An innovation is a product or service with a bundle of features that is new in the market, or that is commercialized in some new way that opens up new uses and consumer groups for it. Innovation is invention implemented and taken to market. Invention however is the creation of something that was previously unknown. In summary, INNOVATION= INVENTION+COMMERCIALIZATION. Today companies who, want to deliver consistent organic growth to their shareholders, customers, and their employees can do that only through innovation. Concept of Open Innovation According to American organizational theorist Henry Chesbrough, Open innovation is the use of purposive inflows and outflows of knowledge to accelerate internal innovation, and expand the markets for external use of innovation, respectively. Open innovationContinue reading
Modern Management Practices
10 Steps to Successful Crisis Management
A crisis is an abnormal situation, or even perception, which is beyond the scope of everyday business and which threatens the operation, safety and reputation of an organisation. Crises do not discriminate based on a company’s size or notoriety, and they can hit when a company least expects them. They come in many forms — strikes, layoffs, product recalls or allegations of misconduct, but while some of these may seem small, every crisis has the potential to damage the reputation of a company. Regardless of the severity of the situation, crises pose a serious threat to companies — not only to their reputation but their fiscal health as well. When Odwalla’s apple juice was thought to be the cause ofContinue reading
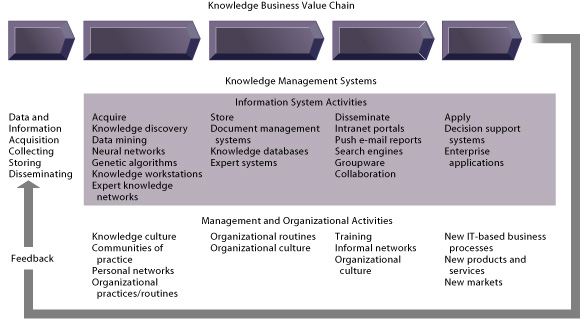
Knowledge Management Value Chain
Knowledge management refers to the set of business processes developed in an organization to create, store, transfer, and apply knowledge. Knowledge management increases the ability of the organization to learn from its environment and to incorporate knowledge into its business processes. Following figure illustrates the five value-adding steps in the knowledge management value chain. Each stage in the value chain adds value to raw data and information as they are transformed into usable knowledge. In the figure, information systems activities are separated from related management and organizational activities, with information systems activities on the top of the graphic and organizational and management activities below. One apt slogan of the knowledge management field is, “Effective knowledge management is 80 percent managerialContinue reading
What is Crisis Management?
An individual, an organization, a government, or the global economy at any point of time may face debacles. This may come in any form and can devastate the present circumstances and can lead to difficult situations. Such occurrences are often termed as crisis. It is therefore defined as a major, unpredictable and upsetting event that intimidates to harm. Even though crisis is an unpredictable form of event, but it is not unanticipated. Crisis is a threat to organizations, an unexpected element and short periods of risk. For an organization, crisis can be illustrated as an anomalous and uncharacteristic situation or perception, which is beyond the control of an organization and also threatens to impact their operation. A company has toContinue reading
Impact of Information Technology on Organizations
The impact of information technology will have significant effects on the structure, management and function of most organisations. It demands new patterns of work organisation and effects individual jobs, the structure of groups and teams, the nature of supervision and managerial roles. Information technology results in changes to lines of command, authority and the need for reconstructing the organisation structure and attention to job design. Computer based information and decision support systems influence choices in design of production or service activities, hierarchical structures and organisations of support staffs. Information technology may influence the centralization or decentralization of decision making and control systems. New technology has resulted in a flatter organisational structure with fewer levels of management required. In the caseContinue reading
Emotional Intelligence in the Workplace
At the work place the ability to exercise clear and sound judgement in situations that the jobs role presents solely depends on the emotional intelligence employees possess. It encompasses the ability to manage their own impulses, cope with change, effectively communicate with others, and solve problems and being able to make use of humor to defuse a tense situation. Such employees have the ability to empathize with others, are optimistic in the face of down turns and are effective in resolving customer complaints. Therefore emotional intelligence plays a vital role in separating top performers from weak ones at the work place. At the work place certain emotional quotient competencies correlate with each other to make it a successful place, suchContinue reading