Research is the foundation of any science, including both hard sciences such as physics, chemistry and the social sciences such as psychology, management and education. The steps and process involved in the research can vary depending on the type of research being done and the hypothesis being tested. Research methods such as Naturalistic observation and surveys are often less structured, where as experimental methods are more structured. Depending upon what is observed or experienced, new theories are developed. There are aspects of a theory or aspects of a study that can change or vary as part of interaction within the theory, defined as variables.… Read the rest
Business Research Concepts
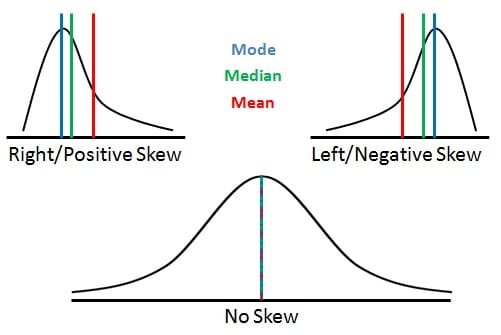
Measures of Central Tendency and Variability
Central tendency is a statistical measure that identifies a single score as representative of an entire distribution of scores. The goal of central tendency is to find the single score that is most typical or most representative of the entire distribution. Unfortunately, there is no single, standard procedure for determining central tendency. The problem is that there is no single measure that will always produce a central, representative value in every situation. There are three main measures of central tendency: the arithmetical mean, the median and the mode.
The mean of a set of scores (abbreviated M) is the most common and useful measure of central tendency. … Read the rest
Documentary Sources of Information in Research
The documentary source is an important source of information for a researcher. A document is anything in writing a record, files or diaries, published or unpublished which can be extracted and used in research. It is a very valuable source of information for a research either in management or in social sciences. It may comprise office files, business and legal papers, biographies, official and unofficial records, letters, proceedings of any courts, committees, societies, Assemblies, and Parliaments, enactments, constitution, reports of surveys, or research of commissions, official statistics, newspaper editorials, special articles, company news, cases or company directors’ reports, etc. Documentation is the process of collecting and extracting the documents which are relevant to research.… Read the rest
Classification and Tabulation of Data in Research
Classification is the way of arranging the data in different classes in order to give a definite form and a coherent structure to the data collected, facilitating their use in the most systematic and effective manner. It is the process of grouping the statistical data under various understandable homogeneous groups for the purpose of convenient interpretation. A uniformity of attributes is the basis criterion for classification; and the grouping of data is made according to similarity. Classification becomes necessary when there is diversity in the data collected for meaningful presentation and analysis. However, in respect of homogeneous presentation of data, classification may be unnecessary.… Read the rest
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design, which can otherwise be called hypothesis-testing research design, were originally made by R.A. Fisher in agricultural research in England. Experimental research design is generally used in experimental studies where hypotheses are tested. Experimental research design is now used in almost all the areas of scientific studies.
The principles of experimental research design which Fisher prescribed are, viz.: (a) the principle of replication, (b) principle of randomization, and (c) the principle of local control.
- The principle of replication suggests that the experiment must be repeated also that the treatment is applied in many experimental units. This increases the statistical accuracy of the experiments.
Contents and Layout of Research Report
The researcher must keep in mind that his research report must contain following aspects:
- Purpose of study
- Significance of his study or statement of the problem
- Review of literature
- Methodology
- Interpretation of data
- Conclusions and suggestions
- Bibliography
- Appendices
These can be discussed in detail as under:
(1) Purpose of study:
Research is one direction oriented study. He should discuss the problem of his study. He must give background of the problem. He must lay down his hypothesis of the study. Hypothesis is the statement indicating the nature of the problem. He should be able to collect data, analyze it and prove the hypothesis.… Read the rest