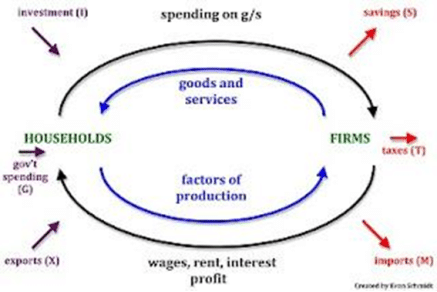
The Circular Flow Model of the Economy
The circular flow model is used to represent the monetary transactions in an economy. It helps to show connections between different sectors of an economy. It shows flows of goods and services and factors of production between firms and households. The circular flow of income is a model that helps show the movement of income and spending throughout the economy. In the economy, households help provide firms with factors of production, e.g. labour. Organisations use these factors to provide goods and services to the household. The households will then spend their money on the goods and services provided by the firms.… Read the rest