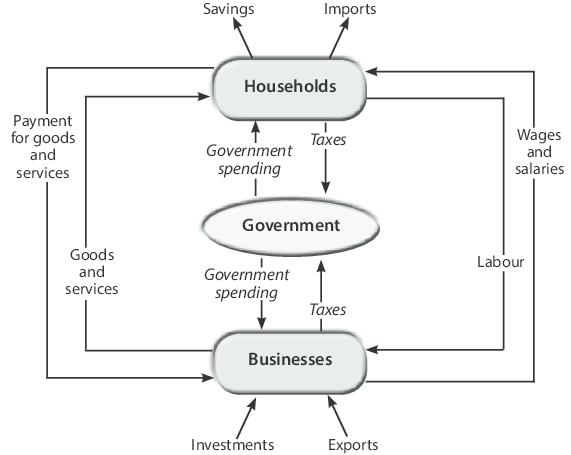
There are three main sectors of economy consists of household sectors, business sectors and government sectors. Household sector provides the factors of the production such as land, labor and capital and enterprise that the producers require to produce goods and services. They also receive payments as in rent, wages, interest and profits from the business sector. It is also stated that in general, household sector consists of the greatest number of consumers among all sectors and satisfying the wants will cause consume of their climate aim. Business sector act as a part as in receiving economy resources from household sector and in exchange for consumer expenditure, they also provide household sectors goods and services. Business sector is also given money to buy scarce economic resources from the resource market. While they’re in the product market, business sector sells their products and services, which is also the way they receives their income. To complete the circular income of income and expenditure in a three-sector closed model, the Government sector is added. Taxation is a leakage from the circular flow and government purchases are injections into the circular flow. To do so, government sector implements taxes on businesses and consumers. They also act as a part to spend the money back on business and consumers for the other sectors’ benefits. Government incurs expenditure on goods and services.
- The circular flow between the household sector and the government sector: Household sector pay direct taxes and commodity taxes in terms of building up the leakage from the circular flow. On the other hand, government sector also purchase the services from household sector and make transfer payments to the household sector which has low income. All the expenditure is said to be injected into the circular flow.
- The circular flow between the business sector and the government sector: The action of business sector pay taxes to the government also constituting leakage from the circular flow. Government sector will purchase the final goods from the business sector as well as make transfer payments to firms to induce production from the other sectors.
- The circular flow among the household sector, business sector and government sector: Taxation is a leakage from the circular firm. Taxation reduces savings and consumption of the households. The reduction in consumption will reduce the sale and the income of firms. The government offsets these leakages by making purchases from the business sector and the household sector. It equal to the amount of taxes and total sales again equal production of firms. The equilibrium will show in the circular flows of income and the expenditure too.
The diagram above shows that taxes flow out of the household and business sectors and go to the government. The government makes investment and the purchases goods from firms and also factors of production from households. On the other hand, government purchases of goods and services are an injection in the circular flow of income and taxes are leakages.
If government purchases exceed net taxes, the government will incur a deficit equal to the differences between the public expenditure and taxes. Besides, government purchases will also cause a budget surplus when the net taxes are being exceeded. When such situation occurs, the government will initiate reduce in the public debt. The government also supplies funds to the capital market which are received by firms.
National Income Calculation
In a business, accounting is essential to measure the profit and loss of a company. It keeps it as a business record for references to guide a company right on track. Similar event apply to a nation GDP. The measurement incomes of a country are measured by three different methods which consist of expenditure approach, income approach and value added approach. These three methods must have the same results due to the interrelation in the circular flow of production, income and expenditure.
Expenditure Approach
The expenditures approach concedes the consumption of output in a country within a period of time. The consumption of output comprises of four components, which consists of household consumption, investment, government purchases and net exports.
In order to calculate the national income, a summation of formula is necessary to determine the outcome.
GDP= C+I+G+ (X+M)
“C” means consumption and it represents the total spending of household on durable goods, nondurable goods and services for own use. Durable goods are goods that expected to last long and do not have to repurchase frequently, such as machinery goods, vehicle and furniture. Non-durable goods which known as perishable goods which have less expectation of shelf life, it good that suppose consume or use immediately, such as milk, eggs, bread and shampoo. Services are intangible goods with no ownership claim for the item after purchase, such as car maintenance, foot reflexology and tuition.
“I” means Investment which represents the expenses by the private firm to uphold their business to ensure their business will keep growing. Such investment will fall on fixed capital, business inventories and property assets.
“G” means government purchases. It reflects the government on consumption and gross investment in local infrastructure. Example of expenditure comprises of salaries and wages of the civil servant as well as the material and equipment used, including the maintenance for the entire infrastructures. Under the expenditure approach, transfer payments are excluded in GDP.
“(X-M)” refers to net export of the country. X represents the export of goods and services of the country produced by the country itself. M represent import of goods and services produced by others country.
Income Approach
Income approach is another way to compute the national income. It seeks to measure the total amount of income generate by the production of goods and services in the form of wages, rent, net interest and profit. Individuals are paid for their physically and mentally contribution in the production process. Wages are paid to household for providing labor force to the firm or government in a production and services. It is consider one of the largest components in the national income. However, rent is paid to the household who’s owned the property by renting their premises which involve in a production process. Net interest is paid to the household for the capital invested in a business. Last, which is profit, it refers to entrepreneur gains from the production of goods and services from the binding of factors production after sales, exclude the total cost.
National income = wages + rents + interest + profits
While measuring the national income transfer payment, black money, lotteries prize and merit from share must be excluded from the summation in national income. The main reason of the restriction is because the above gains did not contribute in any production of goods as well as services and parts of it are illegally.
Value Added Approach
Every items which available on the rack with price tag involve the intervention of manufacturer, distributor, supplier and retail. Each time the intermediate good reallocate, the price off the goods will stack up. Therefore, value added approach take account of the value added in to the final product at each stage.
For illustration, Firm A harvest the cocoa bean from the cocoa tree and it will go through fermentation and drying by manual labor. After they pack the bean, it will be sell and transport to Firm B for $20. In order to get the cocoa solid from the cocoa bean, firm B will roast the cocoa bean, winnow the shell and germ off and grind it. Last they press the cocoa mass and separate the cocoa butter. The huge cocoa mass and cocoa butter will be purchased by Firm C for $60 to make variation of chocolate, differ in percentage and flavor. After refining the chocolate, Firm C will distribute their chocolate products to the supplier which is firm D for $80. The confectionary shop which is Firm E will purchases chocolate from Firm D at $130. The chocolatier from the Firm E will use the chocolate to infuse with other ingredients, decorate it to make chocolate bon bon and sell it to customer at the prices of $220. In this case, if we add up all the added value by each stage of production, it will be $220 which is similar to the final goods sold at firm E.