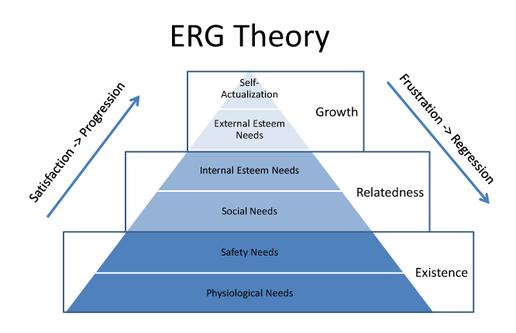
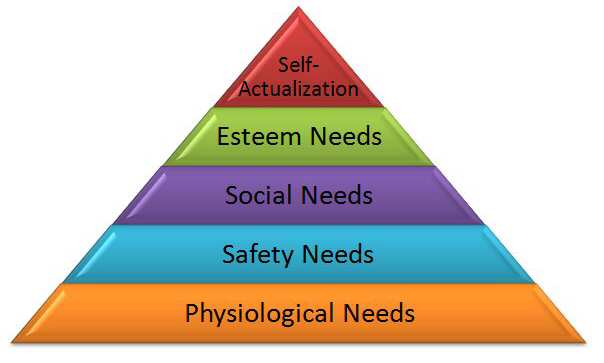
Serious doubts have been expressed about the existence of the five distinct need categories, which Maslow hypothesized. There seems to be some overlapping between esteem, social, and physiological needs. Also, the lines between esteem, social, and self-actualization needs are not entirely clear. With these points in mind, Clayton Alderfer condensed Maslow’s five need categories into three sets:
- The existence Needs: Over here material existence requirements are mentioned. This group is the same as what has been called by Maslow physiological and safety needs. In an organizational context the existence needs are satisfied by money earned in a job and spending them to obtain foods, clothing, shelter etc.