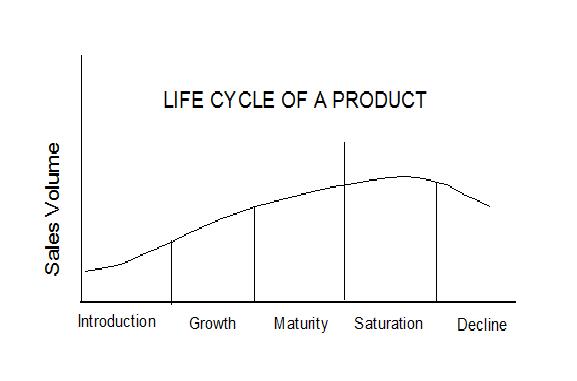
Many products generally have a characteristic known as perishable distinctiveness. This means that a product which is distinct when new degenerates over the years into a common commodity. The process by which the distinctiveness gradually disappears as the product merges with other competitive products, has been rightly termed by Joel Dean as “the cycle of competitive degeneration”. The cycle begins with the invention of a new product and is often followed by patent protection, and further development to make it saleable. This is usually followed by a rapid expansion in its sales as the product gains market acceptance. Then competitors enter the field with imitation and rival products and the distinctiveness of the new product starts diminishing. The speedContinue reading
Marketing Concepts
Diffusion of Innovation Theory
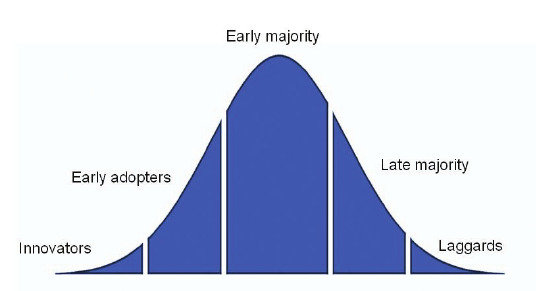
Diffusion of innovation theory was developed in the early 1950s by Everett Rogers. It seeks to explain the spread of new ideas through individuals and members of a social system. This theory is still widely used now to spread innovations and ideas from the scientific world to the political sphere. According to Rogers, the diffusion of innovation is the process by which an innovation is communicated through certain channels over time among the members of a social system. To understand that definition you must first understand some key terms. Innovation is used more generally here to mean an item, thought, or process that is new. Good examples of innovation would be automobiles, brain surgery, and a new kind of runningContinue reading
Improve, Buy or Drop a Product
If a product is not showing profitable performance, the company may consider one of the alternatives, viz., improve, buy or drop the product. Improve If the firm continues to make the product, it may be required to make improvement in its production or distribution so as to yield adequate return. Improvement may mean re-designing the product or producing it at a lower cost. Product improvement is particularly necessary when the existing product has become apparently obsolete or out of fashion. Indian companies need to continuously upgrade their products and technology to withstand the pace of change in their business environment and to meet the challenges thrown up by the emergence of a buyer’ market. Product improvementContinue reading
Factors determining the scope of the product line
The extent to which a company can add new products is not unlimited. Very often, the scope for having new products is in some way related to the existing conditions of the firm. The goods may be : 1. Cost Related Goods A company may decide to add a product which may be the result of a common production process. For example, a company which strikes oil may decide to produce petrol or mobil oil, kerosene, gas, wax, etc. A company producing sugar may decide to produce molasses. 2. Demand Related Goods A firm may decide to add a product which is jointly demanded. For example, manufacturers of Sulekha Ink have gone in for productionContinue reading
Why Firms Introduce New Products Into Markets?
Excess Capacity as a Reason for Expanding Product-line The presence of excess production capacity is, perhaps, the most important single factor leading to product-line diversification. Broadly conceived, excess capacity is said to exist when it would cost the multiple-product firm less to make and sell the new product than it would cost a new company set up to produce only that product. Excess capacity may occur for several reasons. It may be the result of an unduly over-optimistic estimated market for the firm’s products. In such a case, if anticipated level of demand is not forthcoming, the firm develops excess capacity. Excess capacity may be due to seasonal variations in demand also, the latter being a result of weather andContinue reading
Different types of product testing
After the product development, generally firms conduct a product testing that one could testify the accuracy of the information on the basis of which various stages were completed. These commercial experiments are necessary to verify earlier business judgements. Thus, the object of this stage is basically to assess whether the product meets the technical and commercial objectives at various levels in order to ascertain the product acceptability. There are three types of tests usually conducted : Concept Testing, Product Testing, and Test Marketing Concept Testing This is concerned with measuring customer reactions to the idea or concept of a product. In fact, it is a kind of research in which the product ideaContinue reading