Market failure refers to a market that fails to provide efficient outcomes for the society. In other words, market works efficiently only when there exist perfect competition or when exclusion principle could be applied in the free market. Exclusion principle requires that, those who do not pay for as goods should be excluded from its consumption and those who derive any benefit from goods should bear its cost. In free market economy the main responsibility of the government is to prevent the market from failure. Market failure can be summarized in two ways: Market failures due to incentive or incentive failure Market failures due to structure or structure failure 1. Market failure due to incentive or incentive failure The market Continue reading
International Economics
What is Market Failure?
Market failure can be defined as the situation in which the allocation of goods and services by free market is not efficient. It occurs as market fails to fulfill its obligation the most common failures involve cases of inadequate competition, inadequate information, resources immobility, public goods and imperfect competition. These failures occur on both the demand and supply sides of the market. Government failure occurs when the government intervenes in the market to improve the market failure actually makes the situation worse. When market failure exist there is a reason for possible government intervention to improve the outcome, but it`s not clear that government action will improve the result since the politics of implementing the solution often lead to further Continue reading
Role of Government in Economic Development
Any country’s the prosperity and obstacles of economic growth results from activities of government. That means, government plays important role in economic activities. In free market economies government plays important activities. It has to perform role to prevent market failure. As we know that market does not yield economically efficient outcome every time as the result market fails to operate. In free market economy government has designed activities to stimulate and assist private enterprise and to regulate or control business practices so that their operations are consistent with the public interest. There are various forms of government regulation especially to regulate the activities of private firms. Industrial products are subject to Operating Regulations, governing plant and pollutant emission, product packaging Continue reading
Responsibilities of a Managerial Economist
Besides considering the opportunities that lie before a managerial economist it is necessary to take into account the services that are expected by the management. For this, it is necessary for a managerial economist to thoroughly recognize the responsibilities and obligations. A managerial economist can serve the management best by recognizing that the main objective of the business, is to make a profit on its invested capital. Academic training and the critical comments from people outside the business may lead a managerial economist to adopt an apologetic or defensive attitude towards profits. There should be a strong personal conviction on part of the managerial economist that profits are essential and it is necessary to help enhance the ability of the Continue reading
Fiat Money – Meaning, Characteristics and Working
The term fiat money is used to define as any money declared by a government to be legal tender with no commodity backing. Legal tender simply means that there is a law requiring everyone to accept the currency in commerce. Besides, fiat money was state-issued money which is neither fixed in value in terms of any objective standard, nor legally convertible to any other thing that was demanded by someone else. In other word, fiat money is money without intrinsic value. In ancient times when money was not invented trade as a whole was on barter system. “Barter” basically means to pay for something you want with products or services instead of paying for what you want with money. Under Continue reading
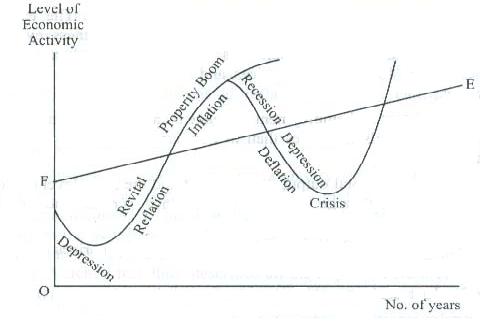
Trade Cycle or Business Cycle Concept in Managerial Economics
Definition of Trade Cycle or Business Cycle According to Keynes, “A trade cycle is composed of periods of good trade characterized by rising prices and low unemployment percentage, alternating with periods of bad trade characterized by falling prices and high unemployment percentage. “ Characteristics of Trade Cycles From the above definition, it should be clear that trade cycle is the rhythmic fluctuations of the economy, that is, periods of prosperity followed by periods of depression. However, the waves of prosperity and depression need not always be of the same length and amplitude. Further, trade cycles varied tremendously in magnitude. While some have smaller cyclical fluctuations in economic activity, others have great intensity of fluctuations. Expansion in some cycles reaches the Continue reading