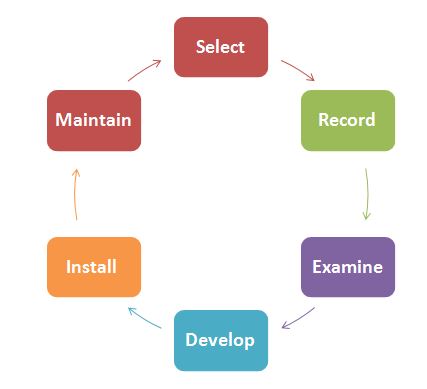
Production is a conversion function by which goods and services are produced. A typical production system comprises of three main components: Inputs, Transformation process and Output.
- Inputs are men, materials, machines, instructions, drawings, and paper work and instructions.
- The Transformation Process involves operations, mechanical or chemical, to Change/convert inputs into outputs. It also includes activities that assist conversion,
- Output is goods and services (e.g. products, parts, paper work, served customers etc.)
The combination of operations and activities stated above employed to create goods and services are known as manufacturing system. A manufacturing system therefore may be looked upon as an independent group of sub-systems, each sub-system performing a distinct function.… Read the rest