profit from changing opportunities. Triumphant adaptation to change is as vital within an organization as it is in the natural world. Just similar to plants and animals, organizations and the individuals in them unavoidably run into changing conditions that they are incapable to control. The more effectively you handle with change, the more probable you are to flourish. Building structured methods for addressing changes in Continue reading
Modern Management Practices
Intergroup Interventions in Organizational Development
Inter-group team building intervention intends to increase communications and interactions between work related groups to reduce the amount of dysfunctional competition and to replace a parochial independent point of view with an awareness of the necessity for interdependence of action calling on the best efforts of both the groups. Inter-group interventions are integrated into Organizational Development programs to facilitate cooperation and efficiency between different groups within an organization. For instance, departmental interaction often deteriorates in larger organizations as different divisions battle for limited resources or become detached from the needs of other departments. Conflict resolution meetings are one common inter-group intervention. First, different group leaders are brought together to get their commitment to the intervention. Next, the teams meet separately to make a list of their feelings about the other group(s). Then the groups meet and share their lists. Finally, the teams meet to discuss the problems and to try Continue reading
Organizational Innovation
Organizational Innovation is a process of receiving and using new ideas to satisfy the stakeholders of an organization. It is the conversion of new knowledge into new products and services. Organizational Innovation is about creating value and increasing efficiency, and therefore growing business. It is a spark that keeps organizations and people moving ever onward and upward. “Without innovation, new products, new services, and new ways of doing business would never emerge, and most organizations would be forever stuck doing the same old things the same old way. “Innovation here is defined broadly, to include both improvements in technology and better methods or ways of doing things. It can be manifested in product changes, process changes, new approaches to marketing, new forms of distribution, and new conceptions of scope.” (Porter, 1990, p. 45) The term organizational innovations covers a wide spectrum of innovations; for example, it can mean innovations in Continue reading
Organizational Development through Team Building
There are a variety of situations where new teams are formed. The project based, cross-functional work team has become the basis of industry in the 1990’s. Virtual team organization is rapidly becoming the model for flexibility and agility in organizing quickly and effectively to get jobs done. New teams usually have a clear task focus in the early going and there is usually a clear understanding of the short term goals. The new team members are also generally technically competent and there usually is a challenge in the project that will draw on their technical capabilities. While the early activities of a team are clearly focused on task and work issues, relationship problems tend do develop as they do in any human system. By the time these interpersonal issues surface the team may be well along in its activities. The issues may become very difficult and very costly to work Continue reading
Process Consultation
The process consultation view has been advocated by Schein since late 60’s (first edition 1969). It belongs to activities of organization development (OD). OD is one of part of the organization processes which aim improving organizational and individual effectiveness. Process consultation (PC) is one of the OD techniques, enlisted with sensitivity training (self €improvement), survey feedback (introspection),team building (socializing), and role negotiation (changing roles and perception. The main argument of Schein for process consulting is to help people in organizations to help themselves. Process Consultation is the creation of a relationship with the client that permits the client to perceive, understand, and act on the process events that occur in the client’s internal and external environment in order to improve the situation as defined by the client. Edgar Schein, (1969) Process Consultation: Its role in organization development Process consultation is the reasoned and intentional interventions by the consultant, into the Continue reading
Sensitivity Training
Sensitivity training is a method of laboratory training where an unstructured group of individuals exchange thoughts and feelings on a face-to-face basis. Sensitivity training helps give insight into how and why others feel the way they do on issues of mutual concern. Training in small groups in which people develop a sensitive awareness and understanding of themselves and of their relationships with others. Sensitivity training is based on research on human behavior that came out of efforts during World War II to ascertain whether or not an enemy’s core beliefs and behavior could be modified by the application of certain psychological techniques. These techniques have been gradually perfected over the years by efforts of business and industry leaders to persuade people to buy products, including the radio and television industry to ascertain how an audience might be habituated to certain types of programming. Kurt Lewin is credited with being the Continue reading