Surveying means contacting for getting certain information. Survey method is a method of collecting data for research purpose. There are personal surveys, mail surveys, telephone surveys and internet surveys. Survey may be sample survey or census survey. The features of each of surveys are given below: Personal Survey Personal survey involves meeting personally every number who has to be surveyed. The features of this method of data collection are as follows. The number of respondents that can be contacted is not very high, as the time taken to contact the respondent, and the time spent on the interview itself is very high in relative terms. When the time available for research in large the personal method is used. The cost involved is highest in the personal method since it requires field interviewers as well as their conveyance/ traveling costs. Also, if a person is not available he may have to Continue reading
Research Techniques
The Case Method in Research
Case study method is one of the methods of investigation. Originally case method was used in medicine. The physician used to maintain a record of treatment and health conditions of each patient. Each such record pertains to a ‘case’. The peculiarities of each ‘case’ are known as well as generalities of all cases together. The cause-effect relationship is established and exceptions there to are also noted down. The basic unit of case study is a case – a particular one of its kind. It may be a single business unit or a whole group of business units in an area or a single producer or a group of producers or a single consumer or a group of consumers and so on. When a group is involved, that group is treated as one unit, with whatever phenomenon found in one group member is taken as a phenomenon of the group as Continue reading
Basic Laws of Sampling
Sometimes it is possible to obtain sufficiently accurate results by studying a part/a segment of the population. Thus the few items are selected from the population in such a way that they are the representative of the universe and these representatives in research are called as ‘sample’. The process of selecting the representatives from the population is called ‘sampling’. Thus sampling is simply the process of learning about population on the basis of sample drawn from it. Under this method a small group of universe is taken as the representative of the whole mass and the results are drawn. It is the method to make social/business investigation practicable and easy. Sampling is, therefore, resorted to when either it is impossible to enumerate all the units in the whole population or when it is too costly to enumerate in terms of time and money or when the uncertainty inherent in sampling Continue reading
Sample Design
A sample design is a definite plan for obtaining a sample from a given population. It refers to the technique or the procedure the researcher would adopt in selecting items for the sample. Sample design also leads to a procedure to tell the number of items to be included in the sample i.e., the size of the sample. Hence, sample design is determined before the collection of data. Among various types of sample design technique, the researcher should choose that samples which are reliable and appropriate for his research study. Steps in Sample Design There are various steps which the researcher should follow. Those are; Type of universe: In the first step the researcher should clarify and should be expert in the study of universe. The universe may be finite (no of items are know) or Infinite (numbers of items are not know). Sampling unit: A decision has to be Continue reading
Simple Random Sampling in Research
In probability sampling, each element of the population has a known non-zero chance of being selected for the sample. Among the probability sampling methods, simple random sampling is simplest as its name indicate and it underlies many of the more complex methods. In a simple random sample of a given size, all such subsets of the frame are given an equal probability. Each element of the frame thus has an equal probability of selection: the frame is not subdivided or partitioned. Furthermore, any given pair of elements has the same chance of selection as any other such pair (and similarly for triples, and so on). This minimises bias and simplifies analysis of results. In particular, the variance between individual results within the sample is a good indicator of variance in the overall population, which makes it relatively easy to estimate the accuracy of results. However, simple random sampling can be Continue reading
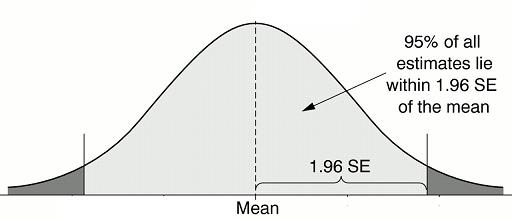
Standard Error in Hypothesis Testing
The standard error is an indispensable tool in the kit of a researcher, because it is used in testing the validity of statistical hypothesis. The standard deviation of the sampling distribution of a statistic is called the standard error. The standard error is important in dealing with statistics (measures of samples) which are normally distributed. Here the use of the word “error” is justified in this connection by the fact that we usually regard the expected value to be true value and the divergence from it as error of estimation due to sampling fluctuations. The term standard error has a wider meaning than merely the standard deviation of simple sampling because of the following reasons; The standard error is mainly employed for testing the validity of a given hypothesis. Mostly two levels of significance (0.05 and 0.01) are used for testing the validity of hypotheses. At 0.05 level of significance, Continue reading