International businesses have the fundamental goals of expanding market share, revenues, and profits. They often achieve these goals by entering new markets or by introducing new products into markets in which they already have a presence. A firm’s ability to do this effectively hinges on its developing a through understanding of a given geographical or product market. To successfully increase market share, revenue, and profits, firms must normally follow three steps,
- Assess alternative markets
- Evaluate the respective costs, benefits, and risks of entering each, and
- Select those that hold the most potential for entry or expansion.
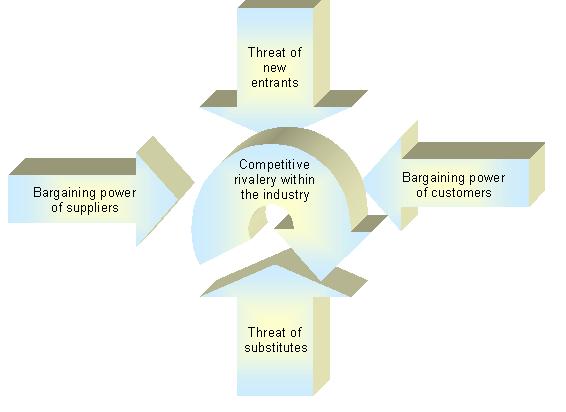
In assessing alternative foreign market a firm must consider a variety of factor including the current and potential sizes of the markets, the levels of competition the firm will face, their legal and political environment, and socio-cultural factors that may affect the firm’s operations and performance.… Read the rest