Culture defines the people’s “way of life”, meaning the way they do things. Culture could be related to a specific country, a section of community or within an organization. A people’s culture includes their beliefs, rules of behavior, language, rituals, art, technology, styles of clothing, ways of producing and cooking food, religion, and political and economic systems. Culture is not inherited genetically; it must be learned and acquired. Socialization occurs when a person absorbs or learns the culture in which he or she is raised.
Marketing research should take into account the local culture of the country in which you wish to market. How marketing efforts interact with a culture determines the success or failure of a product. Advertising and promotion require special attention because they play a key role in communicating product concepts and benefits to the target customer.
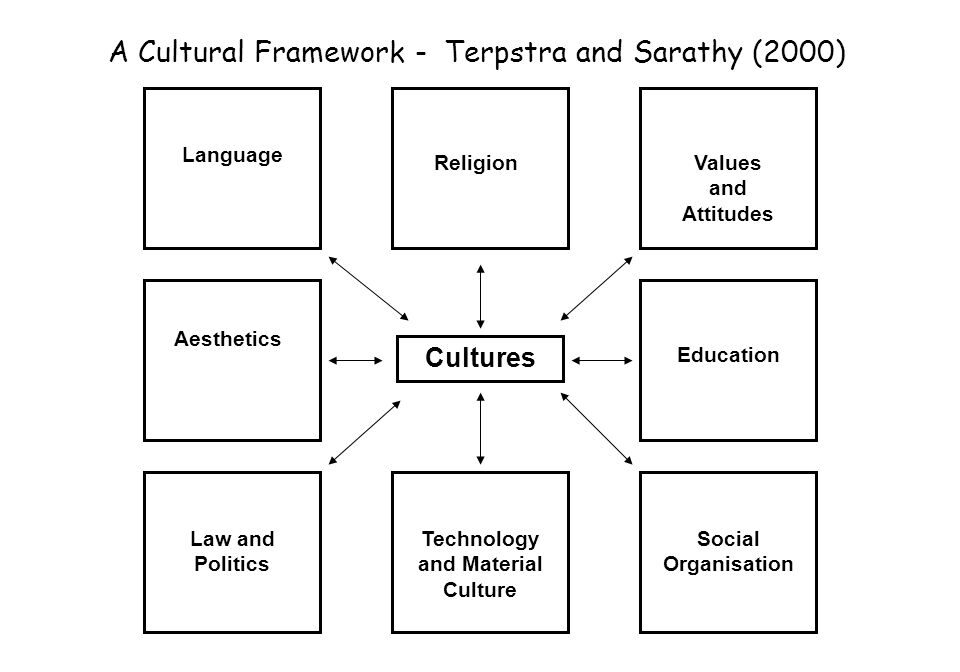
Terpstra & Sarathy (2000) stated that Understanding the cultural environment of a country would assist marketers to adapt their marketing strategies if they take the ingredients(elements) of culture into consideration. The “Terpstra and Sarathy Cultural Framework” helps researchers to assess the cultural nature of an international market. It uses eight categories in its analysis. The Eight categories are Language, Religion, Values and Attitudes, Education, Social Organizations, Technology and Material Culture, Law and Politics and Aesthetics.
- Language – Language is an integral part of culture and is the main mode of communication. It can be divided into two major elements, which are the verbal and non verbal communication. The choice between verbal and non verbal communication needs to be balanced based on whether the national culture is high context culture or low context culture. In countries like Australia what is said is what is meant and spoken language carries the emphasis of communication – low context culture. Whereas in countries like Japan and some Arabic nations what is said may not be what is meant and the communication tend not to carry a direct message in it – high context culture. So the researchers need to make sure the marketing reaches out to the customers in the exact way it was meant to be communicated.
- Religion – Another major cultural variable is religion and has significant effects on marketing strategy. For example, the identification of diverse beliefs and norms as well holidays and rituals is critical for an understanding of a foreign market. In some countries religion is the most dominant cultural force. Hence researchers need to ensure that their product and services doesn’t offend or be distasteful to the local nation. In the year 2007 the Chinese government banned all advertisements containing pictures of pig in order to maintain harmony with the country’s Muslim population.
- Values and Attributes – The values consumers from different countries place on things such as time, achievement, work, wealth and risk-taking will affect not only the product offered but also the packaging and communication activities. The methods used by a firm to motivate its personnel are also strongly influenced by the local culture and practice. For example workers in France tend to take vacation in August while workers in United States tend to take vacation during end of the year. So before entering a market it is important to understand the locality. Advertising campaigns should be altered or customized to suit the locality. In the year 2006, the USD 130 million ad campaign by Tourism Australian was banned by the British Advertising Standards Authority from the United Kingdom as the ad campaign had a tag line ” where the bloody hell are you?”
- Education – The level of education in a country has a direct impact on the sophistication of the target customer. A simple example will be the degree of literacy. In developed countries, main form of communication is advertising and printed method. In developing countries, they rely on training and verbally based educational programs to get their message across.
- Social Organizations – This relates to the way in which a society organizes itself. How the culture considers kinship, social institutions, interest groups and status systems. The role of women and caste systems are representative examples. Social mobility could be restricted in a country like India where caste and class systems are in place.
- Technology and Material Culture – This aspect relates not to materialism but to the local market’s ability to handle and deal with modern technology. Some cultures find the idea of leaving freezers plugged in overnight, or servicing cars that have not yet broken down difficult to understand. It is also very important to understand the availability of infrastructure to distribute the goods to customer. Innovation within technology is based on the need for such goods. The cost of batteries was very expensive in Africa and power supplies to rural areas were non- existent. The launching of clockwork radio by Trevor Baylis was an instant success due to this.
- Law and Politics – The legal and political environments in a market are regarded as consequences of the cultural traditions of that market. Legal and political systems are often a simple codification of the norms of behavior deemed acceptable by the local cultures. For example, the United Kingdom has laws based upon precedent and legislation which is largely market-driven and democratic society, whilst Iran has a political and legal system based upon the teachings and principles Islam and a Sharia tradition.
- Aesthetics – This covers the local culture’s perception of things such as beauty, good taste and design, and dictates what is acceptable or appealing to the local eye. A firm needs to ensure that use of color, music, architecture or brand names in their product and communication strategies is sympathetic and acceptable to the local culture.