The layout of a plant or facility is concerned with the physical placement of resources such as equipment and storage facilities, which should be designed to facilitate the efficient flow of customers or materials through the manufacturing or service system. The layout design is very important and should be taken very seriously as it can have a significant impact on the cost and efficiency of an operation and can involve substantial investment in time and money. The decisions taken with regards to the facility layout will have a direct influence on how efficiently workers will be able to carry out their jobs, how much and how fast goods can be produced, how difficult it is to automate a system, and how the system in place would be able to respond to any changes with regards to product or service design, product mix, or demand volume.… Read the rest
Production Management
Mass Production Systems
Mass production (also called flow production or repetitive flow production) is the production of large amounts of standardized products on production lines. It was popularized by Henry Ford in the early 20th Century, notably in his Ford Model T. Mass production is notable because it permits very high rates of production per worker and therefore provides very inexpensive products. Mass production is capital intensive, as it uses a high proportion of machinery in relation to workers. With fewer labor costs and a faster rate of production, capital is increased while expenditure is decreased. However the machinery that is needed to set up a mass production line is so expensive that there must be some assurance that the product is to be successful so the company can get a return on its investment.… Read the rest
Job Production
Job production is characterized by the manufacture of one or few numbers of a single product designed and manufactured strictly to customer’s specifications, within, the given period and wit/tin the price fixed prior to tile contract. Some typical examples of industries engaged in jobbing production are: general repair shops; special purpose machine tool manufacturers; workshops to manufacture jigs and fixtures for other units; building contractors; tailoring shops manufacturing made-to-measure suite of clothes; manufacturers of ships, cranes, furnaces, turbo-generators, pressure vessels; and others manufacturing articles made to customers orders.
Characteristics of Job Production- Disproportionate manufacturing cycle time: A considerable amount of pre-planning and organization is necessary in such a venture.
Continuous Manufacturing Systems
In continuous manufacturing systems the items are produced for the stocks and not for specific orders. Before planning manufacturing to stock, a sales forecast is made to estimate likely demand of the product and a master schedule is prepared to adjust the sales forecast according to past orders and level of inventory. Here the inputs are standardized and a standard set of processes and sequence of processes can be adopted. Due to this routing and scheduling for the whole process can be standardized.
After setting of master production schedule, a detailed planning is carried on. Basic manufacturing information and bills of material are recorded.… Read the rest
Intermittent Manufacturing Systems
In Intermittent manufacturing systems, the goods are manufactured specially to fulfill orders made by customers rather than for stock. Here the flow of material is intermittent. Intermittent production systems are those where the production facilities are flexible enough to handle a wide variety of products and sizes. These can be used to manufacture those products where the basic nature of inputs changes with the change in the design of the product and the production process requires continuous adjustments. Considerable storage between operation is required, so that individual operations can be carried out independently for further utilization of men and machines. Examples of intermittent systems are: machine shops, hospitals, general office etc.… Read the rest
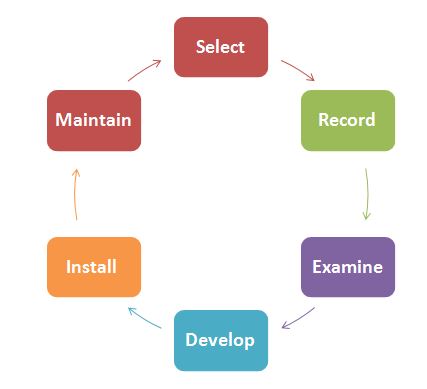
Method Study Procedure
Method study is the systematic recording and critical examination of existing and proposed ways of doing work, as a means of developing and applying easier and more effective methods and reducing costs. So it is the process of analyzing the methods involved in work flow to increase productivity. It deals with doing the work in a better way, with less time and effort. That is why it is also termed as work simplification.
Method study procedure is an organized approach and its investigation rests on the following six basic steps:
- Select the work to be analyzed.
- Record all facts relating to the existing method.