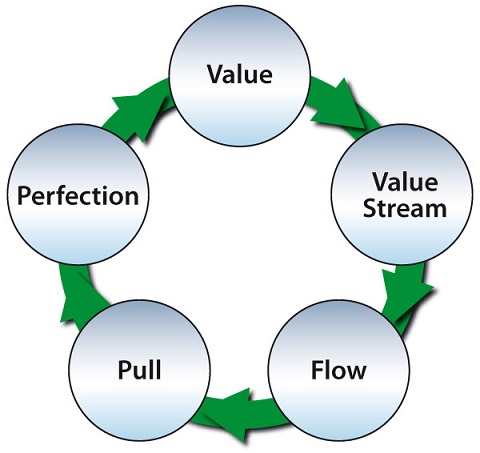
Kaizen is broadly interpreted as the Japanese term for continuous improvement, although it is perhaps more accurately translated as a form of control. It applies to all aspects of organisational output, and can thus be linked to both Toyota Production System (TPS) and types of waste, as well as the means of introducing and managing basic employee working conditions. One of the most popular tools of Kaizen is a Kanban, which of itself translates to differing types of organisational process control, which collectively lead to greater organisational production efficiency.
The overarching principle of Kaizen, and Kanban within that, is to create a ‘pull through’ organisational process, as opposed to push through.… Read the rest