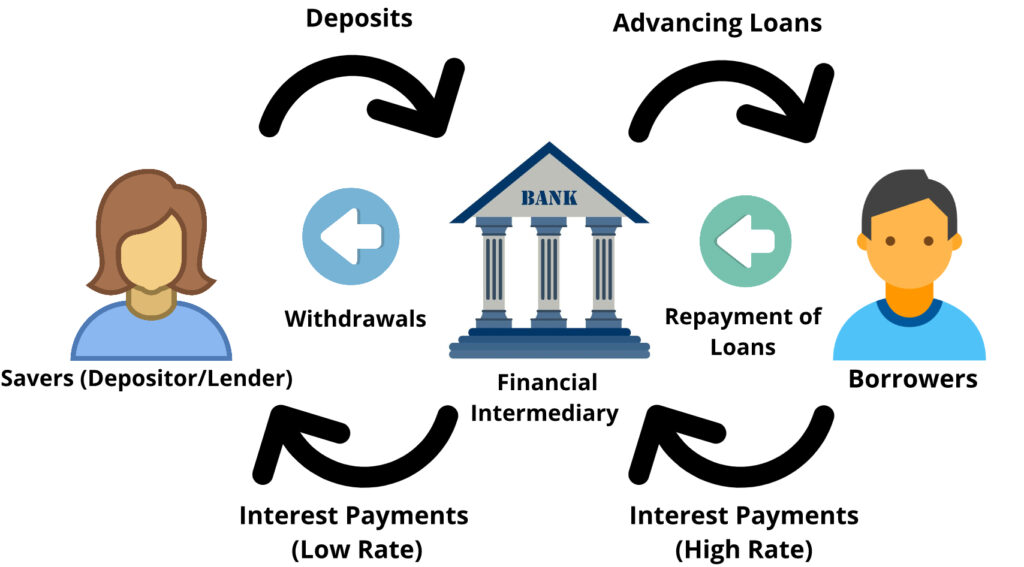
Financial intermediation is defined as the process which had been carried out by the financial intermediaries as the middleman between the borrower (spender) and lender (saver) to smooth the flow of the fund. Financial intermediation called the process of using indirect finance in the financial system, which the primary route to transfer funds from lender to borrower. Those savers who have the surplus money will deposit their funds in the financial institution, which will lend those funds to borrowers such as business firms, households, government, or foreigners who shortage of funds. Financial intermediaries are that financial institutions such as commercial banks, finance companies, or merchant banks. The financial intermediary helps to transfer the funds between the lender and borrower in the ways of borrow money from the lender-saver and then using this money to make a loan to the borrower-spender. For example, the financial institution acquires funds through the public by issuing liabilities such as time deposits and saving accounts. After that, the bank might use that fund to acquire an asset by making a loan to the people who needed funds for investment or buying that company bond in the financial market. As a result, with the help of a financial intermediary, the money successfully transfers from the public to the borrower.
Financial intermediaries play an important role in the financial system because they help to facilitate risk transfer and in dealing with increasingly complex financial instruments and markets. The financial intermediary’s role is to transform the assets which are less desirable by a large portion of the public into assets that are more preferable by the public. This transformation has served four economic functions which are providing maturity intermediation, reduction of risk by diversification, reducing the contracting and information processing costs, and providing an efficient payment mechanism. Besides, many subsequent scholars also have stressed the role of transaction cost in financial intermediaries. Due to the financial intermediaries are very specializing in information processing, they have created well-functioning financial institutions that have greatly reduced the transaction and information for customers. They can achieve the economy of balance through specialization; this is because they are handling a very large number of transactions so they are able to minimize the fixed costs by ward off the same production of information faced by borrowers and lenders. In addition, financial intermediaries develop specialist or expert people in evaluating prospective borrowers and investment projects. Other than that, they can also exploit customer information and reuse that information over time and again. As a result, there are more funds are made available for investments. For example, the fixed cost of assets evaluation means that the financial intermediaries have an advantage over an individual because they allow the costs to be shared. The information acquisition cost maybe still can lower down by establishing a long-run relationship between the borrower and financial intermediaries. Furthermore, financial intermediation has gained confidence and trust from the public by protecting their assets with providing efficient service to help them manage their assets. This is because the financial intermediaries help them channel funds more efficiently to productive investments through funding pooling, better identification and monitoring of profitable investments, and risk diversification. Diversification allows allocating assets and bearing risks more efficiently. Those investments are protected from unconscientiously borrowers by the institution’s qualified loan officers and well-trained investment analysts seek good investment opportunities and screen prospective securities so as to obtain the best yield available for the risk level that suits the investor’s preferences. Thus, financial intermediaries are a vital part of our economic system and in order to maintain the flow of money in the economy.
How the financial intermediaries can improve risk-sharing and thus improve economic welfare?. The financial intermediary help to diversify the risk of the lenders (savers) by helping them to investigate their savings across the different sector of business. They have the ability to get the important information that concern about the borrowers’ financial position compared to those in direct finance route which lender directly lends their money to borrowers in the financial market without any information about the borrowers. Financial intermediaries can have the borrowers’ such important information is because they already have a history of exercising discretion with this type of information, and help to reduce unreliable information concerning the borrowers. This will help to solve the problems created by asymmetric information which is the adverse selection and moral hazards. Financial intermediaries help them to screen risk, monitor risk, and evaluate risk. It is more efficient for a financial institution to screen the investment opportunity and risk on behalf of individuals compare to an individual to screen it. Since the institution has all the important information available about the lenders and borrowers, it helps to reduce the information costs for analyzing their data and save their time. Thus, individuals can enjoy other services provided by the financial institution which can enable them to deposit and withdraw funds without negotiation whereas the borrowers can avoid having a deal with individual investors. It concludes that it helps those individuals not only save their time and money, and also offer low-risk investment opportunities to them. If there are no financial intermediaries, the lenders-savers and borrowers-spenders have to pay higher transaction and information costs and the facing the problem created by the asymmetric information such as adverse selection problems and moral hazards problems. Adverse selection problems arise before the transaction occurs. Usually, those people who agreed to pay higher interest rates will be worse risk and thus the lenders are more likely to have made a loan to high-risk borrowers This problem only occurs on the borrowers but not the lenders. However, the moral hazard problem occurs after the transaction which arises just as the borrowers involved in the chance of their loan will be repaid back to the lenders. It also will happen when the borrowers are taking too much risk as the costs incurred more than the benefit that gains by borrowers. Therefore, it will discourage the individual savers from lending money to those borrowers who have such investment opportunities and affected the whole economic development in the country.
Financial intermediaries also provide maturity flexibility service to individuals by creating financial claims with a wide range of maturities so as to balance the maturity of different instruments so as to reduce the gap between assets and liabilities. As if there are no financial intermediaries, individual savers have to purchase the securities of borrowers it will lead them to have many uncertain risks such as the conflicting of the maturity needs of lender and borrower. For example, most lenders would like to lend money at short maturity, however, normally the borrower will attempt to borrow for a longer maturity. It would make it difficult for the borrower to match their larger loan amount with the small amounts of individual savings which are desired by the lenders then it will make the borrowing more difficult. In addition, financial intermediaries perform an important function as maturity intermediation to make a sure investment from lenders and money borrowing for borrowers flawless. In the existence of a financial intermediary, an individual’s income tax differentials are mitigated which helps to transfer tax deductions from low to high-income taxpayers and to provide tax-free services in place of taxable interest. For example, the income invested in and earned by pension funds is not taxed until retirement when the rates are generally lower than before retirement. Besides, the commercial bank also rewards depositors with free services, which are non-taxable, rather than pay interest, which is taxable. The depositors will receive nontaxable benefits such as checking accounts, traveler’s checks, and low-rate loans in return for the use of the money.
In conclusion, the existence of financial intermediaries played a very important role in the economic development of the country. In this modern world, it would not have been so efficient, aggressive, and progressive without financial intermediation. Financial intermediaries provide a convenient and safe place where lenders can safely invest excess money and borrowers can easily borrow funds with low cost and low risk.