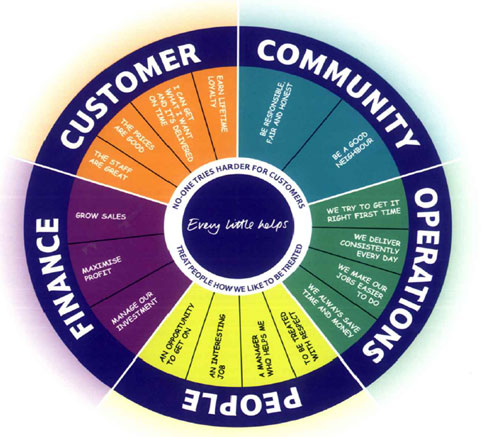
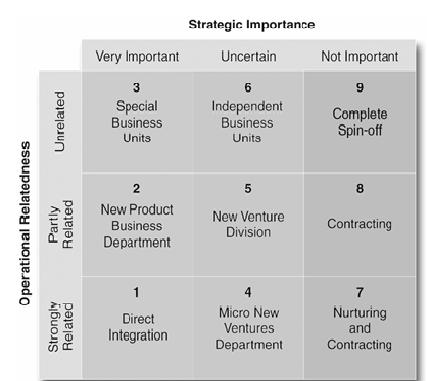
A Strategic Information System (SIS) is a system to manage information and assist in strategic decision making. A strategic information system has been defined as, “The information system to support or change enterprise’s strategy.” Simply says, a Strategic Information System is a type of Information System that is aligned with business strategy and structure.
The alignment increases the capability to respond faster to environmental changes and thus creates a competitive advantage. An early example was the favorable position afforded American and United Airlines by their reservation systems, Sabre and Apollo. (American Airlines worked with IBM to develop an improved booking/reservation system, and the Airline Reservation Systems (ARS) and the Semi-Automatic Business Research System (SABRE) launched thereafter in 1960.… Read the rest