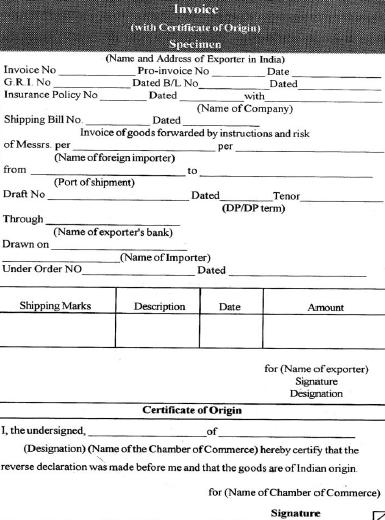
An export invoice is the basic document which gives full details of the contents of the shipment and serves as seller‘s bill of goods and sets out the terms of sale. An invoice usually means a Commercial invoice. An exporter must prepare this document which will fully identify the overseas shipment and serve as a basis for the preparation of all other documents.
There is no standard form for an export invoice and it is the exporter’s choice to design his own form. The invoice is prepared for the buyer abroad. Any special requirement of the importer must be duly complied with.
The following are the essential details which should be available in the export invoice:
- Name and address of the exporter
- Invoice number and date
- Buyer’s and Seller’s Order numbers
- Name and address of the overseas customer
- Name of the vessel and sailing date
- Unit price and total value
- Terms of payment
- Insurance reference
- Customs and consular declaration
- Shipping marks and number on packages
- Quantities and description of commodities
- Net weight and gross weight as well as measurement in metric units
- Specification of packing
- Terms of sale (FOB., CIC., C&F, FAS, etc,)
- Bill of lading number
- Letter of credit number and date.
- Import licence number and date.
Types of Export Invoice
The main types of export invoices are as follows:
- Proforma Invoice: Proforma invoice is a preliminary, provisional, temporary invoice for an anticipated shipment which mayor may not take place. Such invoices serve some useful functions. The overseas buyer is in a position to deal with certain requirements before placing the order, etc. obtaining an import licence. It can be supplied to the bank when a Letter of Credit is to be opened by the overseas buyer with the instructions that the letter of credit be opened in accordance with the invoice.
- Combined Certificate of Origin and Value: This is required by Common wealth countries. The exporter should make inquiries as to the particular form which satisfies the requirements of the port of destination as well as the particular good being exported. The statement of the value of the goods made by the exporter is of great use in determining the import duty which should be paid at the destination.
- Consular Invoice: Sometimes the importer requires the invoice to be certified by the consulate of his country residing in the exporter’s country. Consular invoice facilitates the clearing of goods through the customer at the destination and serves as authentication of the particulars in it.
- Invoice Certified by a Recognized Chamber of Commerce: If the importer has to pay duty on the current domestic value of the goods, he would require the invoice certified by the recognized chamber of commerce of the exporter’s country.
- Legalized Invoice: There is no specific form prescribed for legalized invoice. Mexico needs a legalized invoice. Normally, invoice is acceptable for legalization. Four copies are required along with legalization fee. Three copies will be generally sent to the exporter and one copy will be retained by the Mission.
- Customs Invoice: Countries like Canada and the United States of America need customs invoice. This is needed so that goods could enter at preferential tariff rates.