The Importance of Distribution
Most producers use intermediaries to bring their products to market. They try to develop a distribution channel (marketing channel) to do this. A distribution channel is a set of interdependent organizations that help make a product available for use or consumption by the consumer or business user. Channel intermediaries are firms or individuals such as wholesalers, agents, brokers, or retailers who help move a product from the producer to the consumer or business user.
A company’s channel decisions directly affect every other marketing decision. Place decisions, for example, affect pricing. Marketers that distribute products through mass merchandisers such as Wal-Mart will have different pricing objectives and strategies than will those that sell to specialty stores. Distribution decisions can sometimes give a product a distinct position in the market. The choice of retailers and other intermediaries is strongly tied to the product itself. Manufacturers select mass merchandisers to sell mid-price-range products while they distribute top-of-the-line products through high-end department and specialty stores. The firm’s sales force and communications decisions depend on how much persuasion, training, motivation, and support its channel partners need. Whether a company develops or acquires certain new products may depend on how well those products fit the capabilities of its channel members.
Some companies pay too little attention to their distribution channels. Others, such as FedEx, Dell Computer, and Charles Schwab have used imaginative distribution systems to gain a competitive advantage.
Functions of Distribution Channels
Distribution channels perform a number of functions that make possible the flow of goods from the producer to the customer. These functions must be handled by someone in the channel. Though the type of organization that performs the different functions can vary from channel to channel, the functions themselves cannot be eliminated. Channels provide time, place, and ownership utility. They make products available when, where, and in the sizes and quantities that customers want. Distribution channels provide a number of logistics or physical distribution functions that increase the efficiency of the flow of goods from producer to customer. Distribution channels create efficiencies by reducing the number of transactions necessary for goods to flow from many different manufacturers to large numbers of customers. This occurs in two ways. The first is called breaking bulk. Wholesalers and retailers purchase large quantities of goods from manufacturers but sell only one or a few at a time to many different customers. Second, channel intermediaries reduce the number of transactions by creating assortments–providing a variety of products in one location–so that customers can conveniently buy many different items from one seller at one time. Channels are efficient. The transportation and storage of goods is another type of physical distribution function. Retailers and other channel members move the goods from the production site to other locations where they are held until they are wanted by customers. Channel intermediaries also perform a number of facilitating functions, functions that make the purchase process easier for customers and manufacturers. Intermediaries often provide customer services such as offering credit to buyers and accepting customer returns. Customer services are oftentimes more important in B2B markets in which customers purchase larger quantities of higher-priced products.
Some wholesalers and retailers assist the manufacturer by providing repair and maintenance service for products they handle. Channel members also perform a risk-taking function. If a retailer buys a product from a manufacturer and it doesn’t sell, it is “stuck” with the item and will lose money. Last, channel members perform a variety of communication and transaction functions. Wholesalers buy products to make them available for retailers and sell products to other channel members. Retailers handle transactions with final consumers. Channel members can provide two-way communication for manufacturers. They may supply the sales force, advertising, and other marketing communications necessary to inform consumers and persuade them to buy. And the channel members can be invaluable sources of information on consumer complaints, changing tastes, and new competitors in the market.
Channels
A number of alternate ‘channels’ of distribution may be available:
- Selling direct, such as via mail order, Internet and telephone sales
- Agent, who typically sells direct on behalf of the producer
- Distributor (also called wholesaler), who sells to retailers
- Retailer (also called dealer or reseller), who sells to end customers
- Advertisement typically used for consumption goods
Distribution channels may not be restricted to physical products alone. They may be just as important for moving a service from producer to consumer in certain sectors, since both direct and indirect channels may be used. Hotels, for example, may sell their services (typically rooms) directly or through travel agents, tour operators, airlines, tourist boards, centralized reservation systems, etc.
There have also been some innovations in the distribution of services. For example, there has been an increase in franchising and in rental services – the latter offering anything from televisions through tools. There has also been some evidence of service integration, with services linking together, particularly in the travel and tourism sectors. For example, links now exist between airlines, hotels and car rental services. In addition, there has been a significant increase in retail outlets for the service sector. Outlets such as estate agencies and building society offices are crowding out traditional grocers from major shopping areas.

Channel Members
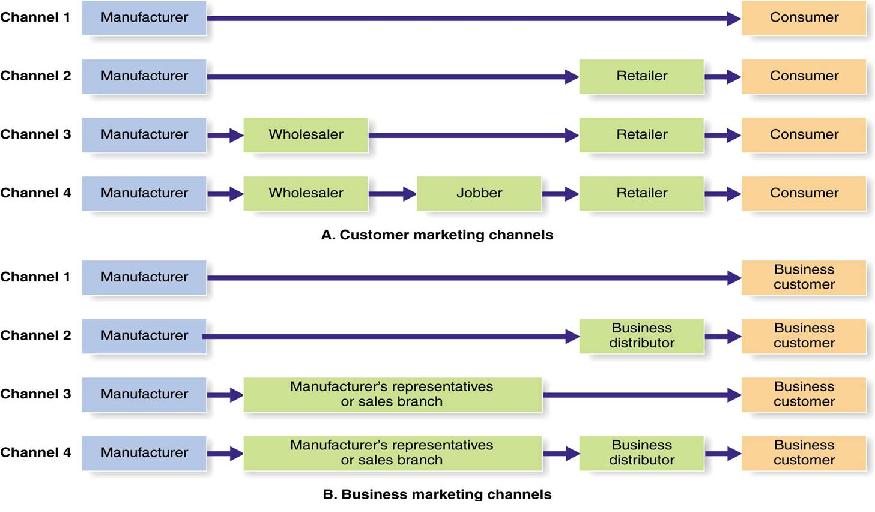
Distribution channels can have a number of levels. Kotler defined the simplest level, that of direct contact with no intermediaries involved, as the ‘zero-level’ channel.
The next level, the ‘one-level’ channel, features just one intermediary; in consumer goods a retailer, for industrial goods a distributor. In small markets (such as small countries) it is practical to reach the whole market using just one- and zero-level channels.
In large markets (such as larger countries) a second level, a wholesaler for example, is now mainly used to extend distribution to the large number of small, neighborhood retailers.
Wholesaling
Wholesaling is all activities involved in selling products to those buying for resale or business use. Wholesaling intermediaries are firms that handle the flow of products from the manufacturer to the retailer or business user.
Wholesaling intermediaries add value by performing one or more of the following channel functions:
- Selling and Promoting
- Buying and Assortment Building
- Bulk-Breaking
- Warehousing
- Transportation
- Financing
- Risk Bearing
- Market Information — giving information to suppliers and customers about competitors, new products, and price developments
- Management Services and Advice — helping retailers train their sales clerks, improving store layouts and displays, and setting up accounting and inventory control systems.
Independent Intermediaries
Independent intermediaries do business with many different manufacturers and many different customers. Because they are not owned or controlled by any manufacturer, they make it possible for many manufacturers to serve customers throughout the world while keeping prices low.
Merchant Wholesalers
Merchant wholesalers are independent intermediaries that buy goods from manufacturers and sell to retailers and other B2B customers. Because merchant wholesalers take title to the goods, they assume certain risks and can suffer losses if products get damaged, become out-of-date or obsolete, are stolen, or just don’t sell. At the same time, because they own the products, they are free to develop their own marketing strategies including setting prices. Merchant wholesalers include full-service merchant wholesalers and limited-service wholesalers. Limited-service wholesalers are comprised of cash-and-carry wholesalers, truck jobbers, drop shippers, mail-order wholesalers, and rack jobbers.
Merchandise Agents or Brokers
Merchandise agents or brokers are a second major type of independent intermediary. Agents and brokers provide services in exchange for commissions. They may or may not take possession of the product, but they never take title; that is, they do not accept legal ownership of the product. Agents normally represent buyers or sellers on an ongoing basis, whereas brokers are employed by clients for a short period of time. Merchandise agents or brokers include manufacturers’ agents (manufacturers’ reps), selling agents, commission merchants, and merchandise brokers.
Manufacturer-Owned Intermediaries
Manufacturer-owned intermediaries are set up by manufacturers in order to have separate business units that perform all of the functions of independent intermediaries, while at the same time maintaining complete control over the channel. Manufacturer-owned intermediaries include sales branches, sales offices, and manufacturers’ showrooms. Sales branches carry inventory and provide sales and service to customers in a specific geographic area. Sales offices do not carry inventory but provide selling functions for the manufacturer in a specific geographic area. Because they allow members of the sales force to be located close to customers, they reduce selling costs and provide better customer service. Manufacturers’ showrooms permanently display products for customers to visit. They are often located in or near large merchandise marts, such as the furniture market in High Point, North Carolina.
Vertical Marketing Systems
A vertical marketing system (VMS) is a distribution channel structure in which producers, wholesalers, and retailers act as a unified system. One channel member owns the others, has contracts with them, or has so much power that they all cooperate. A conventional distribution channel consists of one or more independent producers, wholesalers, and retailers. A vertical marketing system, on the other hand, provides a way to resolve the channel conflict that can occur in a conventional distribution channel where channel members are separate businesses seeking to maximize their own profits–even at the expense sometimes of the system as a whole. The VMS can be dominated by the producer, wholesaler, or retailer. There are three major types of vertical marketing systems: corporate, contractual, and administered.
- A corporate VMS is a vertical marketing system that combines successive stages of production and distribution under single ownership–channel leadership is established through common ownership. A little-known Italian eyewear maker, Luxottica, sells its many famous eyewear brands–including Giorgio, Armani, Yves Saint Laurent, and Ray-Ban–through the world’s largest optical chain, LensCrafters, which it also owns.
- A contractual VMS is a vertical marketing system in which independent firms at different levels of production and distribution join together through contracts to obtain more economies or sales impact than they could achieve alone. Coordination and conflict management are attained through contractual agreements among channel members. The franchise organization is the most common type of contractual relationship. There are three types of franchises: manufacturer-sponsored retailer franchise system (Ford Motor Co.), manufacturer-sponsored wholesaler franchise system (Coca-Cola bottlers), and service-firm-sponsored retailer franchise system (McDonald’s). The fact that most consumers cannot tell the difference between contractual and corporate VMSs shows how successfully the contractual organizations compete with corporate chains.
- An administered VMS is a vertical marketing system that coordinates successive stages of production and distribution, not through common ownership or contractual ties, but through the size and power of one of the parties. Manufacturers of a top brand can obtain strong trade cooperation and support from resellers (P&G). Large retailers such as Wal-Mart can exert strong influence on the manufacturers that supply the products they sell.
