Basic Principles of Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total Quality Management ensures maximum effectiveness and efficiency within a business and secures commercial leadership by putting in place process and systems which will promote excellence and prevent errors. It ensures that every aspect of the business is aligned to the customer needs and the advancement of business goals without duplication or waste of efforts.
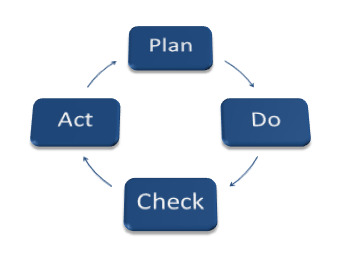
Different companies have different approaches to implement Total Quality Management (TQM). The following principles (which are common to all companies) must be adhered for the successful Total Quality Management (TQM) implementation:
- Continuous improvement. TQM is a long-term process that entails achieving improvements in the company’s operations.