The historical term of nostalgia, initially started as a medical term. The term was coined in 1688 by Johannes Hofer (1669–1752) in his Basel dissertation to refer on ‘homesickness’. Homesickness was one of the most serious sickness during that time. The term of “nostos” which means return and “algos” which means pain, were introduced to described people that suffering pain because of being far away from home and have needs to return to their home.
Subsequently, the term ‘nostalgia’ evolved, and moved away from being a disease. Nostalgia known as a term that refer to time: past, present and future. In order to be classified as nostalgia, there are four factors that need to be fulfilled:
- An emotional feeling of being lost in space and time.
- An emotional feeling due to loss of values and references of civilization.
- A personal loss feeling occurred because of less freedom.
- Insecurity on a mass consumption culture resulted to the loss feeling of simple things, originality and spontaneity.
Nostalgia is defined as a general preference attitude that is very positive towards objects like places, things, or even a particular person that can be shared with others, and felt during young age or even before one was born. Somehow the negative connotation on nostalgia in the past changed to more positive feeling. Furthermore, Nostalgic experiences can be felt through three levels. Those levels are:
- Simple Nostalgia: thinks that the past was better and an individual would always want to go back to the past but somehow realizes that it cannot be done.
- Reflexive Nostalgia: displays a complete analysis of the past where an individual considers that the past was awesome.
- Interpreted Nostalgia: measures the meaning of nostalgic feelings compare to present conditions to improve life situation and to locate the source, the disposition and the psychological purpose.
Nostalgia in Marketing
The concept of nostalgia was later introduced in the marketing field to be focus on customer preferences influenced by their emotions. The concept of nostalgia explored to understand customers’ behavior in present situation as it could be effected by emotional pressure felt in the past. There are many factors that could influence the nostalgia effect on customers. Some of those factors are age, gender and the sensory. Furthermore, the usage of nostalgia can lead to brand attachment and brand preference.
Particular possessions can strengthen self-identity that will result in experiences. Particular possessions can connect customers with their past through their memories, attitudes and emotions. This exploration that is called nostalgia can contribute to the individual identity based on cultural heritage and memories that is shared with group members. In conclusion, nostalgia can be a self-identity or a shared experience by group members. Moreover, when that self-identity emerges in a transaction, the likelihood of that transaction to be chosen is bigger and at the end it will give a reason for the individual to do a purchase transaction on a product.
When people get older, they tend to re-visit a certain period time of their lives; they try to recreate the past experience in the form of a sentimental possession with a symbolic representation. This can drive people to purchase items in order to re-experience their past. These purchases represent an identity that links the present and the past which people long for.
So, nostalgia means a longing feeling for the past or a preference towards a tangible or intangible possessions and activities that can connect to the past. Nostalgia is usually felt when individuals assume they are no longer present on an era they feel attached to. Nostalgia resulted in more positive customer responses than negative, it can influence customer behavior both emotionally and cognitively.
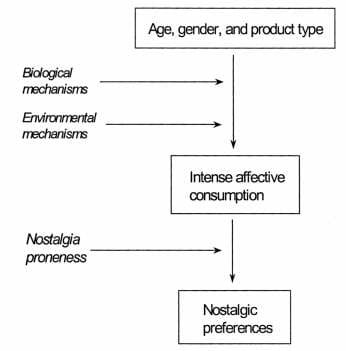
The figure, Nostalgic Preferences Model by Holbrook and Schindler(2003) illustrates that the experience of having intense affective consumption can lead to nostalgic preferences. In order to nurture that intense affective consumption, one has to be in a particular age that attracted to a particular product type that may impact differently towards gender. Moreover, the biological mechanism like age and gender will help to bring up the emotional response. For example, there will be a different emotional push between kids and adults in term of consumption. Kids might not be able to afford the consumption but as an adult, the consumption most likely to happen. Similarly, to product types that evoke interest to particular age and gender will evoke the intense affective consumption push. The environmental forces also come into account such as reference groups and cultural form. Holbrook and Schindler found that men are more prone to nostalgia compared to women when comes to cultural products. For example, for automobiles, men will prefer cars that they encountered in their youth. Holbrook and Schindler also demonstrates that some individuals are attached to a particular significant event in the past and others for a longer period of the past.
There are two ways for people to experience nostalgia. They must have memories about the past either it is lived or learned. Lived memories usually indicated as real or true or direct nostalgia. They are people’s reflections based on their personal experience of the past rather than from external sources like books and stories. Nostalgia from learned memories – usually attributed as simulated or indirect nostalgia is nostalgic feelings toward an object that occurred not because of direct experience during that time but because of influence from books or stories, where the object came or introduced to the individuals.
Collective memory of nostalgia is established, passed and shared by a group of people in modern society era or even in virtual reality. Collective memory usually happens if a particular person experiences historical nostalgia regarding an event in their past that usually combined with fantasy. Historical nostalgic variables include historical event, inspirational characters, romantic events and even exaggerated moments.
Historical nostalgia can lead into cognitive and attitudes changes, leading to purchase intentions. There is a significant increment of purchase intentions every time, there is an increment of nostalgia. Positive attitudes about the past have big potential to affect customer decisions. A particular preference for the past could increase the possibility that items that have been purchased when one was young and will be purchased again as an adult.
Its found that attitudes about the past and that feeling of longing for the past is positively related to purchase intention of the nostalgic products. This purchase action is affected by emotional and cognitive factors. It was also discovered that the nostalgia is measured through emotional level. It is clearly stated that nostalgia is purely an emotional push that can lead to a purchase action by customers who have experienced the nostalgia in the past.
Nostalgia can affect customer behavior and bring competitive advantage when used effectively. The fact that many people want to re-experience the past times gives marketers a chance to boost up sales by enhancing current products and improving image through the “good old days”.
Nintendo Nostalgia Marketing Strategy
In November 2016, Nintendo launched the new and compact Nintendo Entertainment System, which is a smaller size version of the 1985 original. It offers 30 games, including classic games like Super Mario Bros, Zelda, and Punch Out. This hardware includes one controller and an HDMI port. The retail price is around $60 in stores, but online price is around $130 and up. This release is part of Nintendo’s nostalgia strategy by recycling the classic games in order to keep the customer rapport.
Aside from recycling the classic games, the nostalgic strategy was also reflected in their new products launched. Some of the company’s intellectual property still managed to find new stories for its iconic franchise in each hardware console launched. This includes the re-launch of their classic games like Legend of Zelda, Mario Bros, Fire Emblem and many more.
Nintendo Switch is also part of their nostalgia strategy. It tries to bring back the memory of Nintendo Gameboy. It is a recently released console that gained good responses from the Nintendo’s fans. With several iconic Nintendo’s characters to be featured on this new console, it has a potential for Nintendo to improve its market share performance. Another example of combining past and present is that of ‘Pokémon GO’. The game was able to connect the experience of past memories of catching iconic Pokemon with today technology of augmented reality. While this was not fully a Nintendo’s product, it fits well with Nintendo’s nostalgia strategy.
Outside of the entertainment industries, several other industries such as the mobile phone industry and the automobile industry may also employ nostalgia, for example, Nokia with the re-launched of Nokia 3310, Volkswagen re-launched the beetle, or FIAT with the 500. Other examples from the gaming industry other than Nintendo is the RetroEngine Sigma plug-and-play console, which can play games originally released decades ago on Atari VCS, Sega Genesis, and NES, among others.