The buying decisions of industrial buyers are influenced by many factors. Usually, these are influenced by organisational factors or task-oriented objectives viz. best product quality, or dependable delivery, or lowest price and personal factors or non-task objectives viz. like promotion, increments, job security, personal treatment, or favor. When the suppliers proposals are substantially similar, organizational buyers can satisfy organisational objectives with any supplier, and therefore personal factors become more important. When suppliers offers differ significantly, industrial buyers pay more attention to organisational factors in order to satisfy the organisational objectives. There are two models available to provide a comprehensive and integrated picture of the major factors that combine to explain organisational buying behavior. These are:
The Webster and Wind Model
The Webster and Wind Model of organisational buying behavior is quite a comprehensive model. It considers four sets of variables: environmental, organizational, buying center, and individual, which, affect the buying-decision making process in a firm.
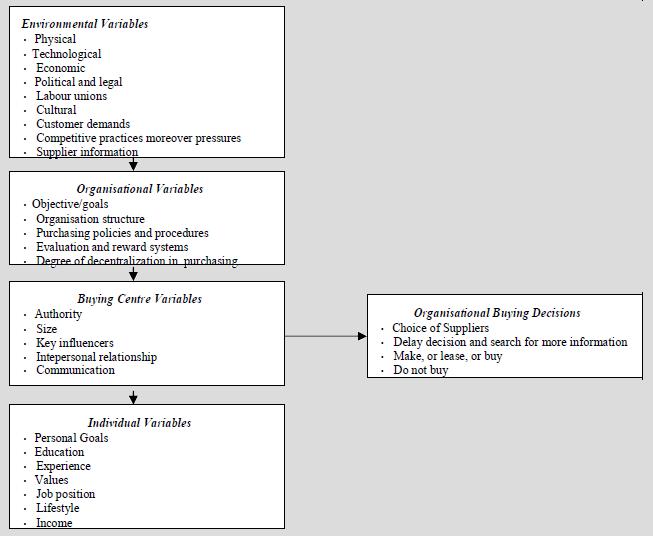
The environmental variables include physical, technological, economic, political, legal, labor unions, competition and supplier information. For example, in a recessionary economic condition, industrial firms minimize the quantity of items purchased. The environmental factors influence the buying decisions of individual organisations. The organizational variables include objectives, goals, organisation structure, purchasing policies and procedures, degree of centralization in purchasing, and evaluation and reward system. These variables particularly influence the composition and functioning of the buying center, and also, the degree of centralization or decentralization in the purchasing function in the buying organisation. The functioning of buying center is influenced by the organisational variables, the environmental variables and the individual variables. The output of the group decision-making process of the buying center includes solutions to the buying problems of the organisation and also the satisfaction of personal goals of individual members of the buying cente. The strengths of the model, developed in 1972, are that it is comprehensive, generally applicable, analytical, and that it identifies many key variables, which could be considered while developing marketing strategies by industrial marketers. However, the model is weak in explaining the specific influence of the key variables.
The Sheth Model
In 1973, Professor Jagdish N Sheth developed the Sheth model of Organizational Buying. This model highlights the decision-making by two or more individuals jointly, and the psychological aspects of the decision-making individuals in the industrial buying behavior It includes three components and situational factors, which determine the choice of a supplier or a brand in the buying decision making process in an organization. The differences among the individual buyers expectations (Component 1) are caused by the factors: background of individuals; information sources; active search; perceptual distortion; and satisfaction with past purchases. The background of individuals depends upon their education, role in the organization, and life style. The factor perceptual distortion means the extent to which each individual participant modifies information to make it consistent with his existing beliefs and previous experiences. It is difficult to measure perceptual distortion, although techniques such as factor analysis and perceptual mapping are available for this purpose. In Component (2), there are six variables, which determine whether the buying decisions are autonomous or joint. According to the Sheth Model, larger the size of the organization and higher the degree of decentralization, more will be possibilities of joint-decision making.
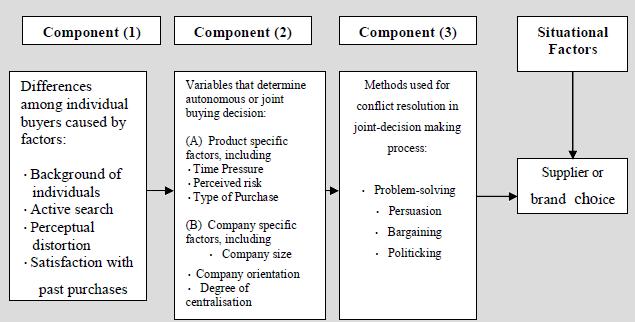
The methods used for conflict resolution in joint-decision making process are indicated by the Component (3) in the model. Problem-solving and persuasion methods are used when there is an agreement about the organizational objectives. If there is no such agreement, bargaining takes place. Conflict about the style of decision-making is resolved by politicking. Situation factors can be varied like economic conditions, labour disputes, mergers and acquisitions. The model does not explain their influence on the buying process.
Read More about different Consumer Behavior Models:
- Howard Sheth Model of Consumer Behavior
- The Engel Kollat Blackwell Model of Consumer Behavior
- Nicosia Model of Consumer Behavior
- Solomon Model of Comparison Process — Model of Consumer Behavior