Definitions of Motivation
The word Motivation derives from the Latin word “Movere”. The Latin word “Movere” means “To move”, “To drive” or “To drive forward” etc. Motivation can be defined as stimulating, inspiring and inducing the employees to perform to their best capacity. Motivation is a psychological term which means it cannot be forced on employees. It comes automatically from inside the employees as it is the willingness to do the work.
Joe Kelly defined Motivation as “Motivation is a process where by needs instigate behavior directed towards the goals that can satisfy those needs.”
According to W. G. Scot, “Motivation means a process of stimulating people to action to accomplish the desired goals.”
According to Michael J. Jucius, “Motivation is the act of stimulating someone or oneself to get a desired course of action, to push the right button to get a desired results.”
Process of Motivation
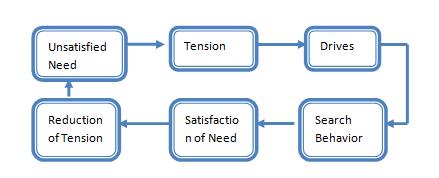
- Unsatisfied need. Motivation process begins when there is an unsatisfied need in a human being.
- Tension. The presence of unsatisfied need gives him tension.
- Drive. This tension creates an urge of drive in the human being an he starts looking for various alternatives to satisfy the drive.
- Search Behavior. After searching for alternatives the human being starts behaving according to chosen option.
- Satisfied need. After behaving in a particular manner for a long time then he evaluates that whether the need is satisfied or not.
- Reduction of tension. After fulfilling the need the human being gets satisfied and his tension gets reduced.
For example, if an employee develops a need to earn more, this need will make him restless and he will start thinking how to satisfy his need. To satisfy his need he may think of working hard in organization and get promotion so he will start working hard. After sometime he will get incentives or increments or promotion which will satisfy his need.
But motivation process does not end by satisfaction of one need. After fulfilling one need another need develops and the same process continues till needs keep emerging in human beings.
Types of Motivation
- Achievement Motivation: It is the drive to pursue and attain goals. An individual with achievement motivation wishes to achieve objectives and advance up on the ladder of success. Here, accomplishment is important for its own shake and not for the rewards that accompany it. It is similar to ‘Kaizen’ approach of Japanese Management.
- Affiliation Motivation: It is a drive to relate to people on a social basis. Persons with affiliation motivation perform work better when they are complimented for their favorable attitudes and co-operation.
- Competence Motivation: It is the drive to be good at something, allowing the individual to perform high quality work. Competence motivated people seek job mastery, take pride in developing and using their problem-solving skills and strive to be creative when confronted with obstacles. They learn from their experience.
- Power Motivation: It is the drive to influence people and change situations. Power motivated people wish to create an impact on their organization and are willing to take risks to do so.
- Attitude Motivation: Attitude motivation is how people think and feel. It is their self confidence, their belief in themselves, their attitude to life. It is how they feel about the future and how they react to the past.
- Incentive Motivation: It is where a person or a team reaps a reward from an activity. It is “You do this and you get that”, attitude. It is the types of awards and prizes that drive people to work a little harder.
- Fear Motivation: Fear motivation coercion’s a person to act against will. It is instantaneous and gets the job done quickly. It is helpful in the short run.
Features of Motivation
- Motivation is a psychological phenomenon. Motivation is an internal feeling which means it cannot be forced on employees. The internal feelings such as need, desire, aspirations etc. influence human behavior to behave in a particular manner. For example, desire to have a new house, respect and recognition etc.
- Motivation produces goal directed behavior. Motivation induces people to behave in such a manner so that they can achieve their goal. Motivated person need no supervision or direction. He will always work in desired manner. For example of a person has a motive to get promotion so he will work efficiently to get promotion.
- Motivators can be positive as well as negative. To motivate employees managers use various motivators. Some motivators are positive and some are negative few examples of positive motivators are promotion, increment, bonus, respect, recognition etc. if employee does not improve his performance with positive motivators then manager uses negative motivators such as warning, issue o memo, demotion, stopping increments etc. sometimes fear of negative motivators also induces person to behave in a desired manner.
- Motivation is a complex process. Motivation is a complex and difficult task. In order to motivate people a manager must understand various types of human need. Human needs are mental feelings which can be measured accurately. If manager measures them accurately then also every person uses different approaches to satisfy his need. Some get satisfied with monetary incentives, some with non-monetary, some with positive and some with negative motivators. So it is not possible to make generalization in motivation.
- Motivation is a dynamic and continuous process. Human beings are ever-changing. Human needs are unlimited and go on changing continuously. Satisfaction of one need gives rise to another so managers have to continuously perform the function of motivation.
Importance of Motivation
- Motivation helps to change from negative attitude to positive attitude. Without motivation the employees try to perform minimum activities in the organization. But the motivation fills in the desire to perform to their maximum level. All the resources of the organization are of no use unless and until the employees use these resources. The motivated employees make best use of the resources.
- Motivation improves performance level of employees. The motivation improves the efficiency level of employees which means the employees start performing the job to the best of their ability with minimum wastage of time and resources because motivated employees always go for best utilization of resources. The motivation bridges the gap between the ability to work and willingness always improves efficiency.
- Help in achieving the organizational goals. The motivated employees always try to achieve the organizational goal and contribute their best efforts for the realization of organizational goal as they know with the achievement of organizational goal only they can achieve their personal goal. All the employees contribute their efforts in one direction of accomplishment of goal.
- Motivation creates supportive work environment. In motivation the relations between superior and subordinates are always improved. When the employees get their need satisfied or get the recognition and respect in the organization then they always offer a supportive hand to superiors. There is more co-operation and co-ordination in the organization and all the employees work with the team spirit.
- Motivation helps the managers to introduce changes. The motivated employees show less resistance in accepting the changes according to changes in the business environment because they know if the changes are not implements in the organization, not only the organization will lose by this but the employees also will find it difficult to get their needs fulfilled. Motivated employees are always supportive and co-operative in accepting changes in the organization.
- Reduction in Employee Turnover. The motivation creates confidence in the employees to get their need satisfied in the organization itself. They always select the alternative to remain in the organization and increase their earning rather than leaving the organization and increasing their earnings. With motivation employee turnovers are less because the satisfied employees never leave the job.
Advantages of Motivation
Advantages to Management or Organization:
- Increase in the efficiency and productivity of employees. Motivation ensures a high level performance of employees.
- Better co-operation from employees and cordial labor-management relations.
- Reduction in the rate of labor absenteeism and turnover.
- Reduction in the wastage’s and industrial accidents.
- Improvement in the morale of employees.
- Quick achievement of business/corporate objectives and favorable corporate image.
Advantages to Employees or Workers:
- Employees get various monetary and non-monetary facilities/benefits which provide better life and welfare to them.
- Security of employment and other benefits due to cordial relations with the management.
- Job attraction and job satisfaction.
- Higher status and opportunities of participation in management.
- Positive approach and outlook of employees towards company, management and superiors.
- Reduction in the rate of labour turnover which is harmful to employees and management.
- Better scope for improvement in knowledge and skills of employees.
Ways to Improve Motivation of Workers
Motivation is the desire that pushes an individual to work well. It is an influence that causes people to behave in a particular way. Organisations can motivate its production line workers through financial rewards such as an increase in wage rates or profit sharing, and through non — financial rewards such as job enlargement and delegation along with the use of motivational theories such as McGregor’s Theory X and Y and Elton Mayo’s Hawthorne Effect.
The main reason for low motivation is the dissatisfaction with their wages for production line workers. They receive half as much as the quality control inspectors who do not participate in the production process. These workers receives a low weekly wage and a bonus for meeting output targets. This means that in case of power failures or machinery break down at the factory the workers would not be able to meet targets and wouldn’t receive the bonus.
This leaves a feeling of frustration as such problems are beyond the control of the workers and they feel that they have been treated unfairly. Thus firstly he pay of the workers should be increased. After all according to Taylor’s Scientific Management worker want the money. Also according to Maslows Need Hierarchy, the most basic needs are the psychological needs of hunger, thirst and shelter which are gotten by the wages. These wages, if not at par should be close to that of the quarterly inspectors because the inspectors do not contribute to the output of a company. Organisation would by this definitely face rising costs of labor but if by higher wages the workers are given an incentive to work hard then the productivity i.e. output per worker would increase.
This may then off set the increase in costs and lead to an increase in production of goods.
Nevertheless, it would be the non-financial rewards that would play an important role in maintaining the high motivation levels that are initiated by the financial rewards. Profit sharing is also a financial reward would help worker feel more part of the business of in years of high profits they are given a percentage of profits. They would then wish to contribute to wards the maintaining of this profitability. Job enlargement (including job enrichment and job rotation), team working, quality circles, target setting, delegation and appreciation and recognition by the organisation (awards) are all methods that organisations can use to motivate employees.
Job enlargement increases the scope of the job so as to provide broader and deeper tasks. This would involve job rotation where the workers could switch jobs after a certain time that allows them to handle a variety of Jobs and job enrichment that organizes work in such a way that employees are able to use their fullest abilities and do work with lesser supervision.
Delegation should also be undertaken which is the passing to subordinates. This would mean telling the workers take certain decisions as to he performing of tasks. Empowerment would go a step further and give them control on how to perform their tasks by employing efficient methods.
Job enlargement, delegation and empowerment are all in accordance with McGregors Theory Y according to which workers like to work and seek responsibility. These methods help workers to feel a greater part of the process and business as they carry but more than one task and are encouraged to become more efficient. Since they are given responsibility, they feel trusted and feel more loyalty to the firm. As they carry out tasks related to the entire process they derive greater satisfaction of having seen the end result. They increase their skills gain more experience and open more opportunities for their future. The only danger is that some workers may be afraid of performing additional tasks as they are afraid of failure and thus losing jobs.
Then team working and quality circles would also be made. According to this the workers should be divided into groups and given an area on the production time of which they are responsible both for production as well as for quality of products. In this way, the quality inspectors could be removed and the major reason of demotivation among employees would end. The teams would meet regularly to deal with the quality of the products its improvements as well as any problems in organisation’s production line. They would then present their researches and results to the management who could them implement the best result on the production line as well as give rewards to the group that came up with the best idea. Quality circles allow the successful participation of the entire staff in the decision making. The workers feel a greater part of organization and eel a greater sense of achieving the targets that they themselves have helped to decide. Workers have hands on experience and are in the best position to understand the problems, more than any hired quality control officials. Workers are best able to provide solutions to exactly meet the situation and thus greatly improve their own productivity as well as the efficiency of the organisation as a whole.
Since their social and self-esteem needs as according to Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Model are met through team working (interaction) and appreciation from the management (rewards) they are highly motivated.
Organisations should make full use of the motivational theories as well as the methods discussed above. It is true that Quality Circles are informal and may lead to certain time wastes in meeting but these can be avoided by rewarding participation after office hours. Also the fear of competition amongst different circles shouldn’t stop managers from employing these methods as healthy competition encourages progress and development of innovative ideas that least to higher motivation, greater productivity and improved profitability.
Motivation is required in every case of life. Without motivation, we can not do any work properly. Education, career, business, goals are the need of motivation in each case. As a result, we can move on to success.
I got the answers to all my questions after reading your content. Thanks a lot for sharing this content.
good day, i would like to cite this article in my report. may i know who is the author of this article, its year published and its publication.
thank you.