Starbucks Coffee Company’s success in the coffee business echoed resoundingly across the globe. Starbucks Corporation is an international coffee and coffeehouse chain based in Seattle, Washington, United States. Starbucks is the largest coffeehouse company in the world, with 16,635 stores in 49 countries, including 11,068 (6,764 Company Owned, 4,304 Franchised) in the United States, followed by nearly 1,000 in Canada and more than 800 in Japan. Starbucks sells drip brewed coffee, espresso-based hot drinks, other hot and cold drinks, snacks, and items such as mugs and coffee beans. Through the Starbucks Entertainment division and Hear Music brand, the company also markets books, music, and film. Many of the company’s products are seasonal or specific to the locality of the store. Starbucks-brand ice cream and coffee are also offered at grocery stores. Starbucks marketed itself as the “Third Place” — a place where people can go aside from home and the workplace. The rapid growth of Starbucks has become a success story in the business world and many people are bewildered by the company’s business strategy.
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis of Starbucks
Michael E. Porter provided a framework that models an industry as being influenced by five forces. The Porter’s Five Forces analysis presents a clear view of the external conditions and the contending forces within a specific business industry. It also allows strategists to create a strategy in order to gain competitive advantage or sustain the same for a longer period of time.
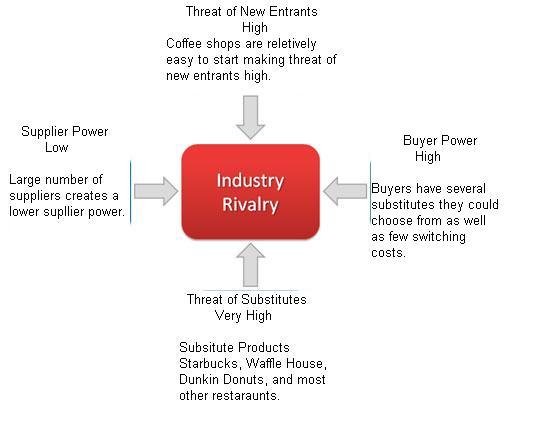
Industry Rivalry
The dynamics of the industry rivalry within the specialty coffee industry has changed dramatically since 1987. Unlike the early days of the specialty coffee industry when Starbucks competed primarily against other small-scale specialty coffee retailers they now compete against companies of varying sizes and different exposures to specialty coffee. Starbucks competes with a variety of smaller scale specialty coffee shops, mostly concentrated in different regions of the country. All of these specialty coffee chains are differentiated from Starbucks in one way or another.
Coffee Bean competes with Starbucks. They are similar to Starbucks in their attempt to create a third-place but distinguish themselves by creating an entirely different atmosphere. Where Starbucks strives to create an upscale European atmosphere, Coffee Bean tries to implement a more American feel to their coffee houses. Often they will use knotty pine cabinetry, numerous fireplaces and soft seating. Also they offer a barrage of magazines and newspapers as well as the guarantee of speedy service and free refills. In addition, they offer free WiFi, drive through accessibility and meeting rooms for rent. Through their subsidiary VKI technologies, they have become the world leader in the design, manufacture and distribution of coffee making equipment and related products.
In addition to these smaller scale specialty coffee companies, Starbucks must now compete against two of the largest companies in the fast food industry who have recently entered the specialty coffee segment. The first of these competitors is Dunkin Donuts, who claims to be “the world’s largest coffee and baked goods chain.” Currently, Dunkin Donuts operates about 5,500 franchises around the United States, 80 stores in Canada and 1,850 throughout the rest of the world. In the past couple years the franchise has put enormous emphasis on their coffee beverages. They serve coffee beverages in an assortment of types and styles including espresso, cappuccino and latte. They also serve their coffee in an assortment of flavors including French Vanilla, hazelnut, cinnamon and numerous others.
The largest industry rival currently facing Starbucks is the McDonald’s restaurant fast food chain. McDonald’s originated from a single San Bernardino, California hamburger stand, which opened in 1948, and has turned into what is now the world’s largest restaurant chain with over 14,000 restaurants in the United States alone. The key to McDonald’s success has been the consistent quality standards they achieve for their food, coupled with their quick service and low prices.
10 years ago Starbucks and McDonald’s were at complete opposite ends of the spectrum in the restaurant industry. However, McDonald’s, encouraged by the success of its upgraded drip coffee, began testing numerous drinks sold under the name McCafe. Starbucks meanwhile, with its rapid expansion, was adding drive-through windows and numerous breakfast sandwiches, similar to the Egg McMuffin’s served at McDonald’s, to their stores. These measures have drawn the two companies closer together as competitors due to an encroachment into the demographic consumer base made by each company.
In summary, the current impact of the industry rivalry force created by the competition between specialty coffee retailers is very high, especially as contrasted to what it was at the time of Starbucks’ rapid expansion twenty years ago. The growth of the industry has slowed while the number of competitors within the industry has increased. Both of these factors, in addition to Dunkin’ Donuts and McDonald’s high strategic stakes in the specialty coffee industry, have caused this change from weak to strong industry rivalry.
Another of the five forces in Porter’s model, which has changed significantly since the late 80s when we analyze the current environment in which Starbucks competes, is the potential for new entrants. As stated earlier, the primary deterrents to entry in the specialty coffee industry are the various barriers to entry. The economies of scale within the specialty coffee industry have increased as the size of the top players has increased. Companies such as Dunkin’ Donuts and McDonald’s have national distribution channels through which they can transport their specialty coffee at a relatively low cost compared to potential new entrants who have no such developed distribution systems.
These larger companies are also able to economize on their accounting operations and marketing budgets by facilitating their specialty coffee operations from the same department as for all segments of their businesses. Finally, these larger corporations are also able to reap economies of scale through their purchasing by negotiating long term contracts with coffee farmers and purchasing coffee beans in bulk quantities at discount prices.
There is numerous cost disadvantages imposed on new entrants that are independent of the economies of scale considerations. As the industry matures, the ability to access distribution channels and select from the highest quality coffee beans has becoming increasingly difficult. Most of the favorable store locations within the larger metropolitan areas have already been occupied by current competitors within the specialty coffee industry. Additionally, many companies now have proprietary product technology involved in the production of their specialty coffee as well as lower per unit costs due to an experience curve.
Product differentiation within the specialty coffee industry has moved away from the purely objective and defined traits such as the taste of the coffee, convenience of the stores and prices charged. The industry has progressed toward more subjective traits such as the ambiance of the store, the social responsibility of the company and brand identification. Many companies have gained very loyal customer bases stemming from their past advertisements, customer service, objective product differentiation’s and early entry into the industry. All of this makes it more difficult for new entrants to gain a solid customer base.
From the analysis above, it can be ascertained that the barriers to entry in the specialty coffee industry have increased substantially. As a consequence, the potential threat of new entrants has gone down. Since, the industry does not have large capital requirements, smaller specialty coffee shops are still prevalent throughout the United States and the potential for more of them to enter the industry is still present. However, these new entrants can be disregarded given the unlikely nature of their concerted expansion and the inconsequential effects they have singly on the overall demand in the consumer market.
Substitute Products
The force created by substitute products in the specialty coffee industry has decreased. Many companies that presented the specialty coffee industry with a threat in the form of substitute products have actually entered the industry and now compete directly by offering their own premium coffee selections. The primary substitute products still posing a threat to the specialty coffee industry are the caffeinated soft drinks offered by Pepsi and Coca-Cola. However, even these substitute products pose little threat to the premium coffee industry. In the past five years, studies done on the percentage of meals or snacks that included a carbonated soft drink as opposed to coffee have shown a reversal in consumer preference. Coffee has gradually gained preference over carbonated soft drinks. This is mostly attributed to the health concerns associated with carbonated soft drinks and the new evidence showing coffee as a relatively healthy alternative.
Supplier Bargaining Power
With the extensive growth in the specialty coffee industry, supplier bargaining power has changed in numerous ways. In 1987, when the first Starbucks was conceived, the farmers from whom Starbucks purchased its premium coffee beans were numerous, small and unconnected to one another. Currently, many of the farmers who sell to Starbucks and other premium coffee chains are united by an initiative known as fair trade certified coffee, which was organized by TransFair USA. Under this initiative, companies such as Starbucks are given the opportunity to advertise their coffee as being fair trade certified if they purchase from coffee suppliers that are democratically owned cooperatives.
This initiative was designed to ensure that the coffee farmers would be compensated fairly for their crops. Their increased unity under this initiative worked as a positive externality by increasing their ability to exert bargaining power over their buyers. The fair trade coffee certification is looked at by consumers in their decision of where to purchase their premium coffee. Thus, although the farmers are still numerous and small they are now connected through the initiative launched by TransFair USA and act in some respects like one large entity. Although the farmers of premium Arabica beans are still in constant competition with the substitute Robusta coffee bean growers, their bargaining power is not significantly diminished by this threat due to the unlikelihood of a big premium coffee retailer adopting the substitution.
When Starbucks first began purchasing premium Arabica coffee beans in the late 1980s, they executed purchases incrementally throughout the year. Currently, they lock their coffee suppliers into long-term contracts to dilute potential price volatility. These contracts have stipulations within them which place a financial burden on the coffee suppliers if they choose to supply a different company. By creating these switching costs for the premium coffee suppliers, Starbucks has diminished their ability to play one buyer against another, which decreases their bargaining power.
A last component to the analysis of supplier bargaining power within the current specialty coffee industry environment is the threat of forward integration. Technically, the farmers can forward integrate by setting up smaller coffee shops and brewing their own batches. This is, however, extremely unlikely and has yet to occur. When comparing the bargaining power of suppliers today in the specialty coffee industry to the bargaining power of suppliers during the late 1980s, it is apparent that suppliers are more powerful today. The increased unity among the coffee farmers, decreased significance of specialty coffee retailer’s purchases as a proportion of premium coffee bean sales and increased importance placed on high quality coffee beans by the purchasers have all acted to increase the bargaining power of the supplier group. Although Starbucks has locked some of the coffee suppliers into long-term contracts not all suppliers are affected; thus, the supplier bargaining power is only marginally diminished by that tactic.
Bargaining Power of Buyers
The last component of Michael Porter’s five forces analysis to be applied to the modern specialty coffee industry is the force created by the bargaining power of buyers. The primary buyers in the specialty coffee industry remain individual consumers, who neither engage in concerted behavior nor individually purchase in large volumes relative to the total sales of a corporation such as Starbucks. Unlike the late 1980s, however, there are a few buyers who purchase in large volumes.
These large buyers are typically other multinational corporations who choose to serve Starbucks brewed coffee in their offices. However, the effects of losing one of these buyers to a competitor would not be detrimental to a company with a large sales volume such as Starbucks.
Neither the individual consumers nor the multinational corporations who purchase specialty coffee commit a significant fraction of their resources to these purchases. This makes the buyers less sensitive to price fluctuations and gives the players within the specialty coffee industry more control over pricing. This acts to decrease the bargaining power of both the buyer groups. The expansion of the specialty coffee industry created a wider array of competitors who offered high quality specialty coffee.
This made it much harder for the players in the specialty coffee industry to differentiate themselves through quality and turned quality into the industry standard. In addition to the increasing quality standardization which specialty coffee has undergone, the buyers face no switching costs and have an enormous selection of retailers from whom they can buy.
The buyers of specialty coffee do pose a credible threat of backward integration. This threat can be carried out if a buyer chooses to start a mom and pop specialty coffee store in close proximity to an established specialty coffee store. Same-store sales are roughly 20% lower in Starbucks stores located within a two block vicinity of mom-and-pop specialty coffee stores. The ability of buyers to backward integrate is enhanced by the availability of all information regarding the demand, market pricing, and supplier costs in the specialty coffee industry through sources such as the World Wide Web.
With full information, the buyer is in a better position to ensure that they pay a favorable price and receive an appropriate level of quality from the product. The amount of bargaining power that can be exerted by the buyers within the specialty coffee industry has increased as a result of the availability of information regarding market variables. This along with the other previously discussed changes to the dynamics of buyer bargaining power has increased its overall magnitude from the level it was at in the late 1980s.