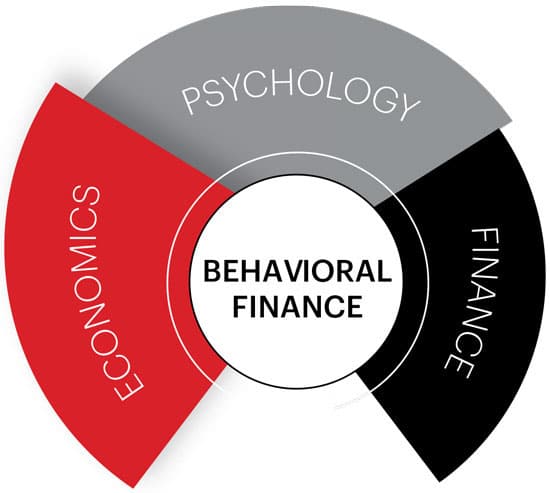
The Prospect Theory was originally conceived by Kahneman and Tversky (1979) and later resulted in Daniel Kahneman being awarded the Nobel Prize for Economics. The work by the authors is considered as path breaking in behavioral finance. They introduced the concept of prospect theory for the analysis of decision making under risk. This theory is considered to be seminal in the literature of behavioral finance. It was developed as an alternative model for expected utility theory. It throws light on how individual evaluate gain or losses. The prospect theory has three key aspects.
- People sometimes exhibit risk aversion and sometimes risk loving behaviors depending on the nature of the prospect.