The behavioral science approach to management focuses on the psychological and sociological processes (attitude, motivations, group dynamics) that influence employee performance. While the classical approach focuses on the job of workers, the behavioral approach focuses on the workers in these jobs. Workers desisted the formal and impersonal approach of classical writers. Behavioral approach started in 1930.
This gave rise to the Behavioral science approach to management. Two branches contributed to the Behavioral approach.
- Human Relations Movements: The human relations movement refers to the approach to management and worker productivity that takes into account a person’s motivation, satisfaction, and relationship with others in the workplace. The human relations movement grew from the Hawthorne studies.
- Development of Organisational Behavior: Pioneers of the human relation movement stressed inter-personal relations and neglected the group behavior patterns. This led to the development of field of organisational behavior. It respects a more. Interdisciplinary and multi-dimensional approach to worker behavior organisation behavior involves the study of the attitudes, behavior patterns and performance of individuals and group in an organisational setting. It says that:
- Man is not a social individual, he is a complex individual.
- The role and contribution of organisation behavior in workers.
- It discussed the psychological variables like motivations, leading etc.
- Man is a self-actualizing being.
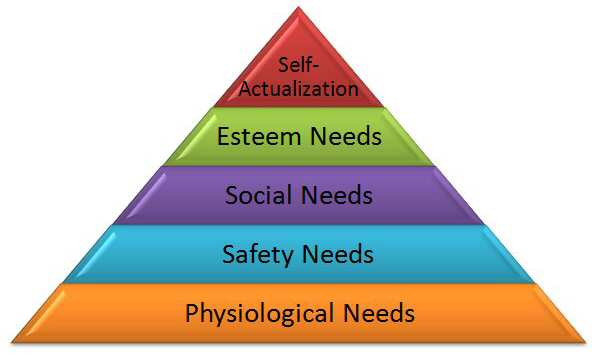
Classification of human needs by Maslow as under:
- Physiological needs: these needs are related to the survival and maintenance of life. These include food, clothing, shelter etc.
- Safety needs: these consist of safety against murder, fire, accident, security against unemployment etc.
- Social needs: these needs include need for love, affection, belonging or association with family, friends and other social groups.
- Ego or esteem needs: these are the needs derived from recognition status, achievement, power, prestige etc.
- Self–fulfillment: it is the need to fulfill what a person considers to be his real mission of life.
Maslow is of the opinion that these needs have a hierarchy and are satisfied one by one. When first needs are satisfied then person moves to second and so on.
Contributions of Behavioral Science Approach to Management
The behavioral science approach to management is concerned with the social and psychological aspects of human behavior in organisation. Many of the conclusions of the Hawthorne studies were reaffirmed by the subsequent research studies, but certain ideas were extended and others highlighted by the behavioral scientists. Some of the important elements of the behavioral science approach are highlighted below.
- Individuals differ in terms of their attitudes, perception and value systems. Therefore, they react differently to the same situation.
- People working in an organisation have their needs and goals, which may differ from the organisation’s needs and goals. Management should achieve fusion between organisational goals and human needs.
- Individual behavior is closely linked with the behavior of the group to which he belongs. A person may be inclined to resist pressures to change his behavior as an individual. But he will readily do so if the group decides to change its behavior. With work standards laid down by the group, individuals belonging to that group will resist change more strongly.
- Informal leadership, rather than the formal authority of supervisor, is more important for setting and enforcing group standards of performance. As a leader (manger) may be more effective and acceptable to the subordinates if he adopts the democratic style of leadership. If the subordinates are encouraged to participate in establishing the goals, there will be positive effect on their attitude towards work. Changes in technology and methods of work, which are often resisted by employees, can be brought about more easily by involving the employees in planning and designing the jobs.
- By nature most people enjoy work and are motivated by self-control and self-development. It is for the managers to identify and provide necessary conditions for the human potential to be used in the service of the organisation. The manager’s attitude towards human behavior should be positive.
The behavioral scientists have shown how human beings bring to their task aspects of behavior, which the effective manager should profitably understand. After all, it is individuals and groups with which a manager is concerned and while organisational roles are designed to accomplish group purposes, people must fill these roles.
Thus, the behavioral sciences have provided managers with a ore systematic understanding of one of the most critical factors in the process of management–the human element. Insights evolving from that understanding have been used to design work situations that encourage increased productivity. It has enabled organisations to formulate programmes to more efficiently train workers and managers, and it has effects in numerous other areas of practical significance.