The Foreign Exchange department, which is also being called as the International Banking Division, is one of the important departments of the banks operating in international market. In India also all scheduled commercial banks, both in the nationalized or non-nationalized sectors, do have Foreign Exchange departments, both at their principal offices as well as offices, in metropolitan centers. This department functions independently under the overall change of some senior executive or a senior officer well-versed in foreign exchange operations as well as in the rules and regulations in force from time to time pertaining to foreign exchange transactions advised by various government agencies. The principal function of a Foreign exchange department is to handle foreign inward remittances as well as outward remittances; buying and selling of foreign currencies, handling and forwarding of import and export documents and giving the consultancy services to the exporters and importers. Besides this, the department Continue reading
Forex Trading
Different Types of Transactions in the Foreign Exchange Market
A very brief account of certain important types of transactions conducted in the foreign exchange market is given below Spot and Forward Exchanges Spot Market: The term spot exchange refers to the class of foreign exchange transaction which requires the immediate delivery or exchange of currencies on the spot. In practice the settlement takes place within two days in most markets. The rate of exchange effective for the spot transaction is known as the spot rate and the market for such transactions is known as the spot market. Forward Market: The forward transactions is an agreement between two parties, requiring the delivery at some specified future date of a specified amount of foreign currency by one of the parties, against payment in domestic currency be the other party, at the price agreed upon in the contract. The rate of exchange applicable to the forward contract is called the forward exchange Continue reading
Types of Selling Rates in Foreign Exchange Markets
When a bank sells foreign exchange it receives Indian rupees from the customer and parts with foreign currency. The sale is affected by issuing a payment instrument on the correspondent bank with which it maintains the nostro account. immediately on sale, the bank buys the requisite foreign exchange from the market and gets its nostro account credited with the amount so that when the payment instrument issued buy its is presented to the corresponded bank it can be honoured by debit to the nostro account. However, depending upon the work involved, viz., whether the sale involves handling of documents by the bank or not, two types of selling rates are quoted in India, they are 1. TT Selling Rate (TT stands for Telegraphic Transfer) This is the rate to be used for all transactions that do not involve handling of documents by the bank. Transactions for which this rate is Continue reading
The Main Features of Interbank Deals
Interbank deals refer to purchase and sale of foreign exchange between the banks. In other words it refers to the foreign exchange dealings of a bank in the interbank market. The main features of interbank deals are given in this section. 1. Cover Deals Purchase and sale of foreign currency in the market undertaken to acquire or dispose of foreign exchange required or acquired as a consequence of the dealings with its customers is known as the ‘cover deal’. The purpose of cover deal is to insure the bank against any fluctuation in the exchange rates. Since the foreign currency is a peculiar commodity with wide fluctuations in price, the bank would like to sell immediately whatever it purchases and whenever it sells it goes to the market and makes an immediate purchase to meet its commitment. In other words, the bank would like to keep its stock of foreign Continue reading
Role of FEDAI in Foreign Exchange
Authorized Dealers in Foreign Exchange (Ads) have formed an association called Foreign Exchange Dealers Association of India (FEDAI) in order to lay down certain terms and conditions for transactions in Foreign Exchange Business. Ad has to given an undertaking to Reserve Bank of India to abide by the exchange control and other terms and conditions introduced by the association for transactions in foreign exchange business. Accordingly FEDAI has evolved various rules for various transactions in order to protect the interest of the exporters, importers general public and also the authorized in dealers. FEDAI which is a company registered under Section 25 of the companies Act, 1956 has subscribed to the 1. Uniform customs and practice for documentary credits (UCPDC) 2. Uniform rules for collections(URC) 3. Uniform rules for bank to bank reimbursement. Various rules of FEDAI Rules No 1. of FEDAI deals with hours of business of banks which is Continue reading
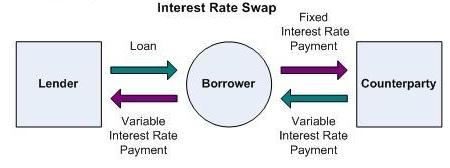
Interest Rate Swaps
The basic structure of an interest rate swap consists of the exchange between two counter-parties of fixed rate interest or floating rate interest in the same currency calculated by reference to a mutually agreed notional principal amount. This principal amount, which would normally equate to the underlying assets or liabilities being “swapped” by the counter-parties, is applicable solely for the calculation of the interest to be exchanged under the swap. At no time it is physically passed between the counter-parties. The counter-parties are able to convert an underlying fixed rate asset/ liability and vice-versa, through this straight forward swap structure. The majority of the interest rate swap transactions are driven by the cost savings to be obtained by each of the counter-parties. These cost savings are substantial and result from differentials in the credit standing of the counter-parties and other structural considerations. Generally investors in fixed rate instruments are more Continue reading