Corporate Parenting is a strategy employed by highly centralized and diversified firms with large resource pools. It views the corporation in terms of resources and capabilities that can be used to build business units value as well as generate synergies across business units. Corporate parenting generates corporate strategy by focusing on the core competencies of the parent corporation and on the value create from the relationship between the parent and its businesses.
There are basically three styles of corporate parenting as follows; financial control, strategic planning and strategic control.
- Financial Control: Under this style the role of the corporate parent is to monitor and evaluate the financial performance of investment portfolio of the respective business units. The corporate managers act as agents on behalf of share holders and financial markets to identify and acquire viable assets and businesses. The business unit managers are given the autonomy to carry out business activities and make decisions at their level. However the corporate parent sets performance standards for control purposes.
- Strategic Planning: Under this style the role of the corporate parent is to enhance synergies across the business units. This may be achieved through envisioning to build a common purpose, facilitating cooperation across businesses and providing central services and resources.
- Strategic Control: Under this style the corporate parent leverages its resources and competences to build value for its businesses. For example a corporate could have a valuable brand or a specialist skill. The corporate parent uses its parenting capabilities to seize opportunities for growth.
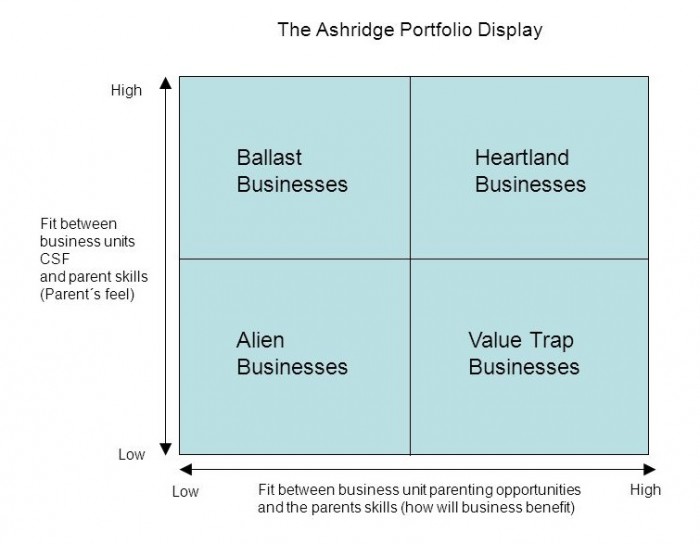
Ashridge portfolio matrix is used to evaluate the attractiveness of potential acquisition target or existing business to the parent. This matrix has two variable according to which the attractiveness of businesses is to be judged. One is Benefit and the other is Feel. In practice, other variables, like previous experience, management attitudes and culture, stakeholders expectations, may also influence the decision regarding potential acquisitions to be included in the portfolio of the business. All the relevant factors needs to be considered taking the decision. Let discuss each of the above variables.
- Benefits: It is the value business can add to potential business by utilizing their resources and competencies. Business may have many resources and capabilities, but only those resources and capabilities are counted towards benefits which the potential business needs to grow. In other words, benefits are the opportunities to help. More the business can help, more it can add value.
- Feel: Feel is the similarity between Parent and the potential business. Similarities can be determined by industry, organization structure, culture and law. There can be many other elements need to be considered. Feel is about critical success factors (CSF) related to the elements stated above. If the business understands how to makes potential business successful as it know its CSF, it can use its resources and capabilities more effectively.
The combination of Benefits and Feels gives the following types of business acquisition targets which varies in attractiveness according to situation.
- Alien Businesses: These are the business outside the industry of the business considering takeover or merger proposal, so business has no knowledge of internal and external factors affecting the business operating in that industry, needed to make it successful. It can be said that it has low feel. There are no opportunities for the parent to add value by helping it because potential business has the skills necessary for its success. It can be said that it has low benefits.
- Value Trap Businesses: These are the business outside the industry of the business considering takeover or merger proposal. It can be said that it has low feel. There are opportunities for the parent to add value by helping it because the business possess resources and capability to help the potential acquisition target lacks the skills necessary for its success. It can be said that it has high benefits.
- Ballast Businesses: These are the business inside the industry of the business considering takeover or merger proposal. It can be said that it has high feel. There are no opportunities for the parent to add value by helping it because potential acquisition target has the skills necessary for its success. It can be said that it has low benefits.
- Heartland Businesses: These are the business inside the industry of the business considering takeover or merger proposal. It can be said that it has high feel. There are opportunities for the parent to add value by helping it because potential business lacks the skills necessary for its success. It can be said that it has high benefits.
| Category | Description | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Heartlands | Parent can add value without risk of harming SBU. | Core of the future corporate strategy. |
| Ballasts | Parent understands SBU well but can do little to add value. | Needs a light touch from the parent. |
| Value Traps | Parent can add value but may do more harm than good. | Only focus if can be moved to heartlands. For this parent must be willing to learn SBU business. |
| Aliens | Parent has poor fit with the SBU and can do little to help anyway. | Dispose of them. |
External Links:
- Corporate Strategy: The Quest for Parenting Advantage (Harvard Business Review)