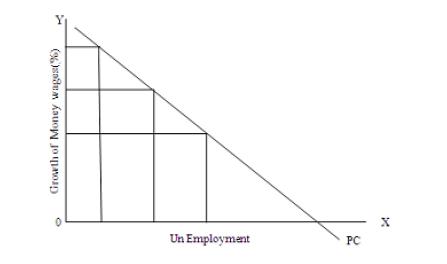
The economists describe unemployment as a condition of jobless within an economy. Unemployment is lack of utilization of resources and it eats up the production of the economy. It can be concluded that unemployment is inversely related to productivity of the economy.
Unemployment generally defined as the number of persons (It is the percentage of labor force depends on the population of the country) who are willing to work for the current wage rates in society but not employed currently. Unemployment reduces the long run growth potential of the economy. When the situation arises where there are more other resources for the production and no man power leads to wastage of economic resources and lost output of goods and services and this has a great impact on government expenditure directly.… Read the rest