Though global organizational structures tend to depict certain kind of rigidity, structure tends to change and new trends emerge. Mixed Nature of Structures Because of growth dynamics, companies change their organizational structures. Simplified organizational structures get replaced by complex or mixed structures. Until organizational re-structuring is made, new acquisitions might report to headquarters. Circumstances prevailing in a particular country, product, or function might necessitate separate handling until a re-structuring is effected, apart from the overall structure. The structure of 100% subsidiaries is different from that of JVs. 100% subsidiaries enable a deeper network of communications. Overall structure may be incomplete and less revealing. PepsiCo is organized by product lines, namely soft drinks and snacks. This would seem to imply that each product line is integrated globally. However, each line has its own global division, which separates it from domestic operations. Structures Evolve to Suit Growth and Need A company thatContinue reading
International Business Basics
Theories of International Investments
International investments mean investments beyond borders. International investments refer to investments by entities of a nation in nations other than their own. Foreign investments involve export of capital. The opportunity for International investments is directly emanating from economic reformist policies adopted by most of the countries of the world including centrally planned and command economies. Liberalization, Privatization and Globalization (LPG) are vigorously pursued by the countries giving an up-thrust on investment opportunities. Broadly there are two types of foreign investment, namely, foreign direct investment (FDI) and foreign portfolio investment (FPI). FDI refers to investment in a foreign country where the investor retains control over the investment. It typically takes the form of starting a subsidiary, acquiring a stake in an existing firm or starting a joint venture in the foreign country. Direct investment and management of the firms concerned normally go together. If the investor has only a sort ofContinue reading
Global Matrix Structure of MNE’s
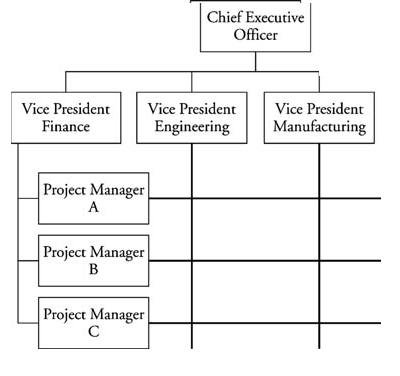
A matrix organization structure involves horizontal, vertical and diagonal flows of responsibilities. Mathematically arrangement of anything by rows and columns is called matrix structure. In a matrix organization the products or projects may be the column element, while the horizontal or row elements might be the functional lines of production, marketing, etc. Third dimensionally, the geographic responsibilities might run. Matrix structure is a combination of two or more different structures. Thus in a global matrix organization structure a foreign subsidiary reports to more than one group, namely product/project, functional or geographic. Following figure gives the Matrix structure of an Multinational Enterprise. Large multinational corporations that use a matrix structure most commonly combine product groups with geographic units. Product managers have global responsibility for the development, manufacturing, and distribution of their own product or service line, while managers of geographic regions have responsibility for the success of the business in theirContinue reading
Global Product Division Structure of MNE’s
Global Product division structure contains the functions necessary to the specific goods or services a product/service division produces. The parental organization has headquarters divisions for different major product categories with respective resources, human and others. Overseas subsidiaries producing a particular product or class of product have to report to headquarters division responsible for that product or class of products. Global Product Division Structure locates manufacturing and value creation activities in appropriate global locations to increase responsiveness to competitive opportunities, efficiency, quality, or innovation. Global product divisions are responsible for Global Product Design and operate in divisional, cluster, or holding company formats. Global Product divisions have little in common. They are highly independent of each other. Following figure gives a simple model of Global Product Division Structure. Ford adopts this structure, abandoning its Global Geographic Structure. Today most of the multinational enterprises with their diverse acquisitions world-wide have diverse product portfolios.Continue reading
Global Geographic Division Structure of MNE’s
With large foreign operations that are not dominated by a single country or area including the headquarters, but well spread out geographically Multinational Enterprises use geographic divisions. Global Geographic (Region/Nation/Area) Division Structure is more common to European MNEs, such as Nestle. Nestle uses this structure because no one region dominates its operations. Merits of Global Geographic Division Structure The structure is useful when maximum economies in production can be gained on a regional rather than a global basis because of market size or the production technologies for the industry. A global geographic structure puts managers closer to the scene of operations than are managers at central headquarters. Regional managers are well positioned to be responsive to local situations such as the needs of regional customers and to fluctuations in resources. Thus regional divisions are often able to find solutions to region-specific problems and to use available resources more effectively thanContinue reading
Global Functional Structure of MNE’s
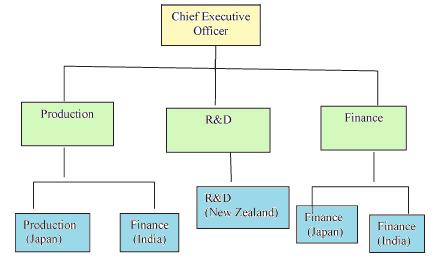
An organization based on functions is the traditional and the most logical. International Functional structure of Multinational Enterprises, involve grouping together functionally like-activities along functional lines like marketing, R&D, production, etc and place them under specialist classes of personnel. Functional heads of foreign affiliates communicate to and get communication from same functional specialists at the parent concern. Marketing people of the foreign affiliate report to marketing people of the parent or their order. Finance people of the foreign affiliate report to finance people of the parent or their order and so on. But a firm offering many product lines will find this structure less successful. Following figure gives a simple model of Global Functional Structure. Merits of the Global Functional Structure Some advantages of the functional structure are: The structure is simple and clear, making communication lines distinct and direct Reduces overhead Provides clearly marked career paths for hiring andContinue reading