A financial system is a network of financial institutions, financial markets, financial instruments and financial services to facilitate the transfer of funds. The system consists of savers, intermediaries, instruments and the ultimate user of funds. The level of economic growth largely depends upon and is facilitated by the state of financial system prevailing in the economy. Efficient financial system and sustainable economic growth are corollary. The financial system mobilizes the savings and channelizes them into the productive activity and thus influences the pace of economic development. Economic growth is hampered for want of effective financial system. Broadly speaking, financial system deals with three inter-related and interdependent variables, i.e.,… Read the rest
Business Finance
Business Finance is that business activity which is concerned with the acquisition and conservation of capital funds in meeting financial needs and overall objectives of business enterprises.
Terms commonly used with reference to capital market
There are several terms which are commonly used with reference to capital market. Several such terms have already been discussed in the previous articles. Understanding of following terms (given in alphabetical order) will help the readers in better grasping the structure and trading system in the capital market in India :
Arbitrage: Arbitrage refers to taking advantage of price differential in a particular security on to different stock exchanges. An investor/speculator can sell at one stock exchange and buy the same at lower price at other stock exchange. The difference in prices is the profit of the investor/speculator.
Categories of Shares at BSE: At the Mumbai Stock Exchange, the shares have been categorised in different categories such as A, B1, B2, S, T, TS and Z.… Read the rest
Margin trading at stock exchanges
Margin Trading (MT) is an arrangement whereby an investor purchases securities by borrowing a portion of the purchase value from the authorised broker by using securities in his portfolio as collateral. Since April 1, 2004, SEBI has allowed member brokers to provide margin trading facility to their client in the cash market. Only corporate brokers with net worth of at least Rs. 3 crores would be eligible to participate in Mragin Trading. The brokers interested to provide margin trading facility to their clients have to seek approval from the stock exchange. The broker may use his own funds or borrow from scheduled commercial banks/NBFC regulated by the RBI.… Read the rest
Risk management system at NSE
A sound risk management system is integral to an efficient clearing and settlement system. NSE introduced for the first time in India, risk containment measures that were common internationally but were absent from the Indian securities markets. NSCCL (National Securities Clearing Corporation Ltd.) has put in place a comprehensive risk management system, which is constantly upgraded to pre-empt market failures. It ensures that trading member obligations are commensurate with their networth. Risk containment measures include capital adequacy requirements of members, monitoring of member performance and track record, stringent margin requirements, position limits based on capital, on-line monitoring of member positions and automatic disablement from trading when limits are breached, etc.… Read the rest
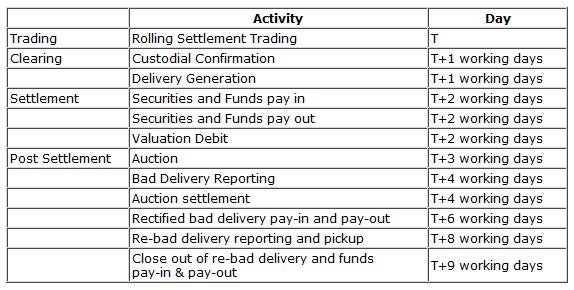
Rolling Settlement System
Rolling Settlement process , also known as Compulsory Rolling Settlement (CRS) where trades on a stock exchange were to be accounted for and settled on T i.e. trade day plus “X” trading days, where “X” could be 1,2,3,4 or 5 days. Thus, in essence, it means that if say a T+n, where n is the number of days system of rolling settlement was to be followed, trades accounted for on the T i.e. trade day were to be settled on the nth working day minus the T day.
The Account period of settling transactions was followed in India for a long time.… Read the rest
Trading Procedure at Stock Exchanges
The trading procedure at stock exchanges can be complex, and the specific procedures can vary depending on the exchange and the types of securities being traded. However, in general, the trading procedure at stock exchanges involves several key steps, including market opening, order placement, order matching, trade confirmation, and trade settlement.
Market Opening: The stock exchange’s market opening is typically announced, and trading begins at the designated time. The exact time of the market opening may vary depending on the exchange, but it is typically during normal business hours. The opening is often signaled by a bell or other announcement, and traders begin placing orders to buy or sell securities.… Read the rest