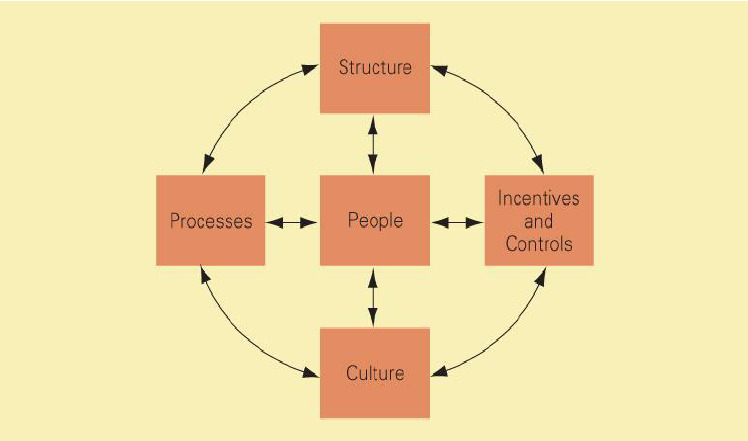
By organizational architecture, we mean the entire organization, including organizational structure, control systems and incentives, processes, organizational culture and people. In this case, there are three conditions to be fulfilled by an organization to make the organization profitable. First, various elements of the organization shall be parallel to each other. Second, organizational strategy should always be consistent with the organizational structure, and finally, strategies and organizational structure must be consistent with the competitive conditions prevailing in the firm’s market that are the strategy, architecture and competitive environment.
As noted above, the organizational architecture is the totality of the organization itself which consists of various components. The components are the structure, control systems and incentives, processes, organizational culture and people. The organizational structure is a formal organizational structure used to manage a firm. Control system is the system used to measure the performance of managers and units while the incentives are tools used to reward the performance of managers. Processes are the manner in which decisions are made and work is performed while the organizational culture is the values and norms in the organization shared by its employees.
Factors Affecting Organizational Architecture
There are five factors that influence the architecture organizational architecture which are size, strategy, technology, environment and country culture.
1. Size
The larger the organization, the more complex its structure. When a small organization such as a single grocery store, a two person consulting company or restaurants it can be a simple structure. In fact, if the organization is very small, it may not have a formal structure. It may not have or follow the organizational chart or a specific job function. The employees only operate based on what they like or do not like, their abilities, and needs. Rules and guidelines just exist in order to provide the parameters within which organizational members can make decisions. Small organizations are often organic systems.
However, as the organization grows, it becomes increasingly difficult to manage without a formal structure and delegation of powers within the organization. Therefore, large organizations will have a formal structure where the tasks performed have been determined and has the proper work procedures.
2. Strategy
As noted in an introduction, the strategy of organizations has to be consistent with the organizational structure. Whether it is differentiation strategy, cost-leadership strategy, cost reduction or local responsiveness, all the strategies requires a structure that help the organization achieve its objectives. In other words, the structure must fit the strategy.
3. Technology
The advances in technology of the organizations or area will also affect the structure of an organization. For example, in international business, a company based in a developed country with high technology, while its branches are located in a developing country which is not so advanced technologically, the organizational structure of Head Quarters and its branches could not be the same.
4. Environment
Environment usually described as either stable or dynamic. In a stable environment, firms will understand the needs and desires of its customers and often this condition would remain for an extended period. Therefore, its organizational structure does not need to change regularly.
In a dynamic environment, customers’ needs will always vary in which technology is also keep changing and need to be upgraded and improved as well as the organizational structure where it should be in line with the changes in firm’s strategy.
5. Country Culture
Cultural environment is an essential component of the international business environment and one of the most difficult to understand. This is because the cultural environment basically cannot be seen, but it has been described as a shared commonly held body of values that determine what is right for one group and what is not right. Companies need to understand what beliefs and values they might find in countries where they do business for this will affect their strategy and structure of the organizations.