In organizational culture there are many kind of categorization and typologies have been explained by different scholars of culture. Theses typologies give and over view about the different cultures which exist in organizations. Handy (1985) was the person who discussed how different cultures have their existence in different organizations and within the same organization many diverse cultures can coexist. There are very few organizations exist who have a single culture exists in them. Every individual have its own culture within him and have his own specific personality and culture along with organizational culture. Organizational culture and structure of any organization are connected with each other. In organizations A few subcultures and cultures will be well-suited and other will not be suited. Handy talked about four kinds of eminent cultures and each of these cultures had a linked culture. These cultures are explained below in detail.
1. The Power Culture
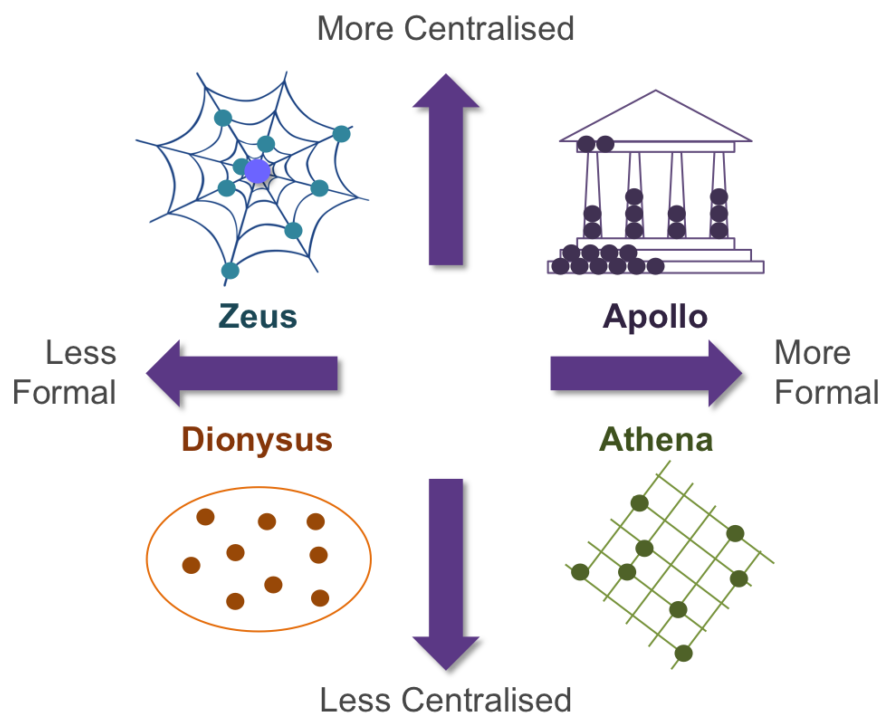
The power culture relies on single central source of power in the organization. It will lead to low morale and high turnover on the positions of middle management. The power culture is like web which has different strings attached to the central point for the facilitation and co ordination of any action. The power is distributed from one single power source in the middle. Handy give linked this terminology with the culture of the ”Zeus”. He was the leader of the gods of mountains.
The power culture can be seen in small entrepreneurial organizations. For the effectiveness of the power culture it is dependable on personal communications, faith and understanding. Individuals have to work what they have been asked to do without asking many questions. Advantage of this system is that there’s no delay in decisions because it has one central source of power so decisions are made quickly. As the size of the organization increases due to many different activities web breaks because of its span and activities. In this system the boss can choose people on key level position with his own will with restrictions to consult someone. If appropriate personnel not have been recruited for these positions.
2. The Role Culture
The role culture is bureaucratic culture. This is most commonly used and understandable culture. Handy present it like Greek temple which represents the god of reasons. Where powers are equally distributed amongst the specialist in their field and at the top small group of executive control and coordinate all the departments comes under their authority. In the role culture Job description procedures and rules are more important than the person who is performing a specific job. In this culture promotions are given on the bases of performances given by the individuals. The power of the role culture is depends on the specialist of the organization like production department, finance department and purchasing department etc. The Role culture organization is most of the time is successful where the market is stable and the life of the product is long. The examples of role culture organizations are retail banking, oil and automobile industries, insurance companies and civil services. The problem with this kind of structure is that recognition and reaction to change in these organizations is very slow. These organization will not be satisfying for those individuals who power-oriented and it will be very satisfying for those people who liken who like certainty and protection and for those people who want to get success by accomplishing a role and getting professional proficiency without taking risk.
3. The Task Culture
The task culture is mostly result, performance and project oriented and management is mostly concerned with the solutions of the problems in successful manner. Handy represented this culture like a net with some of its strands are thinner and thicker than each other. Matrix organizational structure is one of the examples of the task culture where manipulation and supremacy lies where the strands meet. Task culture is very flexible and adaptable to the changes and is a team culture. The emphasize of this culture is task so after every project teams , task forces, task teams and groups can be continued , reproduced or abundant quickly. To attain the desirable outcomes suitable means, right people for the right job with all the decision making power are brought together. The task culture is suitable for the market where competition exists, where product life stays for the short span of time and where importance is given to the speed of reaction to the environment. Examples for the task cultures can be advertising, marketing agencies and general management consultancies. There is high degree of control over the work by the individuals in task culture. In the task culture individuals are judged by the results, flexibility, and adaptability at the bases of their ability rather than age or position in the group. It is difficult to control the task culture. The task culture has a tendency to change into power or role culture when the total organization is not successful or there are limited resources or as a flexible group organization is too large to organize.
4. The Person Culture
The person culture is formed when in the best interest of a group of people decide to create organization on combined bases rather than solely. These kinds of organizations are established by the doctors, lawyers, architects and some other small consultancy firms they make this to share the space of the office, cost, equipment etc. The person culture can be seen as galaxy of stars or scattered dots. In this culture individuals are self oriented. The individuals allocate work for themselves with their own rules. Mutual consent can be the only mechanism of control in the task culture. According to the expertise roles are appointed and influence is shared and it is not easy to manage the individuals within them. When this organization start achieving its objects then it start imposing task culture on its
Individuals and it start acting like task culture and then often reshape as role culture or power culture in the organization.