Wal-Mart, the mega-retailer, was founded by Sam Walton in 1962 in Bentonville, Arkansas. It started with $700,000 in its first year and scaled up to $5.4 million by 1974. The retailer continues to grow while others struggled with inflation and recessions. In 1980, Wal-Mart became the youngest US retailer to exceed $1 billion in net sales. During the 1980s, Wal-Mart began to further expand and thus pushing some retailers to closing some of their regional stores. The company engaged in diversification by creating membership-stores such as Sam’s Club, smaller, more conventional pharmacy/grocery stores called Neighborhood Markets, and finally Supercenters with a wide selection of consumer goods. … Read the rest
Organizational Behavior
Learning Styles
Learning style refers to the ability of an individual to learn. A manager’s long-term success depends more on the ability to learn than on the mastery of the specific skills or technical knowledge.
Kolb’s Learning Styles ModelKolb’s model of learning styles is one of the best-known and widely used learning style theories. Kolb’s learning theory sets out four distinct learning styles (or preferences), which are based on a four-stage learning cycle. Much of Kolb’s theory is concerned with the learner’s internal cognitive processes.
… Read the rest“Learning is the process whereby knowledge is created through the transformation of experience. Knowledge results from the combination of grasping experience and transforming it.”
Learning Curve in an Organizational Context
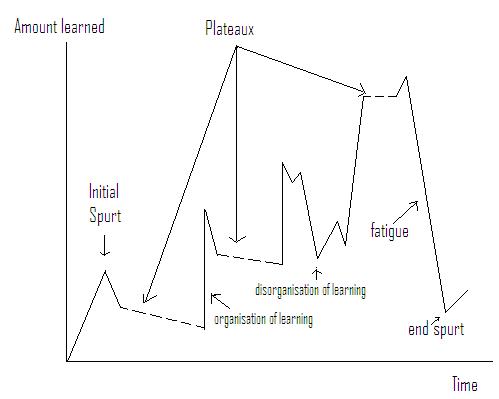
A highly useful learning concept which is valid for a wide range of situation is the organizational learning curve, a diagrammatic presentation of the amount learned in relation to time. A typical learning curve will show on the Y-axis the amount learnt and the X-axis the passage of time.
Characteristics of the Organizational Learning CurveCertain characteristics are common to all learning curves. One such feature is the initial spurt. At the beginning, it is natural that the rate of learning exhibits spurt. Usually, the graph levels off at some stage, indicating that maximum performance has been achieved. Apparently at the beginning of the learning process, the subject is highly motivated and seems to exhibit a significant surge of effort.… Read the rest
Concept of Reinforcement in Organizational Behavior
Reinforcement is the attempt to develop or strengthen desirable behavior. There are two types of reinforcement in organizational behavior: positive and negative.
Positive reinforcement strengthens and enhances behavior by the presentation of positive reinforcers. There are primary reinforcers and secondary reinforcers. Primary reinforcers satisfy basic biological needs and include food and water. However, primary reinforcers don not always reinforce. For instance, food may not be a reinforcer to someone who has just completed a five course meal. Most behaviors in organizations are influenced by secondary reinforcers. These include such benefits as money, status, grades, trophies and praise from others. These include such benefits as money, status, grades, trophies and praise from others.… Read the rest
Components of Learning Process
Learning is an important psychological process that-determines human behavior. Learning can be defined as “relatively permanent change in behavior that occurs as a result of experience or reinforced practice”.
There are four important points in the definition of learning:
- Learning involves a change in behavior, though this change is not necessarily an improvement over previous behavior. Learning generally has the connotation of improved behavior, but bad habits, prejudices, stereotypes, and work restrictions are also learned.
- The, behavioral change must be relatively permanent. Any temporary change in behavior is not a part of learning.
- The behavioral change must be based oh some form of practice or experience.
Goal-Setting Theory of Motivation
This approach to motivation has been pioneered in the USA by Edwin Locke and his associates in 1960s and refined in 1980s. Goal-setting theory of motivation suggests that managers and subordinates should set goals for an individual on a regular basis, as suggested by Management by Objectives (MBO). These goals should be moderately difficult and very specific and of type that an employee will accept and make a commitment to accomplishing them. Rewards should be tied directly to accomplished goals. When involved in goal-settings, employees see how their effort will lead to performance, rewards and personal satisfaction.
Salient features of Goal-setting theory of motivation are as follows:
- Specific goal fixes the needs of resources and efforts.