A business organization can be formed with certain properties and specific characteristics. Since business organization is an association of persons, the manner of forming and the objectives of the association decide the form of organization. Individuals form an organization because they are unable to achieve their goals individually. An organization provides opportunities to exploit the existing potential of men and materials. It explores the future possibilities of exploiting human and physical resources. Individuals interested in getting benefits out of the present and potential resources form an association, better known as an organization, to attain the group goals. The dynamics of individuals and the organization are used to gain maximum benefits. They work in a particular manner to obtain the Continue reading
Management Principles
Committee Organizational Structure
A committee organization is an association of people set up to arrive at solutions to common problems. The line people are given opportunities to discuss their problems in the committee. The committee organizational structure is not like line or functional organization, but is similar to staff organization. Its decisions are implemented, whereas staff decisions are not necessarily implemented. It is a formal part of the organizational structure wherein the members are specifically mentioned. For example, the Finance Committee will include all the functional managers, viz. Marketing Manager, Production Manager, Personnel Managers, etc. as members, and the Managing Director as the Chairman. It will decide the financial requirements of each and every department. The decisions taken by the committee are Continue reading
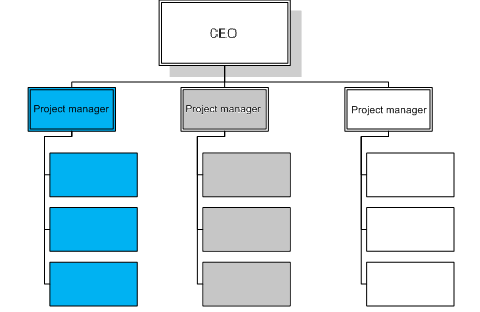
Project Organization Structure
Project organization structure is used to complete a project or task. The project manager has people from several functional departments such as production, finance, marketing and so on. Specialists are drawn to perform their respective roles in the total project. The project organization structure is derived not from some principles but from the job requirements. Project organization structure brings together people of different expertise for the completion of the project. As soon as the project is completed, the experts are returned to their original departments in the head office. For example, in a bridge construction project, the engineers, financial manager, human resources people and other related people are brought to the sit of the project Continue reading
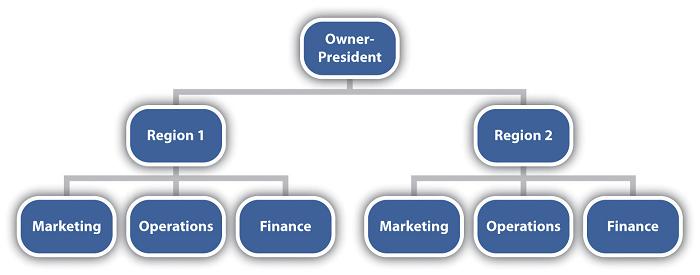
Geographical Organizational Structure
Geographical organizational structure involves grouping of the activities according to regional or geographical locations. The territorial divisions become a complete administrative unit to cater to the need of the localities. The Regional Manager will practically be the chief controller of his region. He is given full powers of managing his own region or zone. His office functions as a head office for all practical purposes. The functions pertaining to finance, marketing, personnel and production development of low-level employees are completely vested in the zonal office which has separate departments of these functions to guide and control the respective activities of the zone. The zonal office may have several divisional offices for executive functions. The area population Continue reading
Product and Process based Functional Organizations
Product Functional Organizations Product functional organization establishes each product or group of related products as an autonomous unit in the framework of the organization. In product functional organization structure, each product has a separate identity although it functions under the control of the Chief Coordinating Executive. Each product department has several functions broadly divided into finance, marketing, personnel and production, which are also coordinated with the chiefs of the respective functions. The main advantage of product functional organization is qualitative production under the supervision of expert personnel to produce a particular product. For instance, a company may be producing modular kitchens, healthcare products, consumer electronics, computers, etc., which are managed by the respective engineering expert in the areas Continue reading
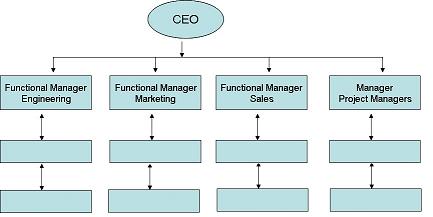
Functional Organization
Functional organization is technically called functional foreman-ship because the function itself becomes a supervisor and the employees automatically perform their respective duties. The emphasis of functional organization structure is on operations rather than on management. Functional organization is commonly used in business organizations. The spirit of organization, which involves grouping tasks together and allocating them to genuine employees is observed in functional organization. Functional sets like marketing, finance, production and personal are grouped systematically. Departments and sub departments are developed according to the requirements of the business. Functional organization is the basic building block or module from which other forms of organization are built. Functional organization is characterized by function, sub-goal emphasis, division of work, functional Continue reading