Production is a conversion function by which goods and services are produced. A typical production system comprises of three main components: Inputs, Transformation process and Output. Inputs are men, materials, machines, instructions, drawings, and paper work and instructions. The Transformation Process involves operations, mechanical or chemical, to Change/convert inputs into outputs. It also includes activities that assist conversion, Output is goods and services (e.g. products, parts, paper work, served customers etc.) The combination of operations and activities stated above employed to create goods and services are known as manufacturing system. A manufacturing system therefore may be looked upon as an independent group of sub-systems, each sub-system performing a distinct function. Different sub-systems may perform different functions, yet they are inter-related and require to be unified to achieve overall objectives of the organization. Manufacturing system needs to interact with both internal and external environment. The internal environment is the combination of Continue reading
Production Management Concepts
Introduction to Crtical Path Analysis
Critical Path Analysis The OR techniques used for planning, scheduling and controlling the large and complex projects are often referred to as Critical Path Analysis or Network Analysis. A network is a graphical diagram consisting of a certain configuration of arrows and nodes for showing the logical sequence of various tasks( or activities) to be performed to achieve project objectives. Network analysis is the quite useful for designing, planning, coordinating, controlling and decision- making so that the project could be economically completed in the minimum possible time with the limited available resources two most popular form of this technique now used in many scheduling situations are the Critical Path Method (CPM) and Program Evaluation and Review Technique. (PERT) CPM: It differentiates between planning and scheduling. Planning refers to the determination of activities that must be accomplished and the order in which such activities should be performed to achieve the Continue reading
Method Study Procedure
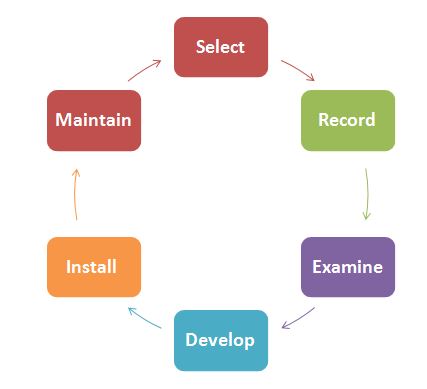
Method study is the systematic recording and critical examination of existing and proposed ways of doing work, as a means of developing and applying easier and more effective methods and reducing costs. So it is the process of analyzing the methods involved in work flow to increase productivity. It deals with doing the work in a better way, with less time and effort. That is why it is also termed as work simplification. Method study procedure is an organized approach and its investigation rests on the following six basic steps: Select the work to be analyzed. Record all facts relating to the existing method. Examine the recorded facts critically but impartially. Develop the most economical method commensurate with plant requirements Install the new method as standard practice. Maintain the new method. The above basic method study procedure was first developed and articulated by Russell Currie at Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI). Continue reading
Objectives and Principles of a Good Plant Layout
Plant layout is a plan for effective utilization of facilities for the manufacture of products; involving a most efficient and economical arrangement of machines, materials, personnel, storage space and all supporting services, within available floor space. A good rather an ideal layout is one which provides maximum satisfaction to all concerned i.e. shareholders, management employees and consumers. Objectives of a Good Plant Layout Only through an efficient layout, the organization can attain the following objectives: Economy in handling of materials, work-in-process and finished goods. Minimization of product delays. Lesser work-in-progress and minimum manufacturing cycle time. Efficient utilization of available space. Easy supervision and better production control. Greater flexibility for changes in product design and for future expansion. Better working conditions by eliminating causes of excessive noise, objectionable odor smoke etc. Principles of a Good Plant Layout Overall integration of factors: A good layout is one that integrates men, materials, machines Continue reading
Batch Production and It’s Key Characteristics
Batch production is one of manufacturing methods where limited quantity of each type of product is authorized for manufacture at a time. It is characterized by the manufacture of a limited number of products produced at periodic intervals and stocked in warehouses as finished goods awaiting sales. Typical examples of such batch production are process industries such as pharmaceuticals, paints, chemicals, medium and heavy engineering industry engaged in the manufacture of electric motors, switch gear, heave motor vehicles, internal combustion engines; manufacturer of readymade garments etc. Characteristics of Batch Production Short Runs: Short production runs and frequent changes of setup also characterize batch production. The equipment and the assembly setup is used for a limited number of parts or assemblies and is then changes to make a different product. The production is generally made to stock. In project production, each project has a definite beginning and a definite end. Skilled Continue reading